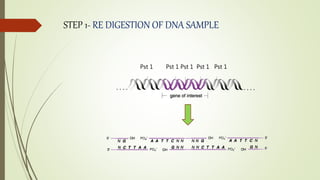
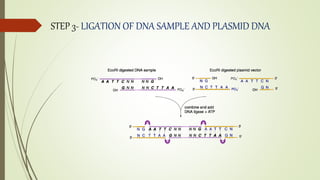
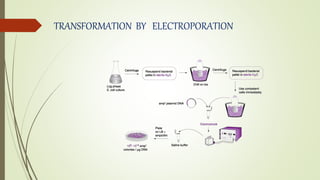
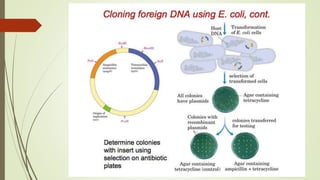
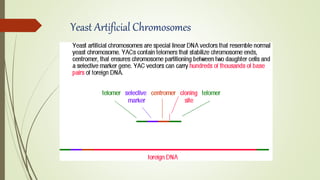
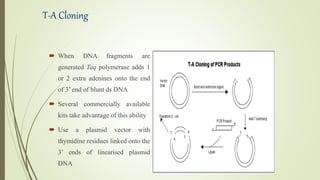
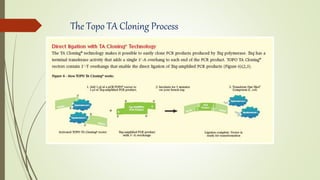
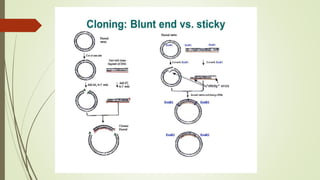
DNA cloning techniques allow for the reproduction of DNA fragments. There are two main approaches: cell-based cloning using living cells and in vitro cloning using PCR. The cloning process involves cutting out the gene of interest and a host plasmid with the same restriction enzyme, ligating the gene into the plasmid, transforming bacteria with the new plasmid, and selecting for transformed colonies. Common cloning vectors include plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, YACs, and retroviral vectors which allow incorporation of foreign DNA into host genomes. PCR cloning strategies like TA cloning take advantage of Taq polymerase adding extra adenines to PCR products, allowing ligation into vectors with thymidine overhangs.