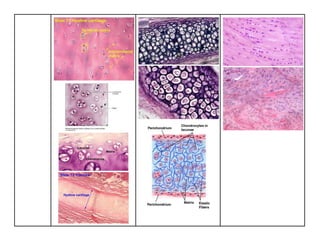
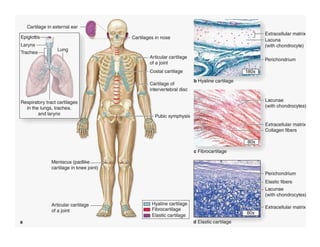
Cartilage functions to form the supporting framework of organs, articulate bone surfaces, and template long bone growth. It develops from mesenchymal cells and lacks blood vessels and nerves. Cartilage has a perichondrium layer and an extracellular matrix containing collagen, elastic fibers, proteoglycans, and water. The three main types are hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage, which differ in matrix composition and collagen content, providing different structural roles.