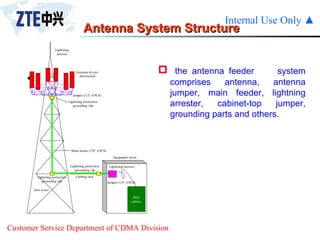
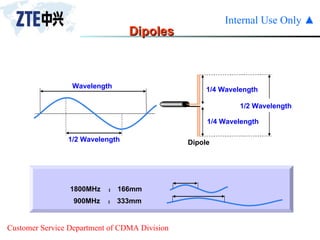
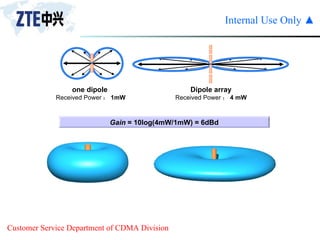
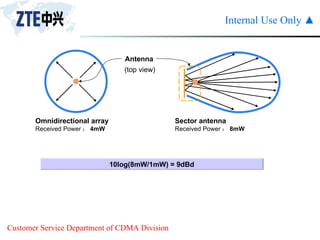
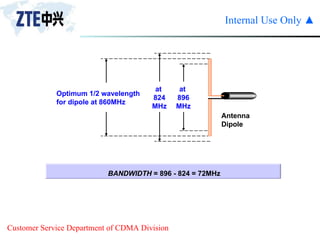
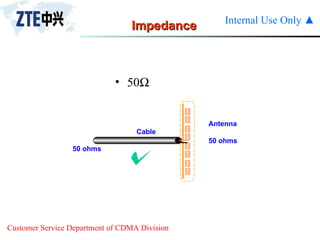
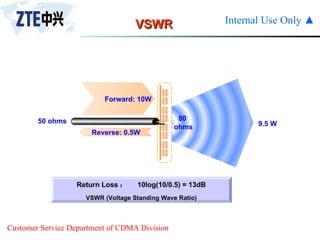
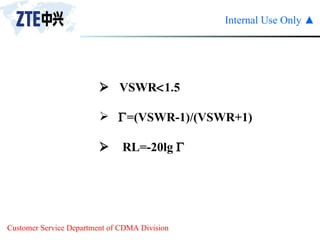
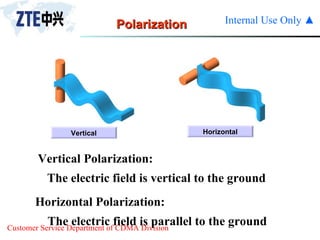
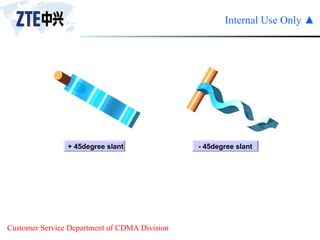
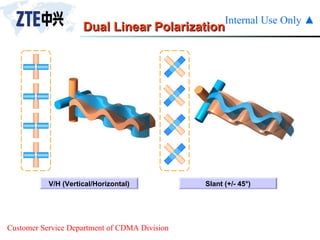
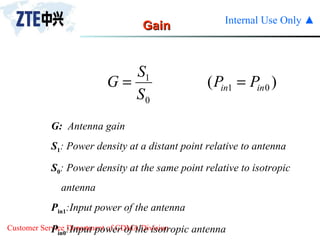
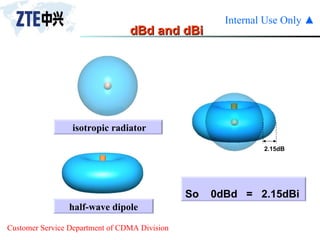
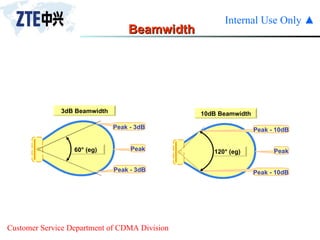
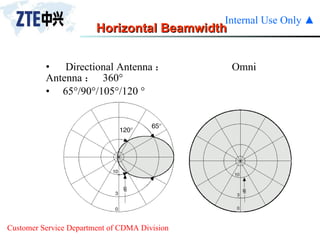
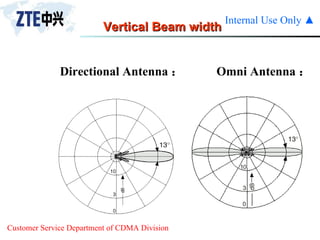
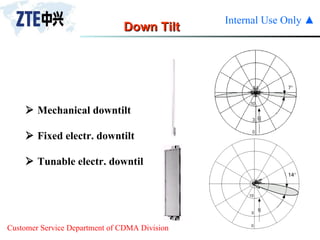
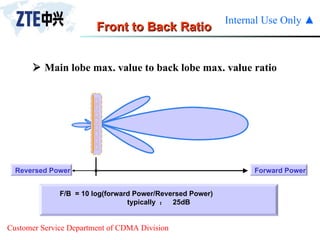
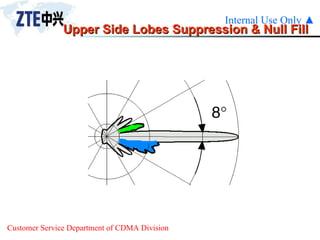
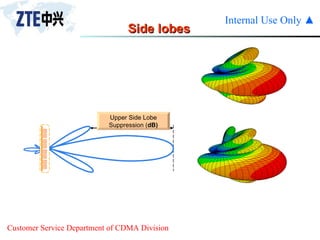
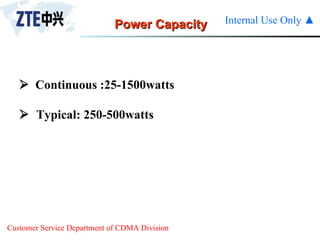
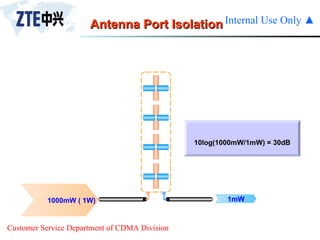
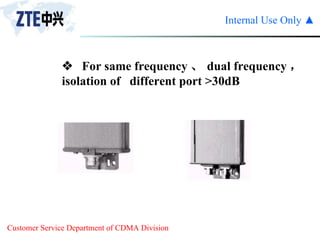
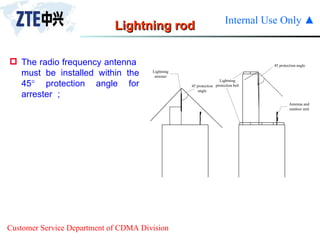
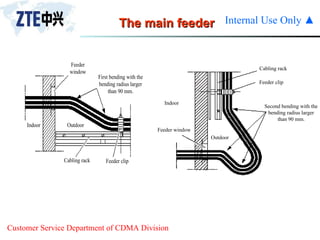
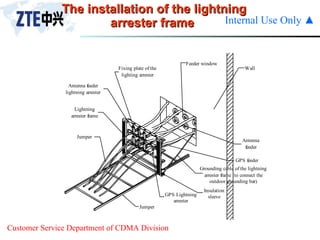
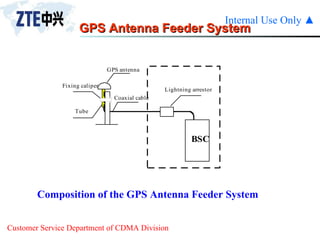
The document summarizes the key components of a CDMA antenna and feeder system. The system comprises antennas, antenna jumpers, main feeders, lightning arresters, cabinet-top jumpers, and grounding parts. Antennas have electrical properties like frequency range, impedance, VSWR, polarization, and gain. They also have mechanical properties like dimensions, weight, operating temperature range, and lightning protection. Common antenna types include directional and omnidirectional antennas. The main feeder connects the antenna to other components and has specifications for material, maximum frequency, impedance, and bending radius. A GPS antenna feeder system is also included to capture clock signals for CDMA use.