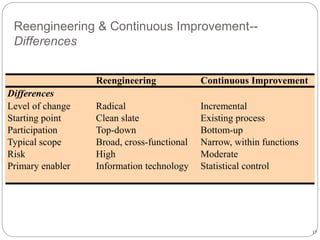
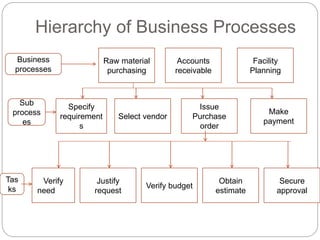
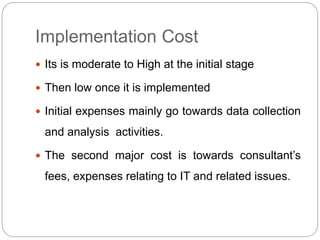
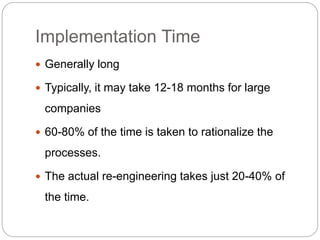
Business process re-engineering (BPR) involves analyzing and redesigning workflows within an organization to help support its mission and vision. The goals of BPR include fundamentally rethinking how work is done to improve customer service, cut costs, and increase competitiveness by leveraging technology and empowering employees. Successful BPR requires top management commitment and aims to eliminate non-value adding tasks while improving productivity and quality.