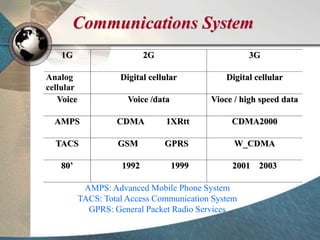
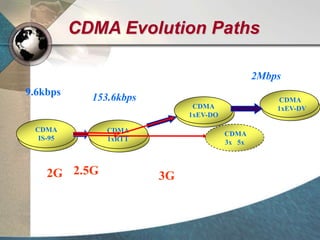
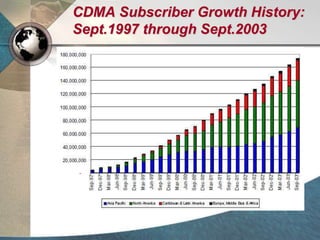
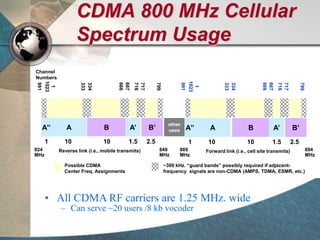
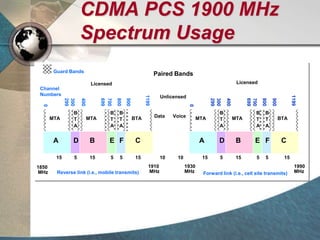
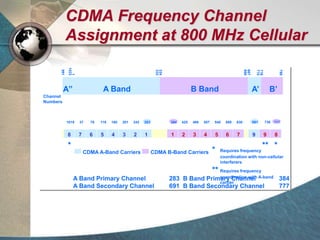
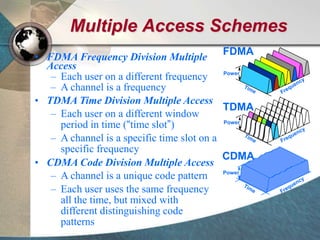
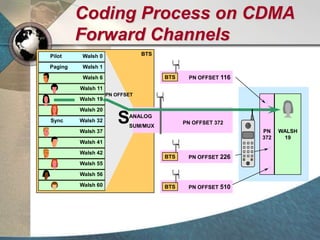
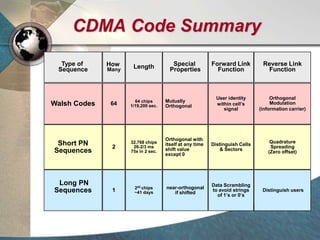
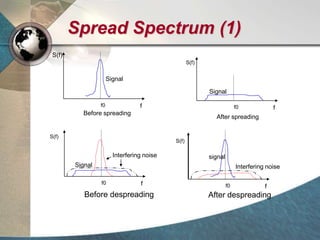
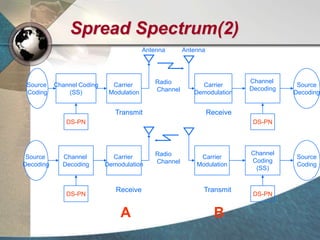
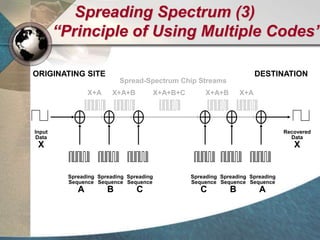
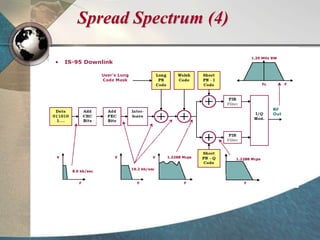
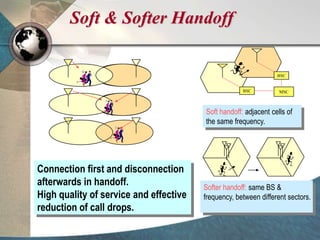
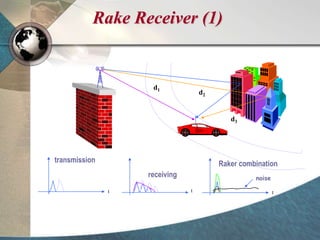
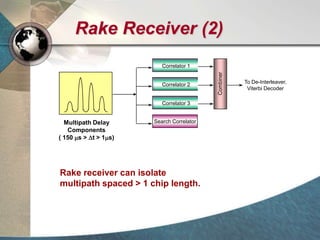
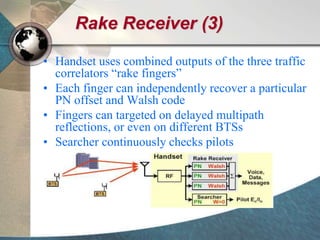
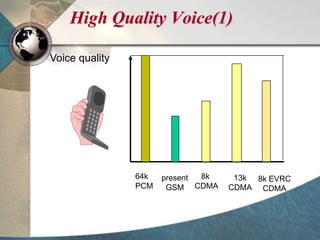
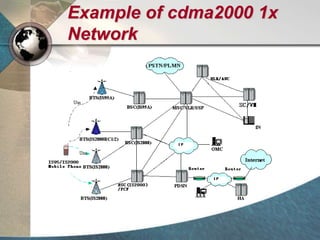
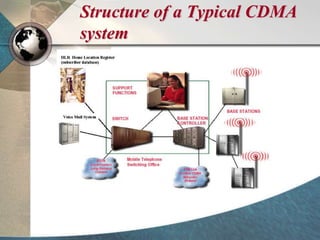
CDMA systems use code division multiple access (CDMA) to allow multiple users to access the network simultaneously using the same frequency band. CDMA uses spreading codes to distinguish between users, allowing signals to overlap in both time and frequency. Key aspects of CDMA include soft handoff which provides better call quality during handoffs, rake receivers which mitigate multipath interference, and intelligent vocoders which provide high quality voice compression. CDMA networks also use power control and simple network planning to provide better coverage than comparable systems while using less infrastructure. The cdma2000 1x standard provided increased data speeds and backward compatibility with earlier CDMA networks.