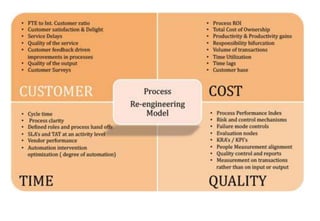
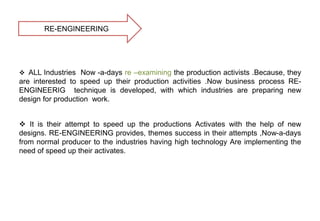
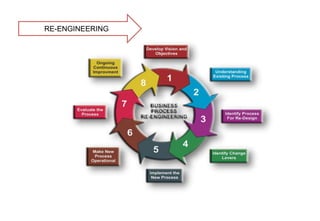
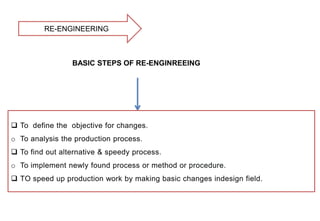
This document discusses re-engineering and provides details about Satish Patel's study of the topic for his Industrial Engineering course. It defines re-engineering as the radical redesign of business processes to achieve improvements in areas like cost, quality and speed. The document outlines the basic steps of re-engineering, why it is necessary due to factors like changing customer demands and technologies. It also discusses skills required, how to avoid failures and the four stages of change that organizations may experience when implementing re-engineering.



![Why BPR Is Necessary
– Change becomes constant.
• reduced product cycles
• reduced time to develop new products
• more environment scanning
• Technology
• Customer Preferences
– “Companies created to thrive on mass production, stability, and growth
can’t be fixed to succeed in [such] a world.”
• Integrate people, technology, & organizational culture to Respond to rapidly
changing technical & business environment and customer’s needs to
achieve Big performance gains](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/re-engineering-i-170517191757/85/Re-engineering-i-e-116010319119-7-320.jpg)