Reproductive health encompasses physical, emotional, and social well-being related to reproduction, with an emphasis on family planning initiated in 1951 to address early marriages and high maternal and infant mortality rates in India. Various methods of contraception, including natural, barrier, intrauterine devices, oral contraceptives, and emergency contraceptives, are discussed to control population growth and promote reproductive health awareness. The document highlights the importance of education on personal hygiene and fertility regulation for both genders to lead a healthy reproductive life.





![• Family welfare and family planning programs
comes forward to avoid uncontrolled human
population explosion.
• The contraception is the main aim of the birth
control.
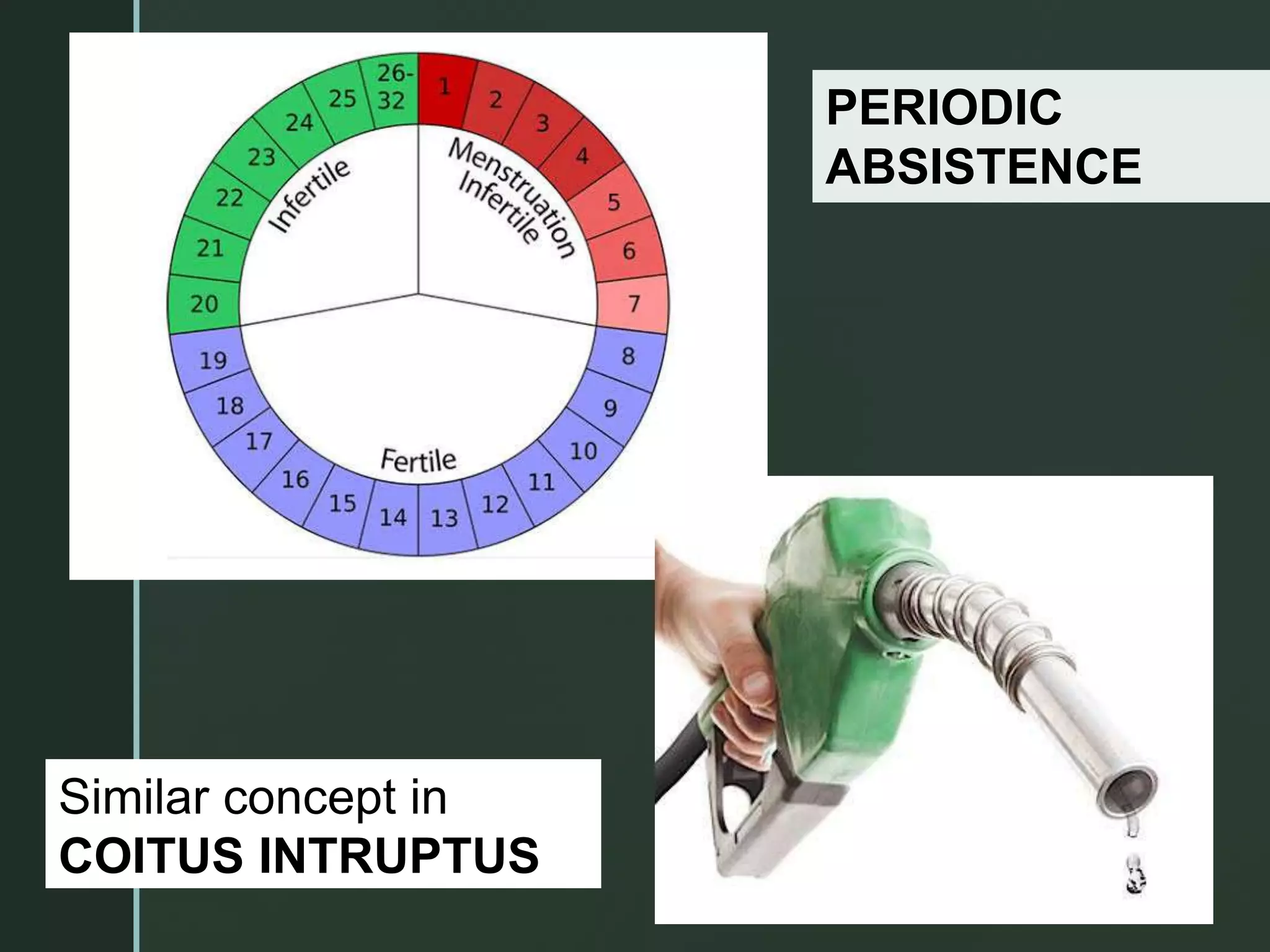
• Prevention of conception or fertilization of ovum
during sexual inter course is called contraception.
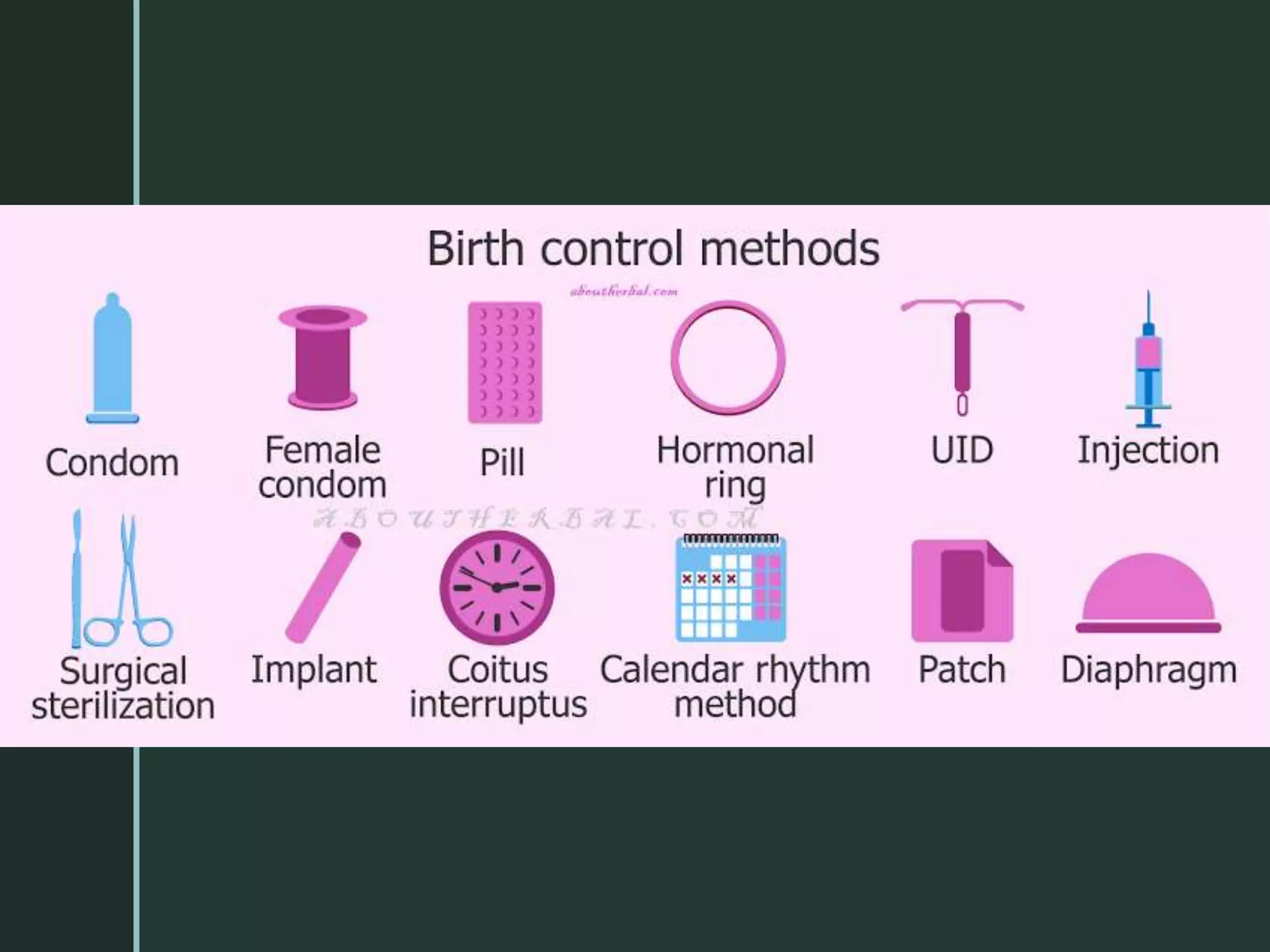
The different types of contraception are,
• Natural method.
• Barrier method.
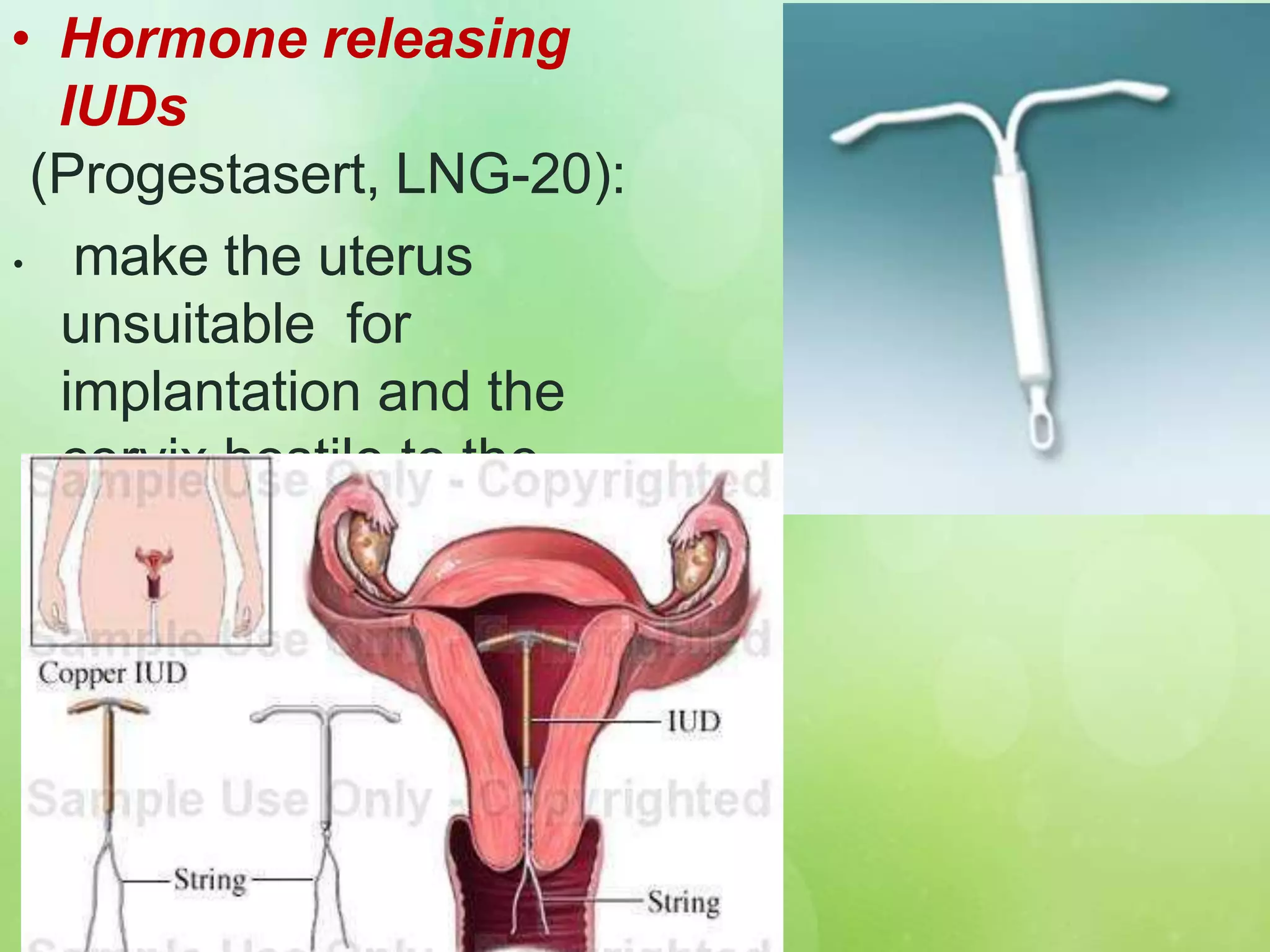
• Intra uterine device [IUD’s].
• Oral contraception.
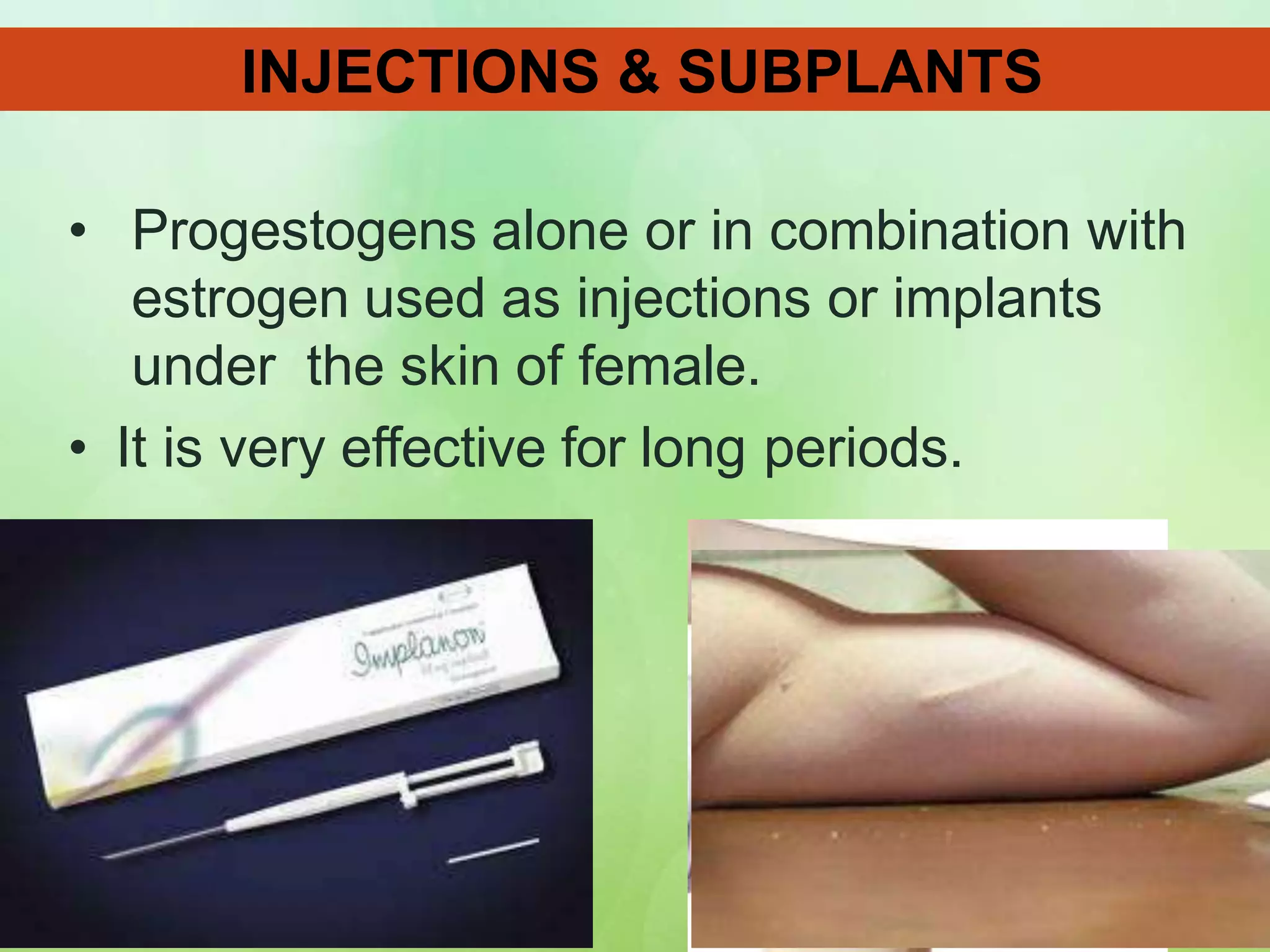
• Injection and implantation.
BIRTH CONTROL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reproductivehealth-i-210603040456/75/Class-XII-chapter-4-Reproductive-Health-6-2048.jpg)