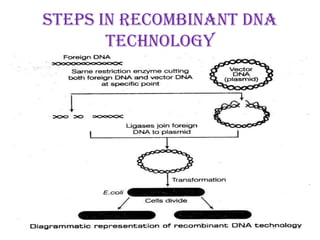
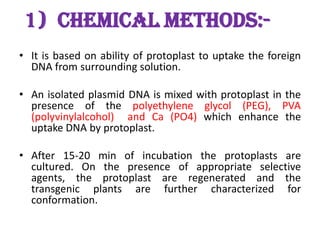
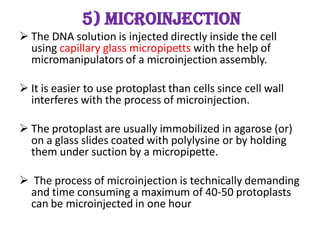
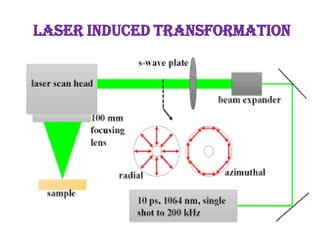
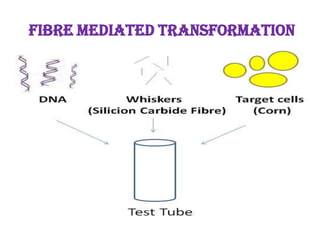
This document discusses various vectorless and direct gene transfer methods for recombinant DNA technology. It describes 10 different methods: chemical methods, electroporation, particle bombardment, lipofection, microinjection, macroinjection, pollen transformation, delivery via growing pollen tubes, laser induced transformation, and fibre mediated transformation. Each method directly introduces DNA into host cells without the use of biological vectors. The document provides details on the mechanisms and procedures for several of these direct gene transfer techniques.