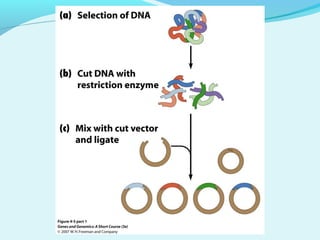
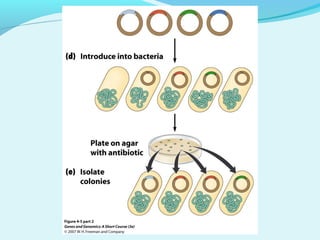
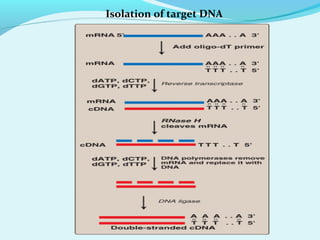
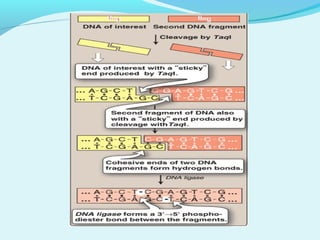
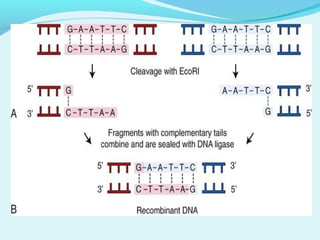
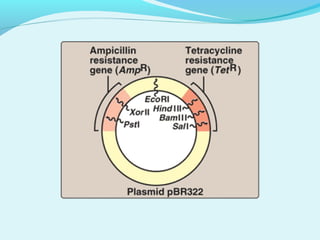
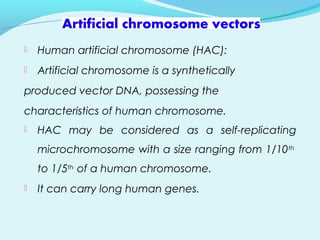
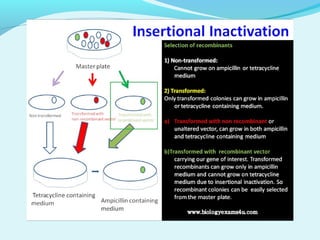
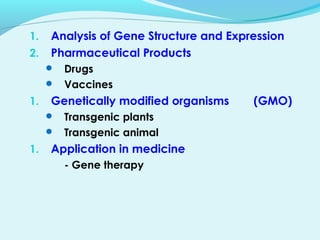
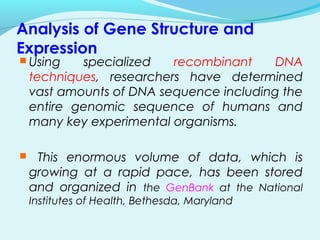
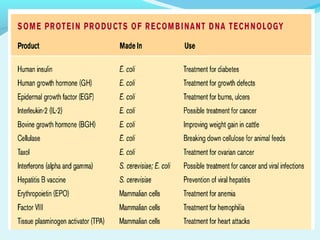
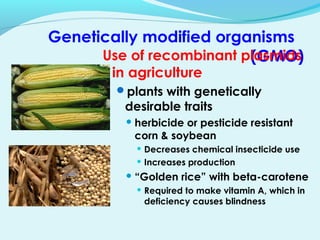
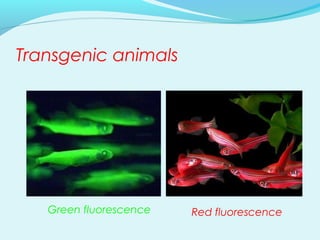
Recombinant DNA technology involves transferring genes between organisms using artificial means. It works by combining DNA from different sources into a single molecule. The process involves generating DNA fragments, inserting the fragments into vectors, introducing the vectors into host cells, and selecting clones containing the recombinant DNA. Common tools used include restriction enzymes to cut DNA, vectors like plasmids to carry DNA, bacterial hosts like E. coli, and techniques like transformation and selection to introduce and identify recombinant DNA. Applications include analyzing gene structure, producing pharmaceuticals, genetically modified organisms, and gene therapy.