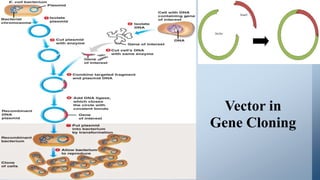
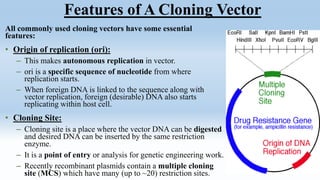
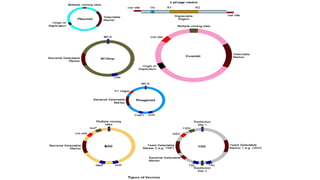
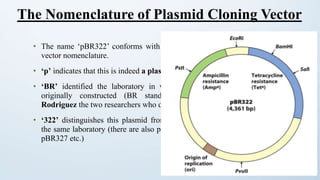
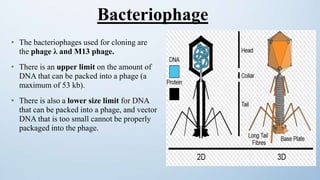
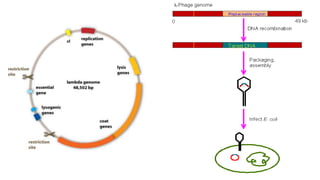
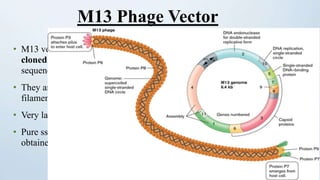
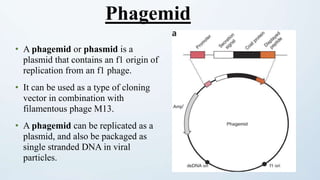
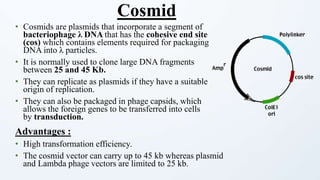
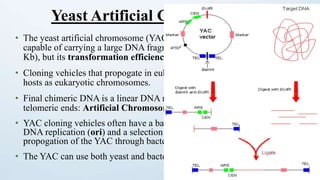
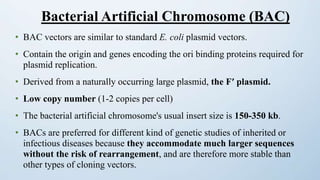
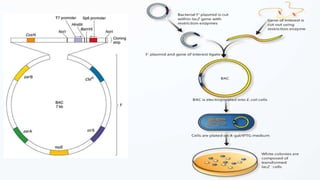
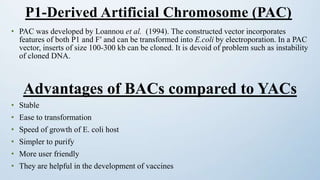
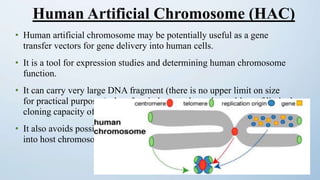
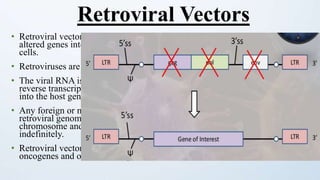
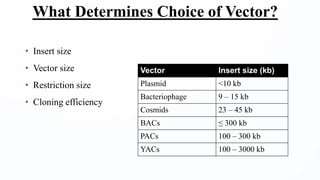
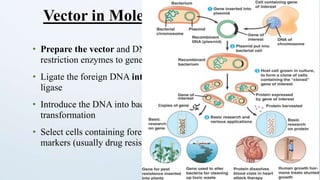
This document discusses cloning vectors, which are DNA molecules used to transport cloned DNA sequences between biological hosts. It defines a cloning vector as a small piece of DNA from a virus, plasmid, or cell that can maintain foreign DNA for cloning. The summary describes the key features of cloning vectors, including an origin of replication, cloning site, selectable marker, and optional reporter gene. It also lists common vector types like plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes, and factors that determine the choice of vector, such as insert size.