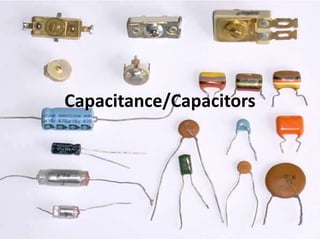
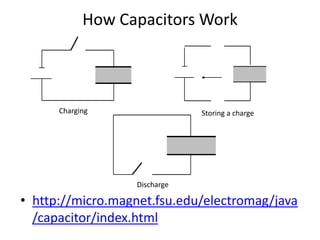
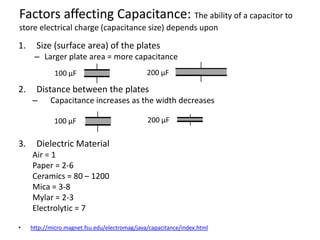
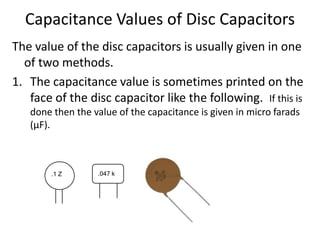
Capacitors are able to store electrical charge. The ability of a capacitor to store charge is known as its capacitance, which is measured in Farads. A capacitor consists of two conducting plates separated by an insulator. The factors that affect a capacitor's capacitance include the size of its plates, the distance between plates, and the material between the plates. When choosing a capacitor, its capacitance value, voltage rating, and polarity must all be considered. Capacitors can be connected in series or parallel, with capacitance adding or reducing depending on the configuration.