The document discusses the Nernst distribution law, which describes how a solute divides itself between two immiscible liquids in a constant ratio at a given temperature. It outlines the law's applications in various processes such as solvent extraction, partition chromatography, and the de-silverization of lead, while also highlighting limitations like the requirement for constant temperature and low concentrations. Additionally, the document compares separating funnels and fractional distillation, detailing their principles, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.

![(8)The degree of hydrolysis of substances
The hydrolysis of aniline hydrochloride in water can be followed from the distribution of aniline hydrochloride
between water and benzene. Thus for this reaction, Aniline hydrochloride (Salt) + Water (H2O) ↔ Aniline
(Base) + Hydrochloric acid (Acid)
Thus, Kh = {[Base] x [Acid]} / {[Salt] x [H2O]}
By applying the principle of equilibrium it can be shown that,
Kh = {C12 (1+vK)} / {C2 – C1 (1+vK)}
Where C1 is the concentration of the base in aqueous layer (C1 and C2 are expressed in Mol L-1), C2 the
original concentration of the salt, K the distribution coefficient and v is the volume of benzene in liters added to
1 liter of water.
1.6 Limitations of Distribution Law
Constant temperature. The temperature is kept constant throughout the experiment.
Same molecular state. The molecular state of the solute is the same in the two solvents. The law does
not hold if there is association or dissociation of the solute in one of the solvents.
Equilibrium concentrations. The concentrations of the solute are noted after the equilibrium has been
established.
Dilute solutions. The concentration of the solute in the two solvents is low. The law does not hold when
the concentrations are high.
Non-miscibility of solvents. The two solvents are non-miscible or only slightly soluble in each other.
The extent of mutual solubility of the solvents remains unaltered by the addition of solute to them.
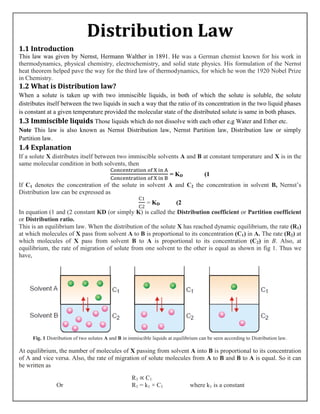
2. Contrast and Comparison between separation through
Separating funnel and Fractional Distillation
Separation through Separating funnel Separation through Fractional distillation
Separating funnel
A separating funnel is used to separate immiscible
liquids. Liquids that do not mix with each other are
said to be immiscible. Two immiscible liquids, such
as oil and water, can be separated by
using a separating funnel.
Example
Ether extraction is the common example of
separation through separating funnel.
Principle
The principle behind separating funnel is that
immiscible liquids separate out in layers depending
on their densities.
Parts:
Stopper
Body
Stopcock
Drain Tip
Stand
Fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is a process by which components in
a chemical mixture are separated into different parts
(called fractions) according to their different boiling
points.
Example
Fractional distillation of Crude oil is the common example
of separation through fractional distillation.
Principle
The principle of fractional distillation is that different
liquids boil at different temperature. So, When the mixture
of immiscible liquids is heated, the liquid with lower
boiling point boils and turns into vapors.
Parts
Thermometer
Condenser
Collecting flask
Benson burner/Stove/Heater
Boiling flask
Stand](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributionlawbykashifali029-200426061426/85/Distribution-law-4-320.jpg)
![3. References
1. Poudel, Subash. (18 Feb 2013). "Distribution law". Science HQ. Retrieved 14 Apr 2020 from
2. Kelly, Ryan T., et al. "The ion funnel: theory, implementations, and applications." Mass spectrometry reviews 29.2
(2010): 294-312.
3. Odebunmi, E. O., Ogunsakin, E. A., & Ilukhor, P. E. P. (2002). Characterization of crude oils and petroleum
products:(I) Elution liquid chromatographic separation and gas chromatographic analysis of crude oils and
petroleum products. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Ethiopia, 16(2), 115-132.
4. Experimental and theoretical applications of thermodynamics to chemistry / by Dr. Walther Nernst.
5. Definition of separating funnel | Dictionary.com. (2020). Retrieved 16 April 2020, from
https://www.dictionary.com/browse/separating-funnel
6. www.dictionary.com. 2020. Definition Of Separating Funnel | Dictionary.Com. [online] Available at:
<https://www.dictionary.com/browse/separating-funnel> [Accessed 16 April 2020].
7. Nernst Distribution law. (2020). Retrieved 16 April 2020, from
https://fch.upol.cz/skripta/fcc_and_zvem_english/FCH/Nernst%20Distribution%20law.htm
8. GCSE CHEMISTRY - What is a Separating Funnel? - How can Liquids be Separated using a Separating Funnel?
- GCSE SCIENCE. (2020). Retrieved 16 April 2020, from https://www.gcsescience.com/e-separating-funnel.htm
9. http://sites.science.oregonstate.edu/~gablek/CH361/bare_sepfunnel.htm
10. Barkan, Diana Kormos, and Diana Kormos Buchwald. Walther Nernst and the transition to modern physical
science. Cambridge University Press, 1999.
11. https://www.meritnation.com/ask-answer/question/what-are-the-applications-of-separating-funnel/is-matter-around-us-
pure/9540049
12. https://itstillworks.com/advantages-disadvantages-fractional-distillation-8513450.html
13. https://connectusfund.org/6-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-fractional-distillation
14. https://www.qsstudy.com/chemistry/applications-distribution-law
15. Cantwell, Frederick F., and Manon Losier. "Liquid–liquid extraction." Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry 37
(2002): 297-340.
***********************************](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/distributionlawbykashifali029-200426061426/85/Distribution-law-6-320.jpg)