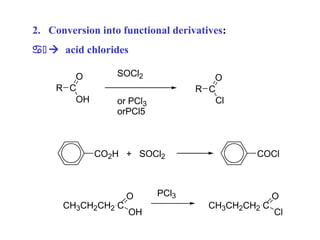
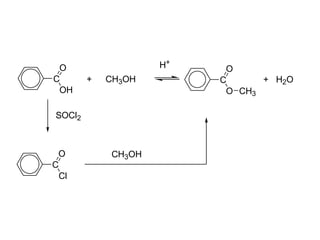
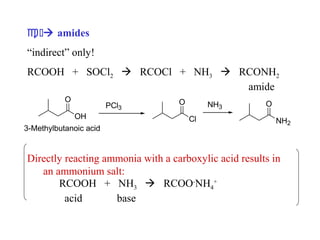
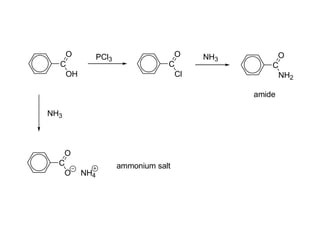
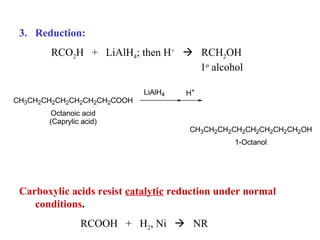
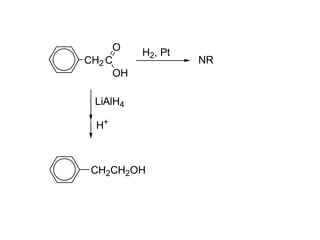
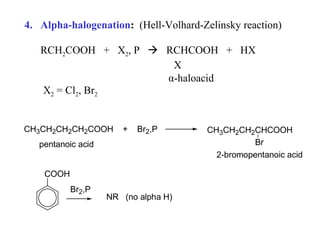
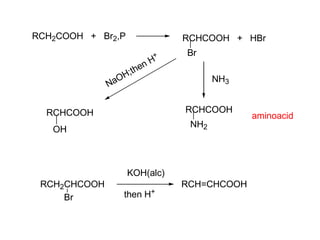
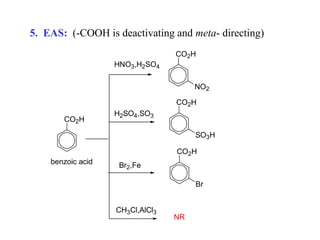
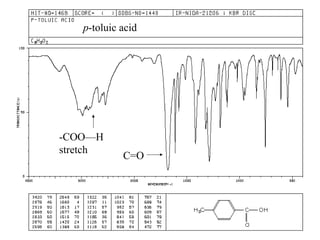
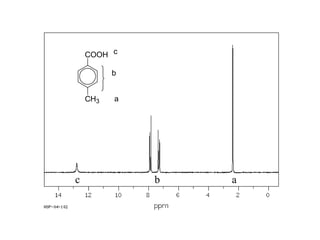
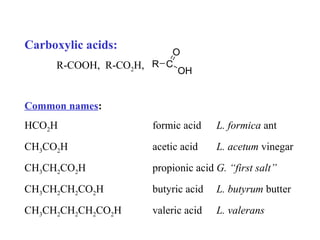
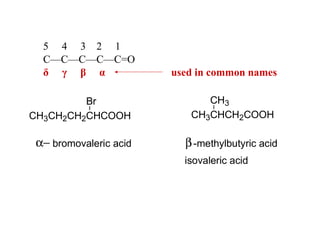
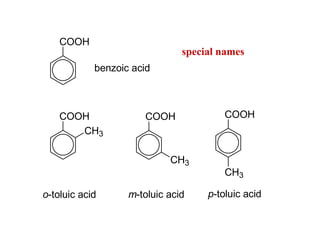
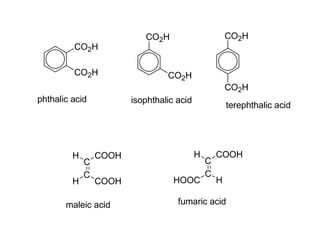
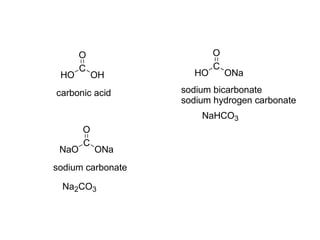
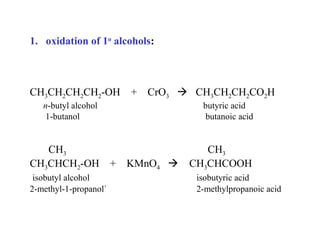
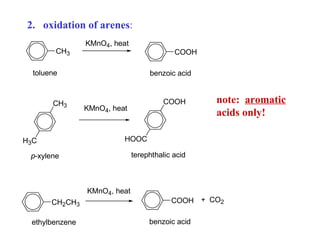
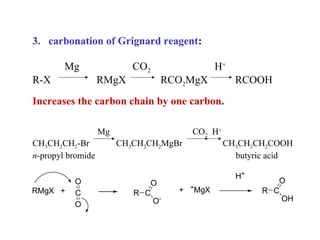
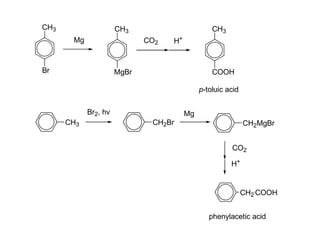
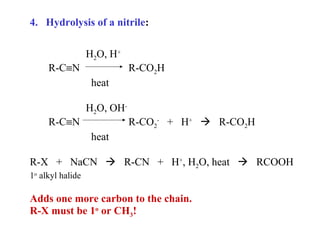
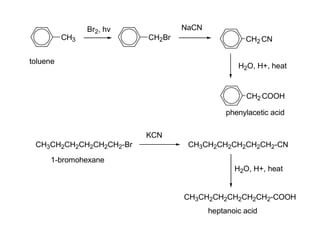
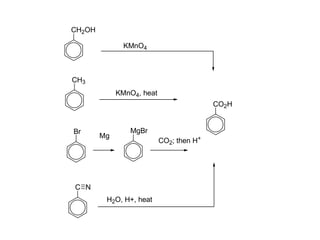
Carboxylic acids have the general formula R-COOH. They can be synthesized through oxidation of alcohols and arenes, carbonation of Grignard reagents, and hydrolysis of nitriles. As acids, they ionize in water and react with bases. They can be converted to functional derivatives like acid chlorides, esters, and amides. They undergo reactions such as reduction, alpha-halogenation, and electrophilic aromatic substitution. Spectroscopically, they show a C=O stretch around 1700 cm-1 and a COOH proton around 12 ppm.








![as acids:
a) with active metals
RCO2H + Na RCO2-Na+ + H2(g)
b) with bases
RCO2H + NaOH RCO2-Na+ + H2O
c) relative acid strength?
CH4 < NH3 < HC≡CH < ROH < HOH < H2CO3 < RCO2H < HF
d) quantitative
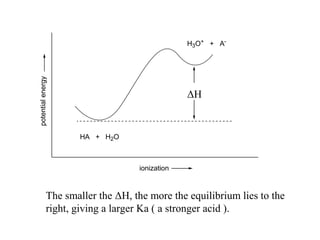
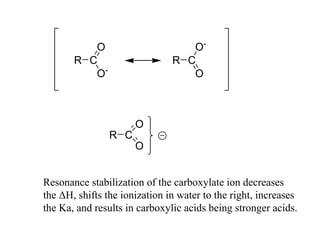
HA + H2O H3O+ + AKa = [H3O+] [A-] / [HA]
ionization in water](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carboxylicacids-131118005606-phpapp01/85/Carboxylic-acids-21-320.jpg)