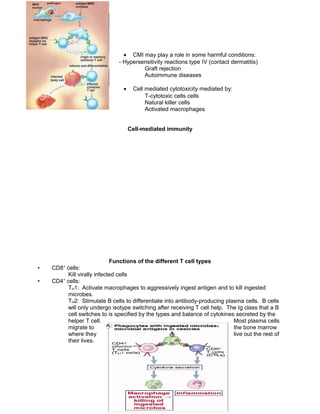
1) Antigen processing and presentation involves extracellular and intracellular proteins being degraded into peptides and bound to MHC class I or II molecules. These peptide-MHC complexes are expressed on antigen presenting cells and recognized by T cells to initiate an immune response.
2) T cells are activated through recognition of peptide-MHC complexes by their T cell receptors along with co-stimulatory signals. Activated T cells proliferate and differentiate into effector and memory T cells.
3) Effector T cells stimulate immune responses like activating macrophages to kill intracellular pathogens, leading to delayed type hypersensitivity reactions which can cause tissue damage if infection is not resolved.