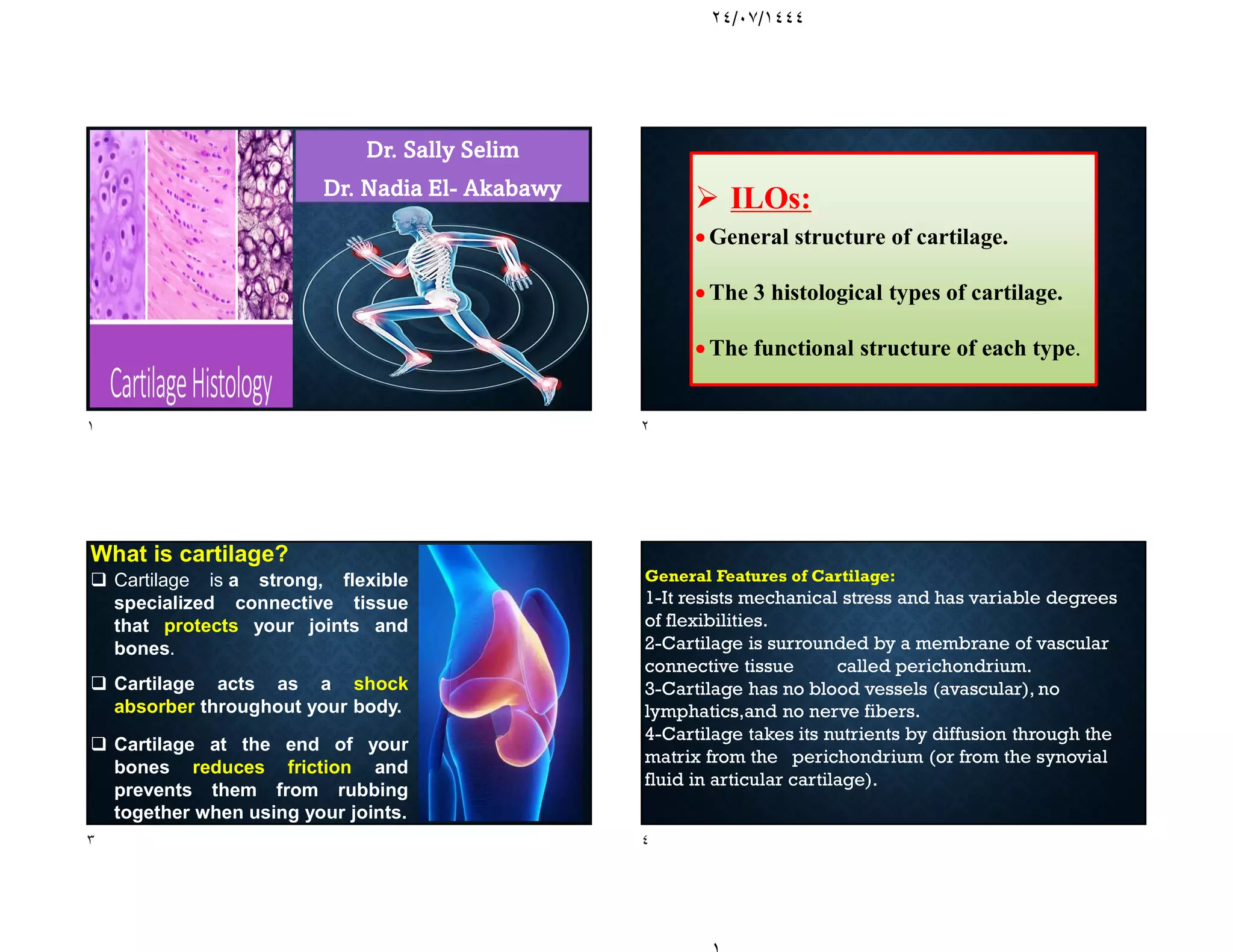
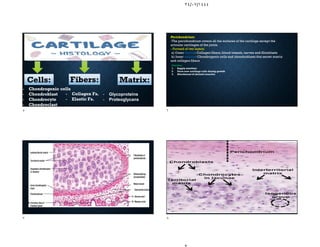
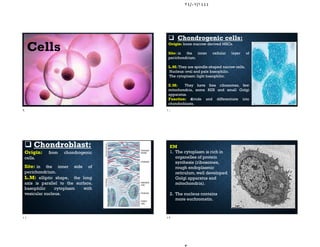
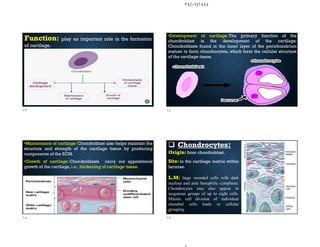
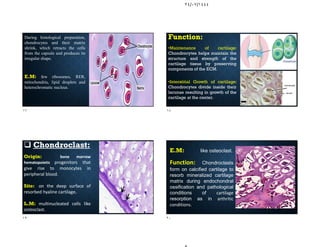
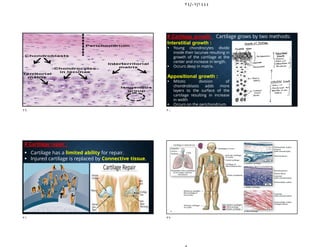
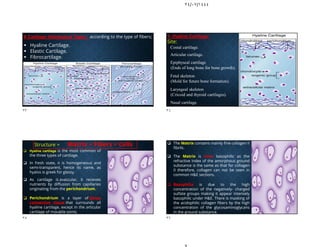
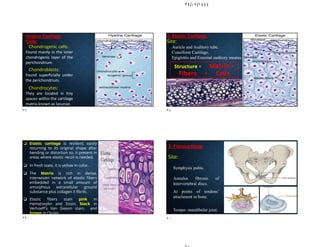
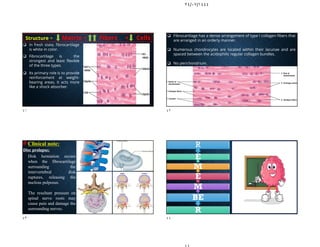
The document discusses the structure and types of cartilage. There are three main types of cartilage - hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage. Each type has a different composition and location in the body. Hyaline cartilage is the most common and found in locations like costal cartilage and joints. It has collagen type II fibers in a basophilic matrix. Elastic cartilage contains elastic fibers and is found in the ear and larynx. Fibrocartilage contains dense collagen type I fibers and acts as a shock absorber at sites like the intervertebral discs. All cartilage types contain chondrocytes in lacunae within the avascular matrix and grow through interstitial or appositional methods.