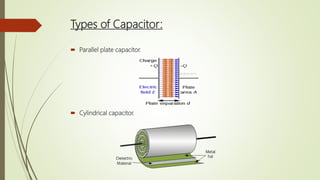
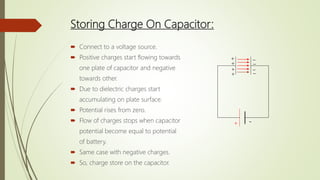
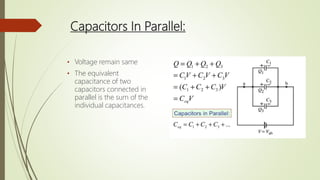
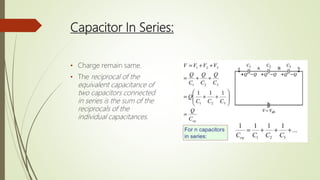
A capacitor is a device that stores electric charge between two conductive plates separated by an insulator. When a voltage is applied across the plates, charges of opposite polarity accumulate on each plate. The amount of charge stored depends on the capacitor's capacitance, which is determined by the size, number, and distance between plates as well as the dielectric material between the plates. Capacitors are used in electrical circuits for functions like energy storage, voltage regulation, timing, and filtering. They can be connected in parallel to increase total capacitance or in series to decrease it. Common applications include power supplies, audio equipment, and sensors.