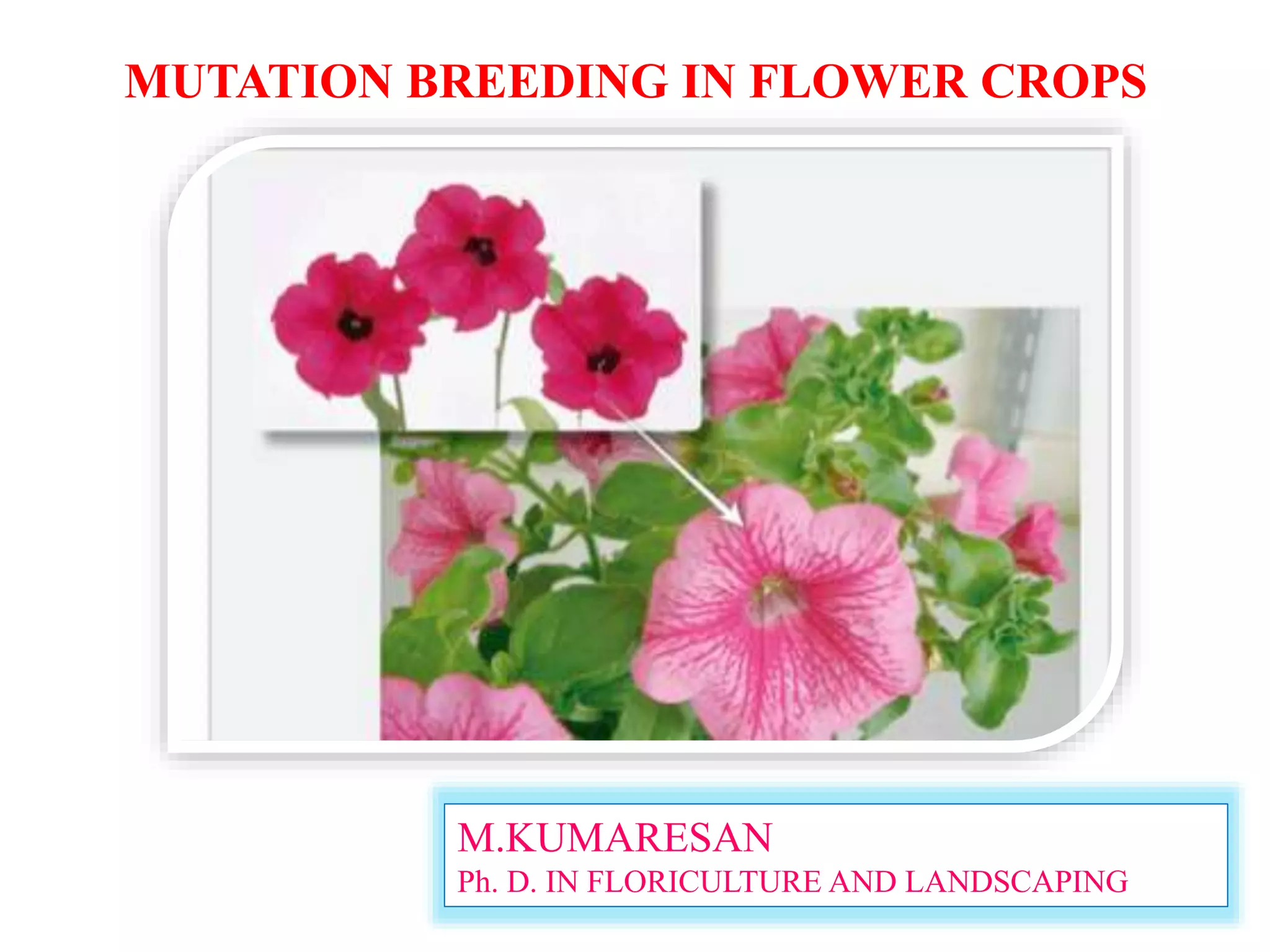
This document discusses mutation breeding techniques for several flower crops. It begins by explaining naturally occurring and induced mutations. Various mutagens like radiation and chemicals are described. Examples of mutation breeding programs for petunia, chrysanthemum, tulip, carnation, rose and gladiolus are provided where mutants with new flower colors and morphologies were obtained. The conclusion states that mutation breeding is a beneficial tool for plant breeders to generate novel traits and expand genetic diversity in crops.