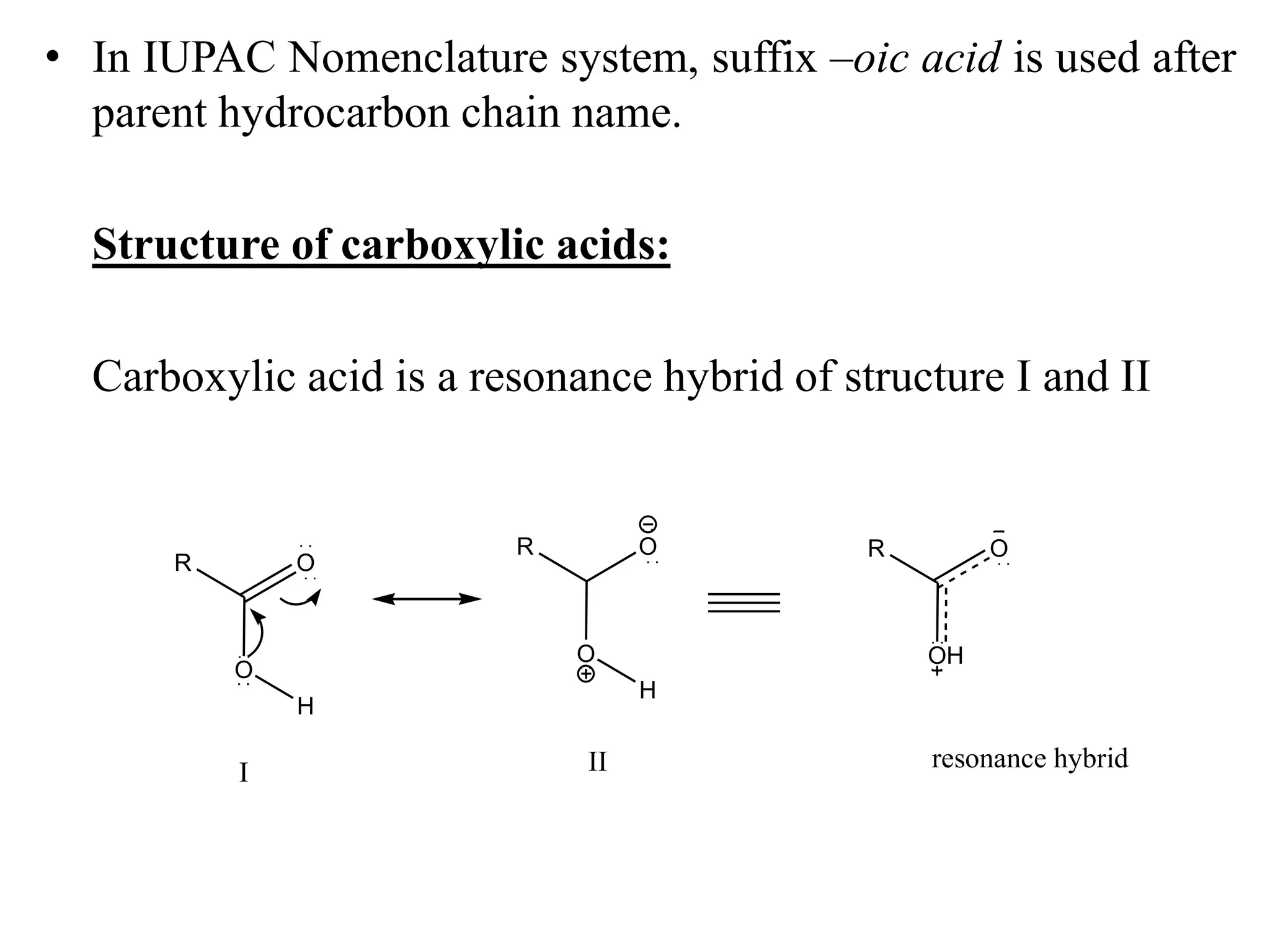
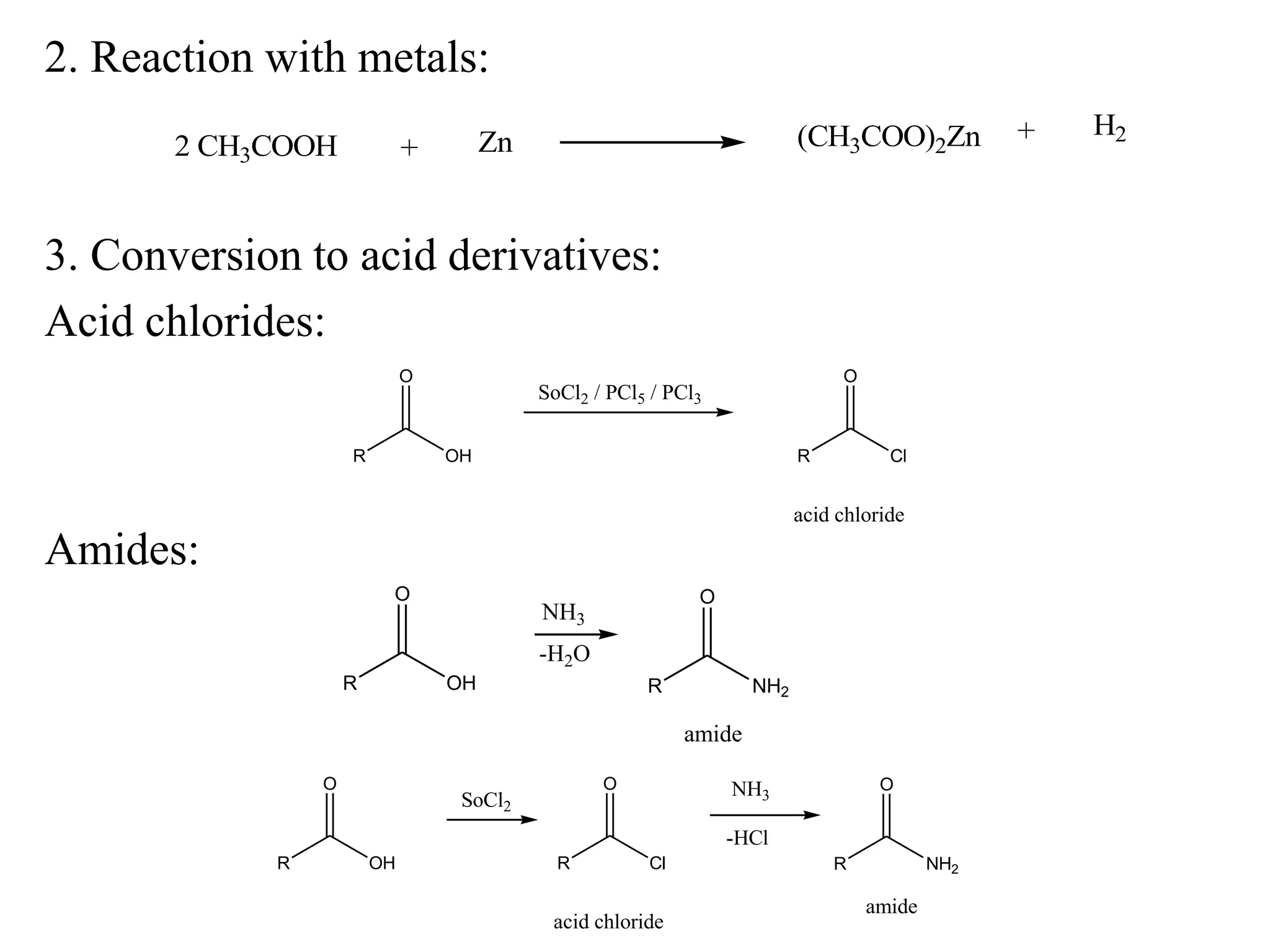
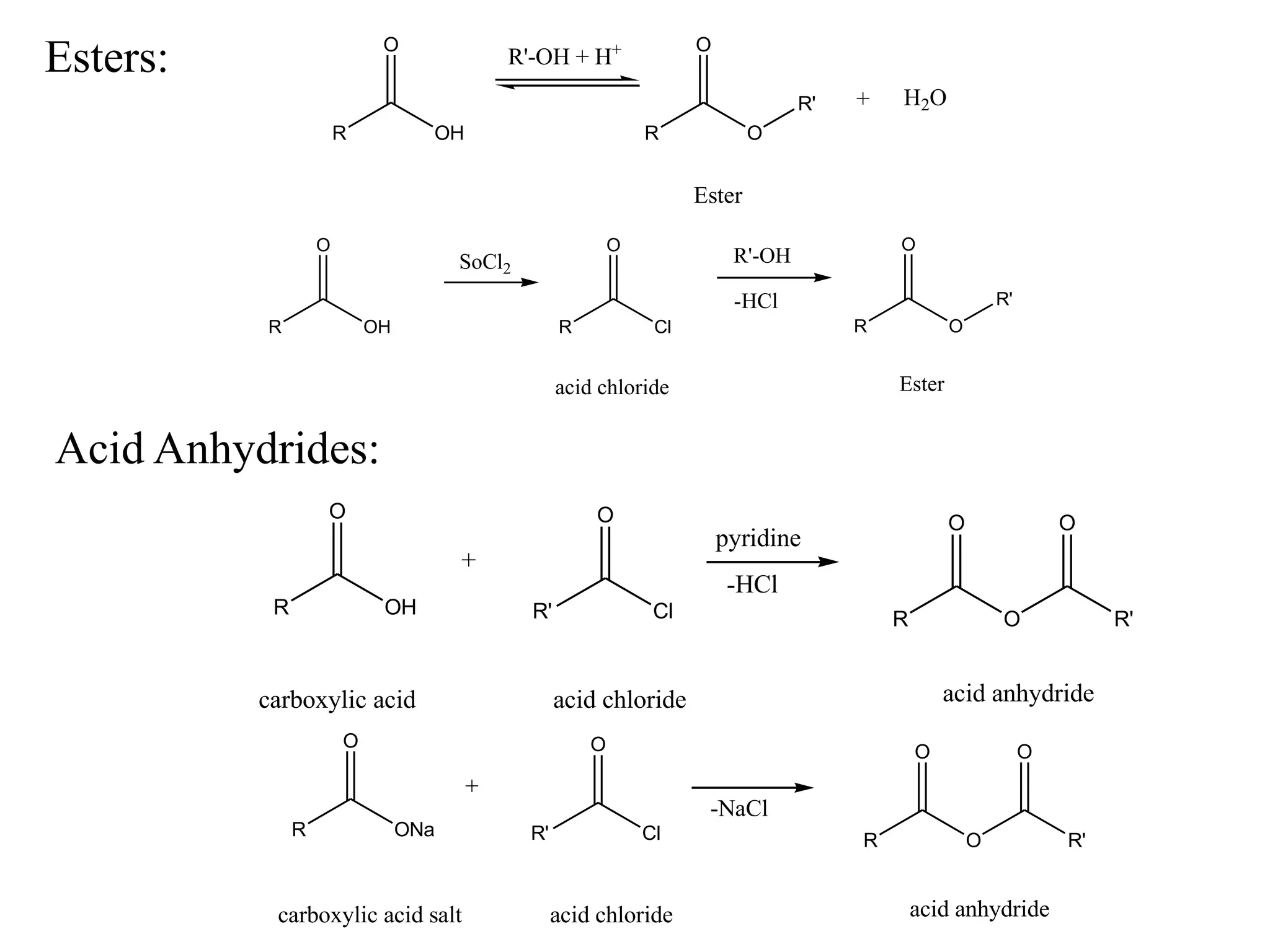
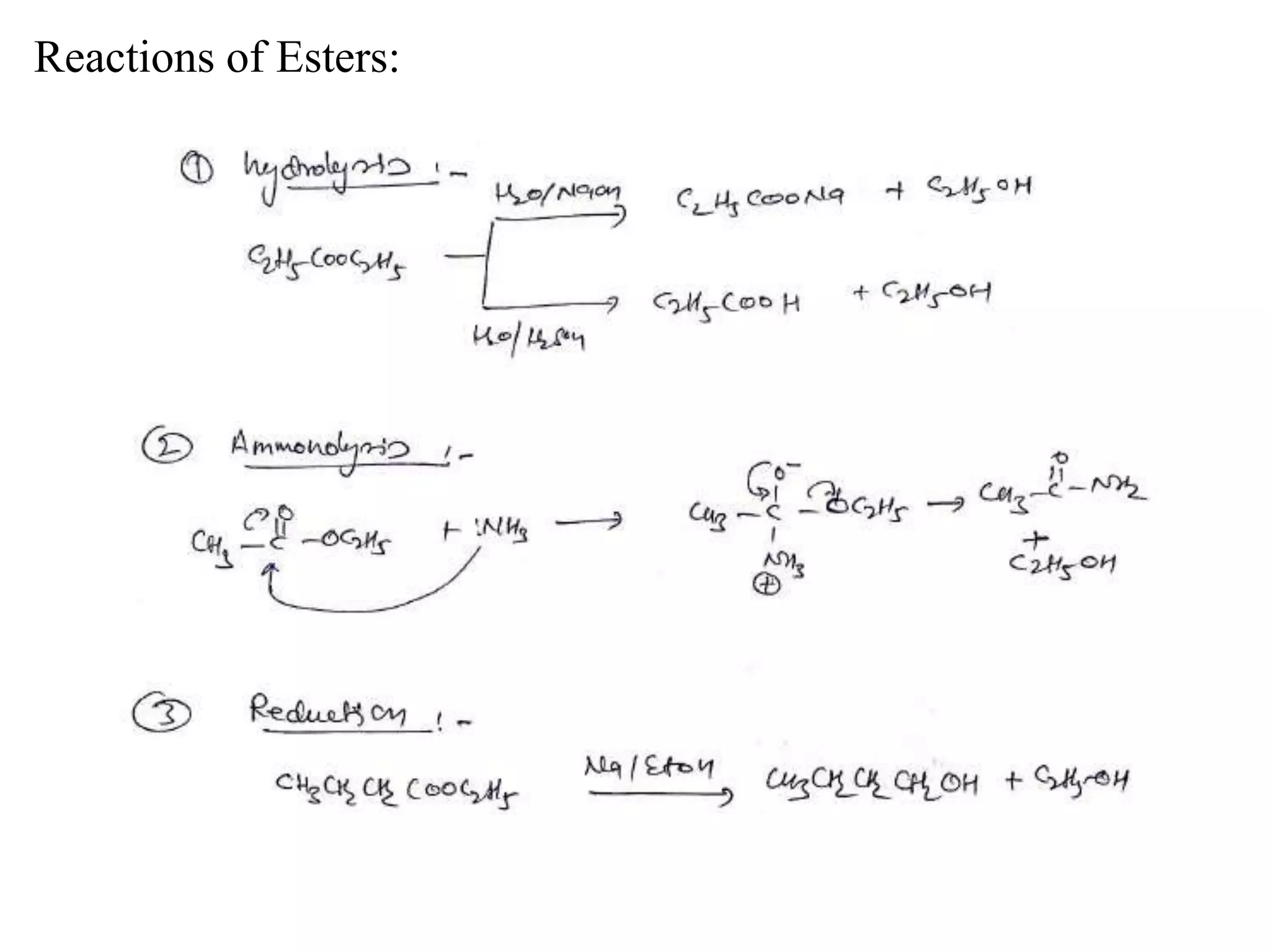
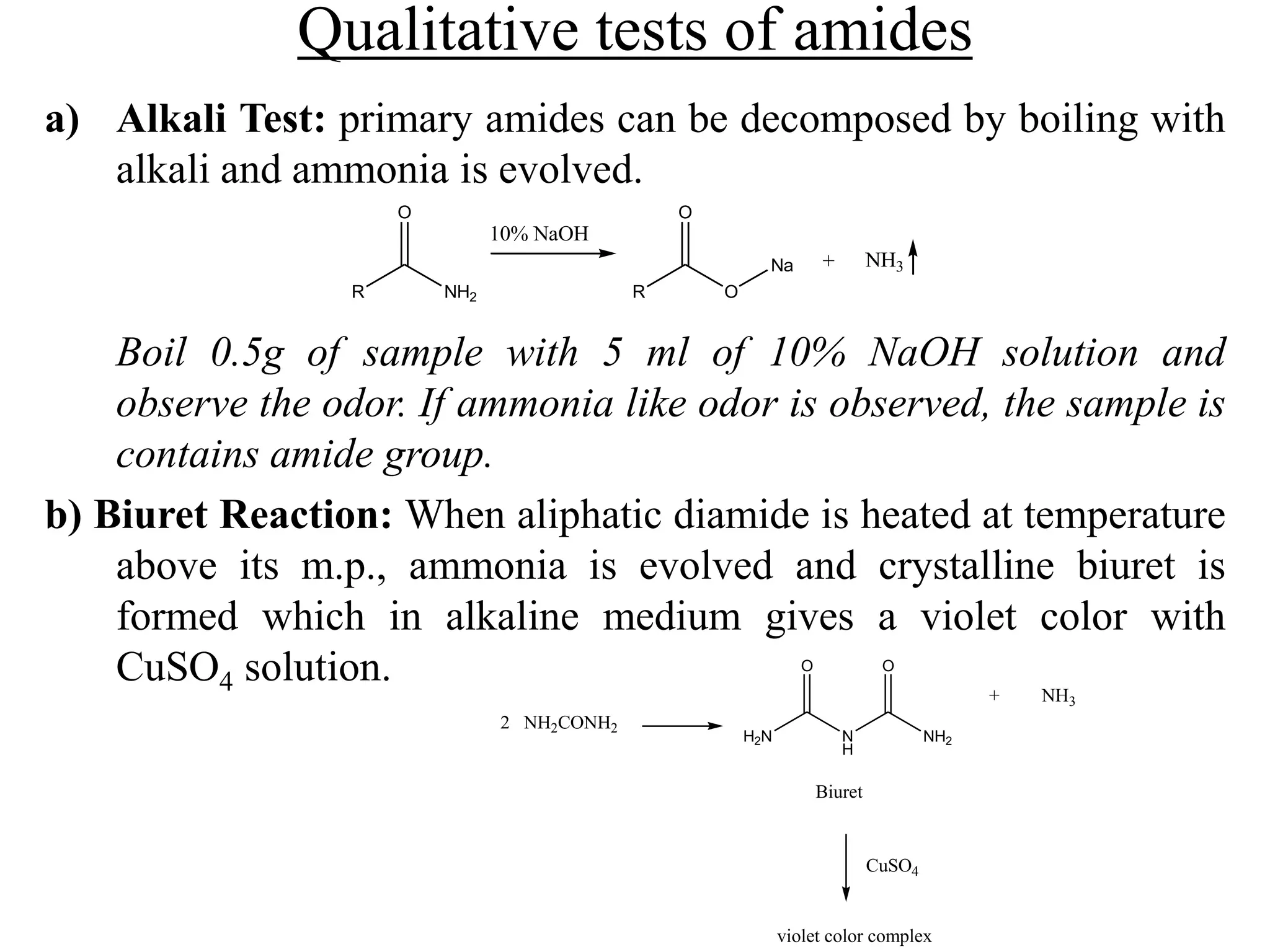
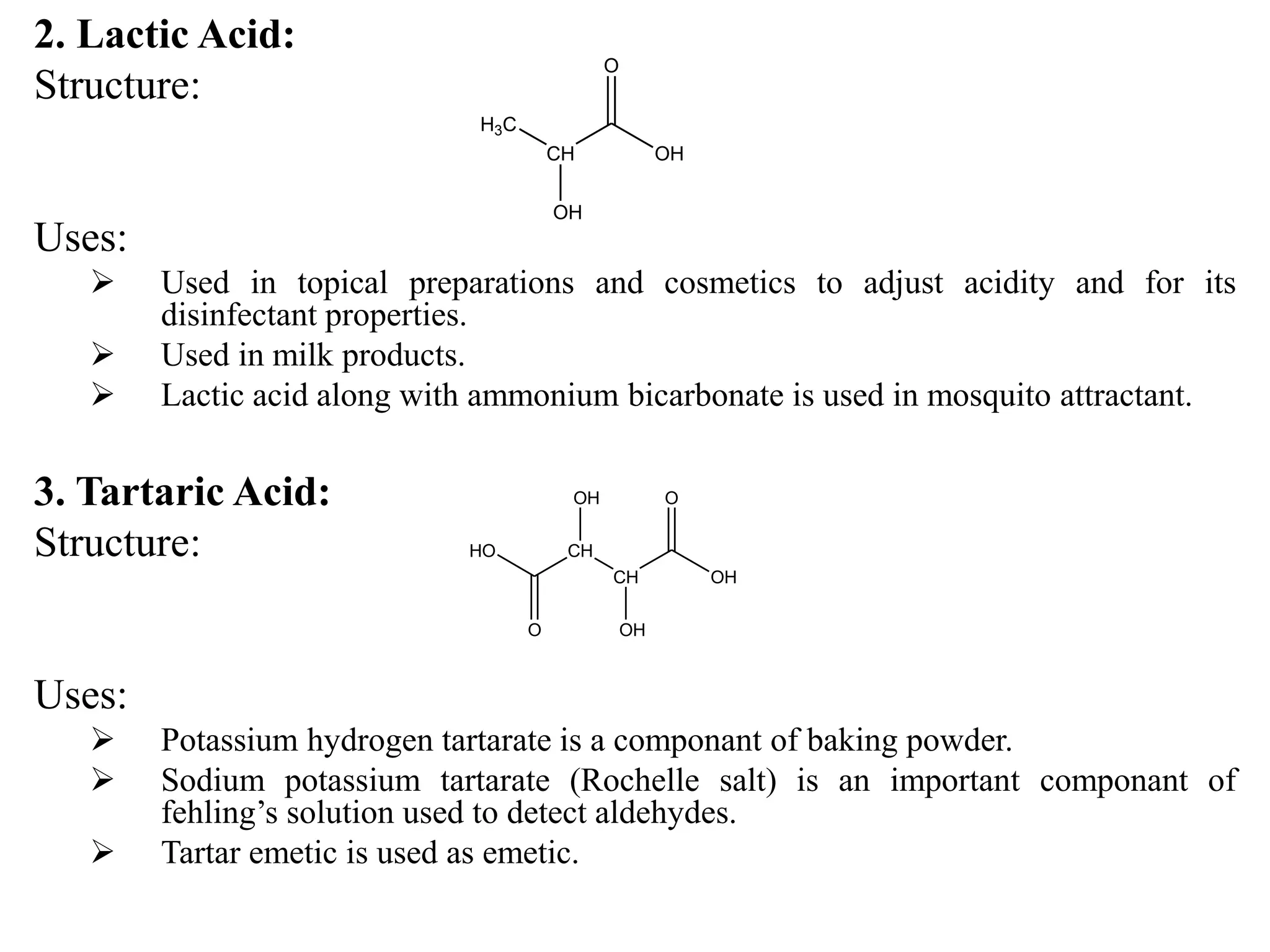
Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl (-COOH) functional group. They are classified as monocarboxylic, dicarboxylic, or tricarboxylic based on the number of carboxyl groups. Carboxylic acids are named using IUPAC or common names. They are resonance stabilized and can form hydrogen bonds. Carboxylic acids are acidic due to the stability of the conjugate base. They undergo characteristic reactions like forming salts, anhydrides, esters, amides, and undergoing oxidation, reduction, decarboxylation. Common carboxylic acids and their uses include acetic acid, lactic acid, citric acid, benzoic acid, and aspirin.