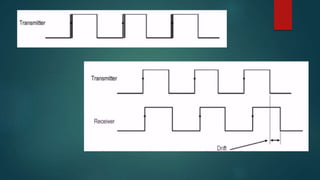
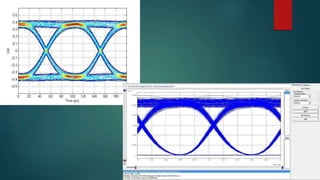
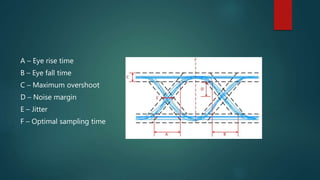
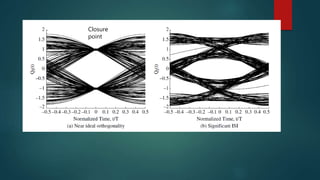
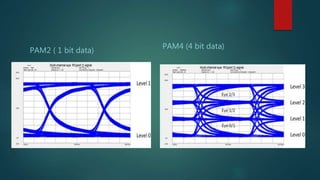
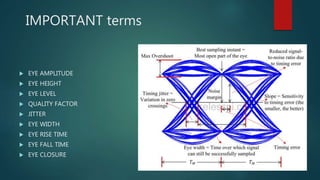
The eye diagram is a visualization technique for analyzing the output of a matched filter, providing insight into signal quality and diagnosing issues such as noise and jitter. Jitter refers to timing deviations in signal transmission, while clock drift leads to synchronization errors due to differences in clock periods between transmitter and receiver. Key measurements in eye diagrams include eye amplitude, eye height, eye width, and various timing characteristics.