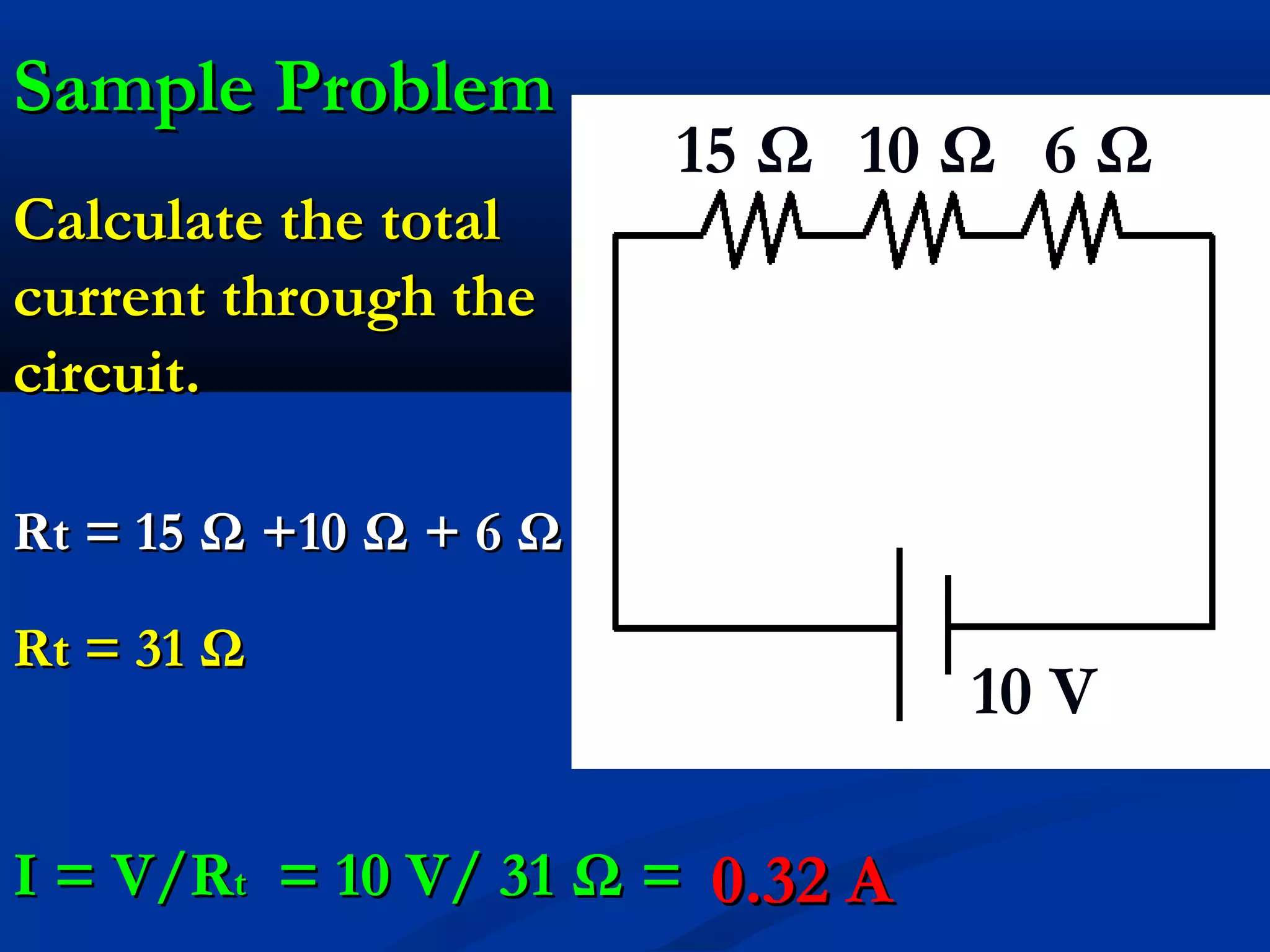
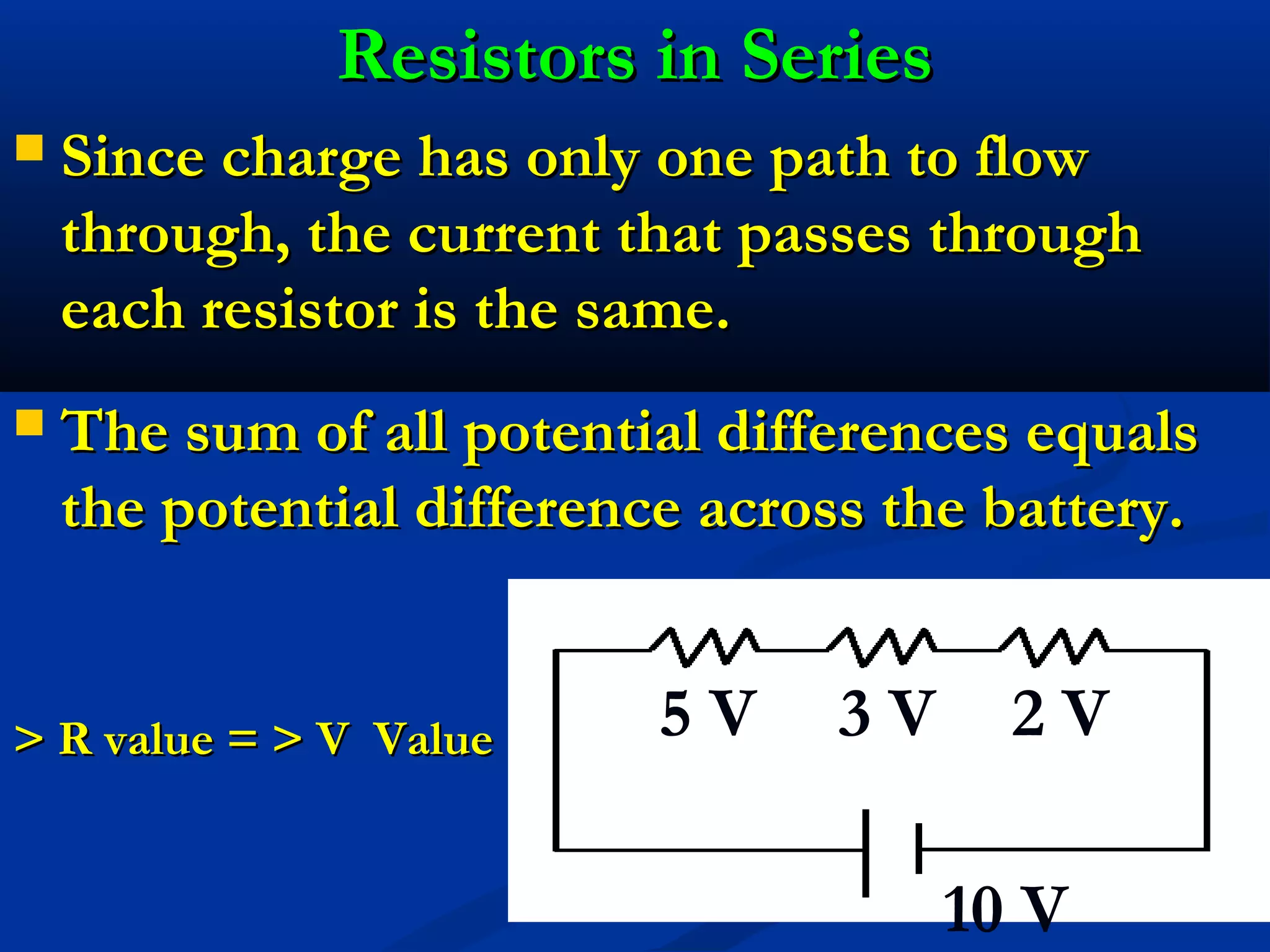
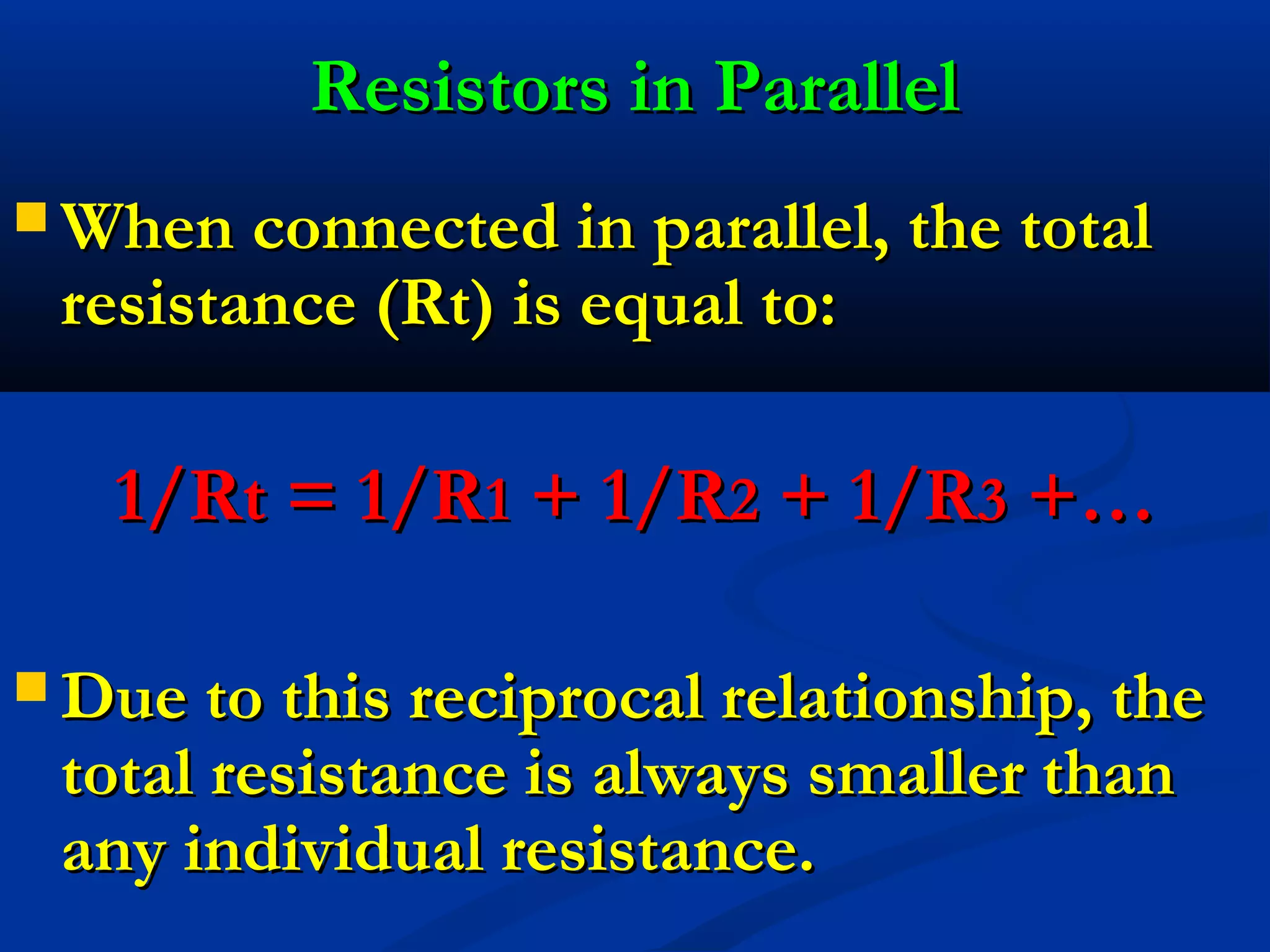
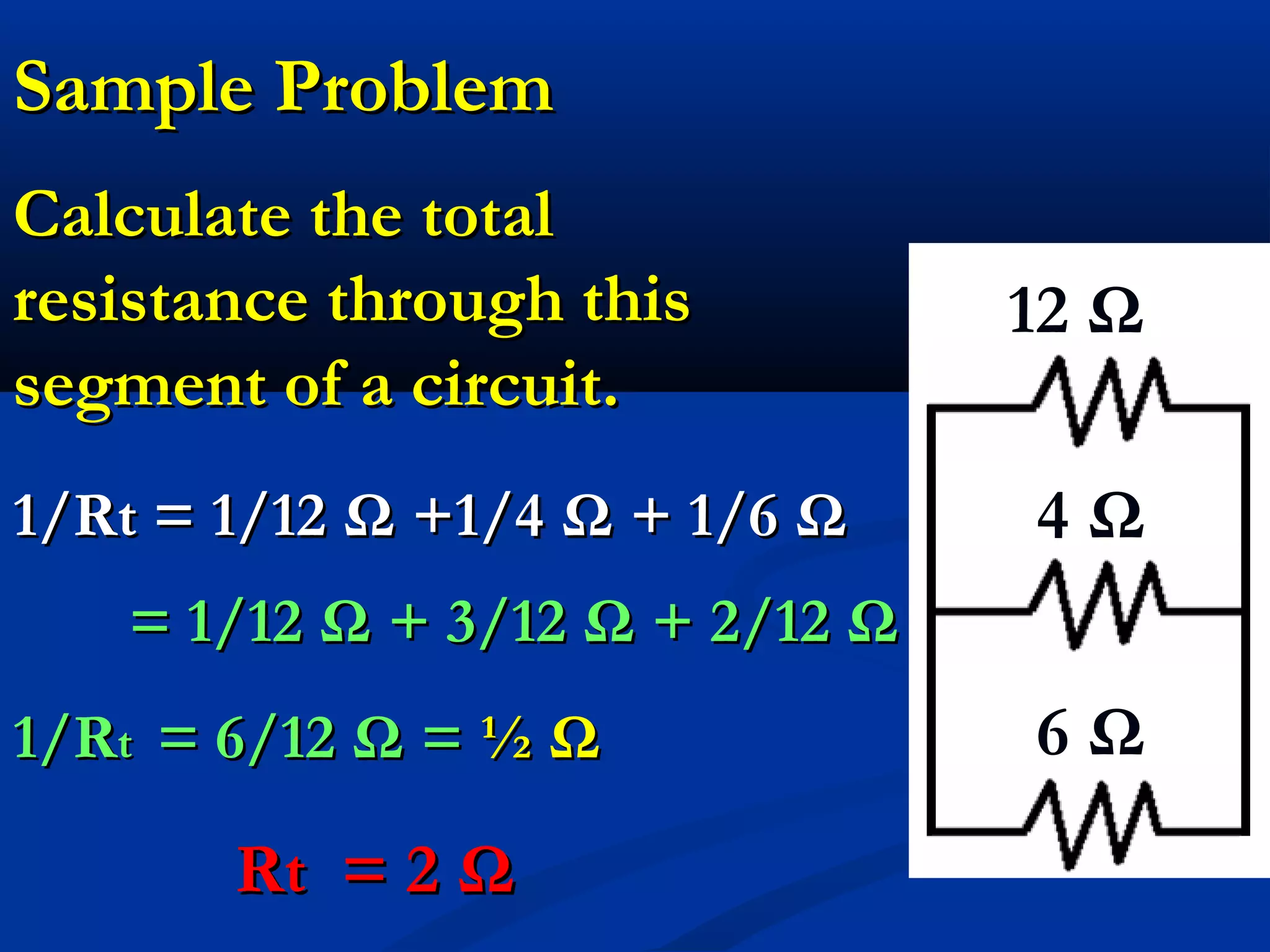
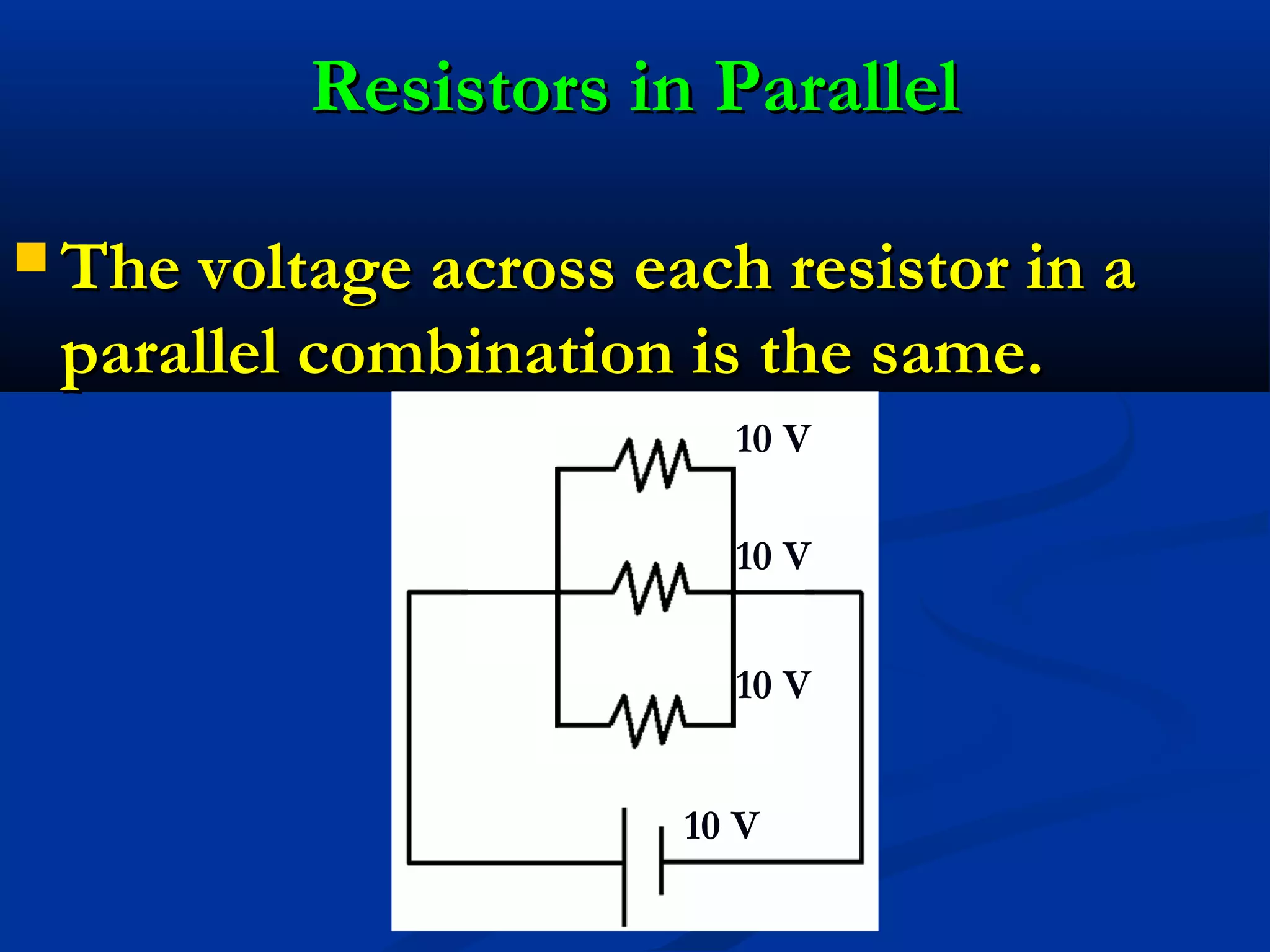
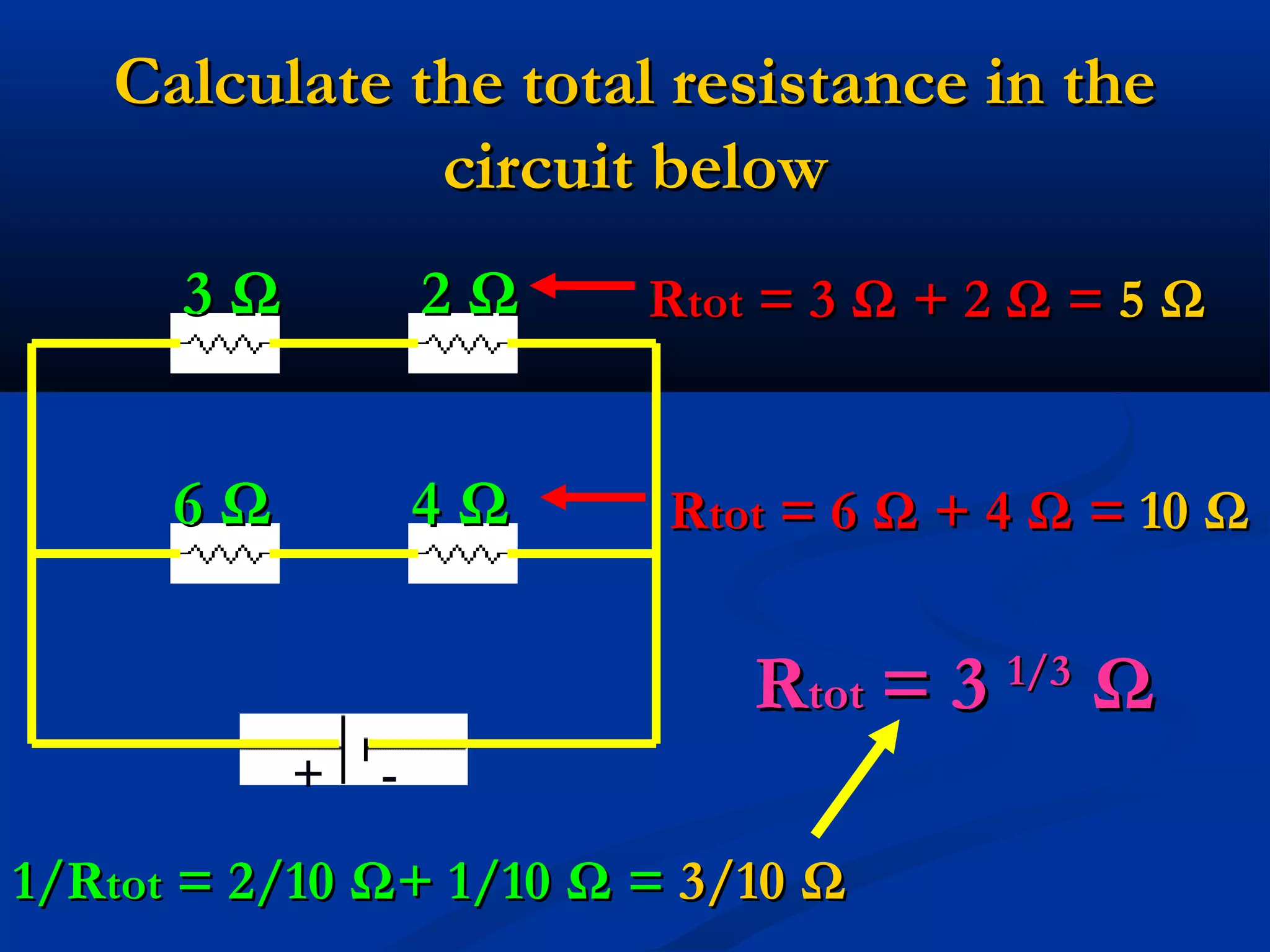
This document discusses resistors in series and parallel circuits. When resistors are in series, the total resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistances. When resistors are in parallel, the total resistance is always smaller than any individual resistance and is calculated using reciprocals. The key differences are that current is the same through components in series, but divides according to resistance in parallel, and voltage divides across components in series but is the same across parallel components.