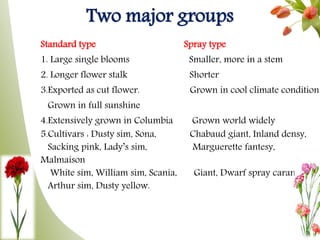
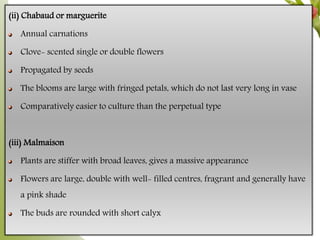
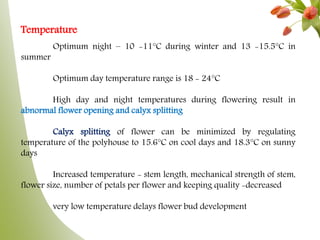
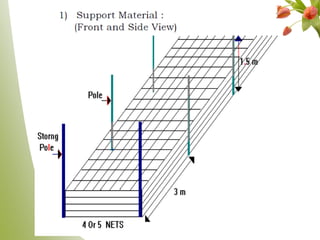
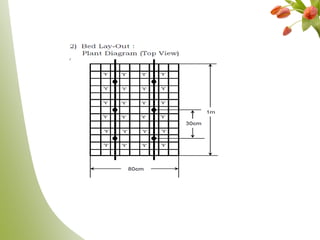
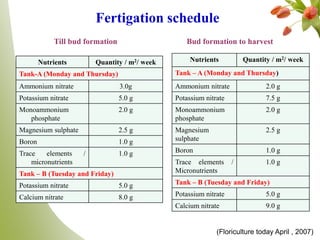
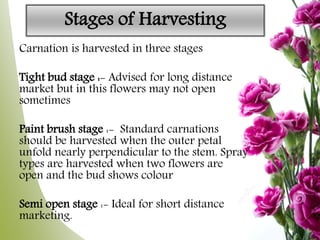
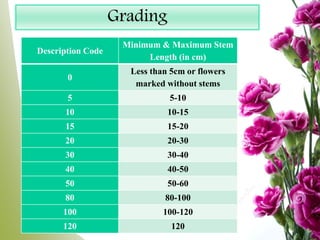
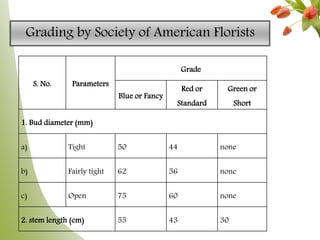
Carnation, the most significant cut flower globally, has a basic chromosome number of 15 and originates from southern France, with varying cultivars like standard and spray types. Grown under specific climate conditions and requiring precise nutrient and pest management, carnations feature a diverse range of flower forms and colors but can face challenges such as calyx splitting and various pests and diseases. Harvesting occurs in multiple stages, with yields varying between standard and spray varieties, highlighting their importance in floriculture.