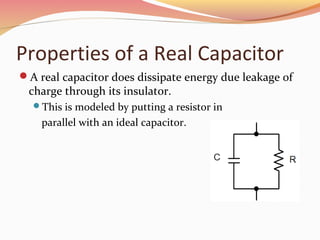
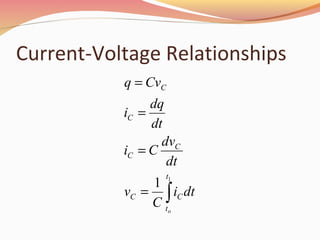
Capacitors are energy storage devices composed of two conductive plates separated by an insulator. The capacitance of a capacitor depends on the plate area, distance between plates, and dielectric material. There are two main types: nonpolarized and electrolytic. Capacitors act like an open circuit with DC but not AC. They store charge on their plates according to the equation Q = CV. The equivalent capacitance of capacitors connected in parallel is the sum of individual capacitances, while capacitors in series have an equivalent capacitance given by the reciprocal of the sum of reciprocals of individual capacitances.


















![Ceq for Capacitors in Series
i
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )[ ] 1
4321eq
t
t
t
t4
t
t3
t
t2
t
t1
t
t4
4
t
t3
3
t
t2
2
t
t1
1
4321
1111C
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
idt
1
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
1
o
−
+++=
=
+++=
==
==
+++=
∫
∫∫∫∫
∫∫
∫∫
CCCC
C
v
CCCC
v
C
v
C
v
C
v
C
v
vvvvv
eq
in
in
in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/keyurbecapacitors-150514140159-lva1-app6891/85/Keyur-be-capacitors-21-320.jpg)


