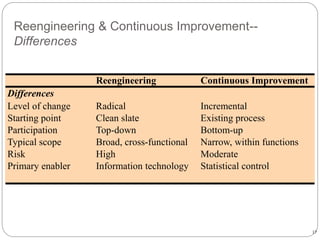
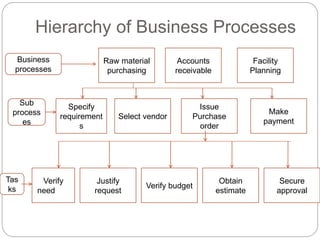
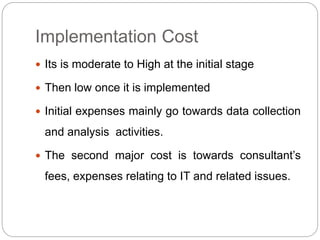
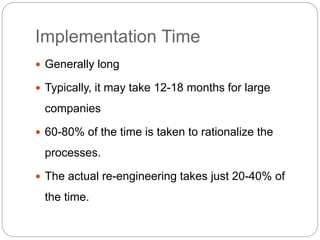
Business process reengineering (BPR) involves analyzing and redesigning workflows within an organization to better support its mission and vision. It aims to fundamentally rethink how work is done to improve customer service, cut costs, and increase competitiveness by leveraging technology and empowering employees. BPR requires top management commitment and involves radical changes to processes across departmental boundaries rather than incremental improvements. The goals are to eliminate unnecessary tasks, reduce costs significantly, and improve product/service quality.