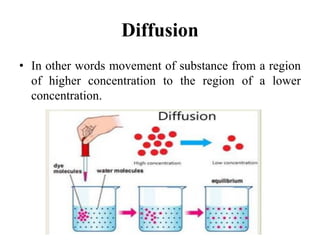
This document discusses diffusion principles in biological systems as they relate to drug absorption and delivery. It begins by defining diffusion and outlining Fick's laws of diffusion. It then discusses several examples of diffusion processes:
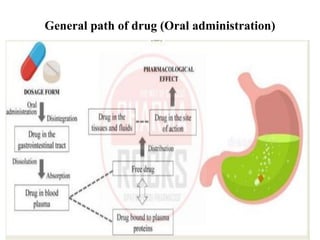
1) Gastrointestinal drug absorption, where drugs must dissolve and diffuse through the GI membrane layers to enter blood circulation. Absorption depends on factors like surface area, partition coefficient, and ionization state.
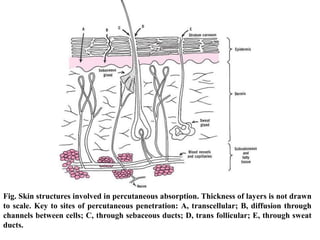
2) Percutaneous absorption, with skin as the barrier. Drugs diffuse through stratum corneum, dermis, and subcutaneous layers.
3) Buccal absorption, where drugs diffuse through the lipoidal buccal membrane, following principles like pH-partition hypothesis.