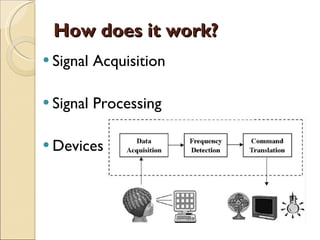
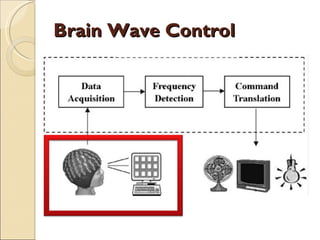
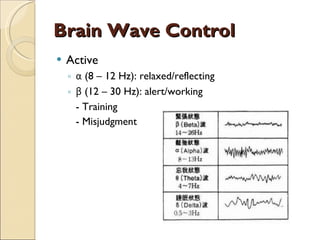
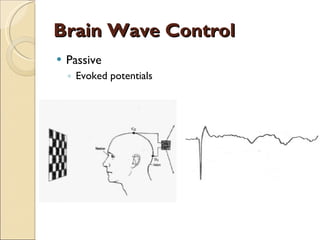
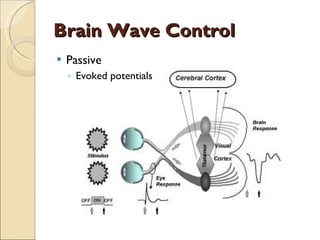
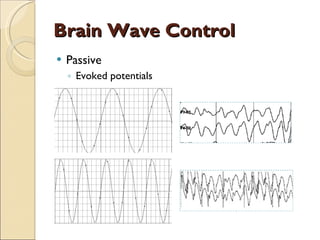
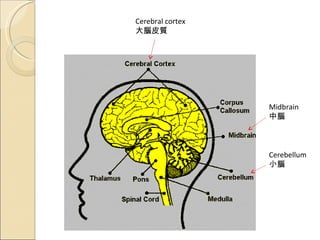
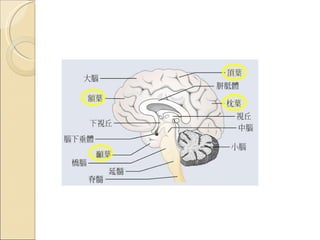
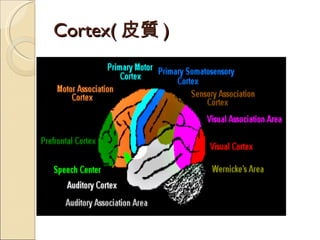
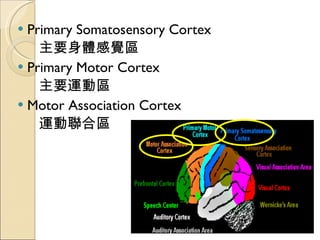
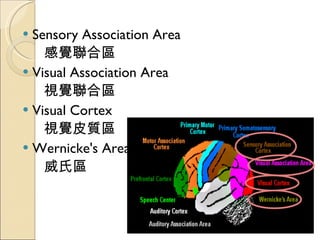
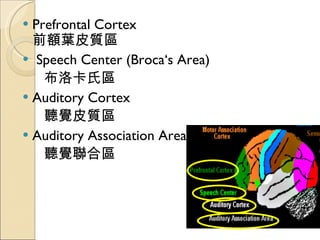
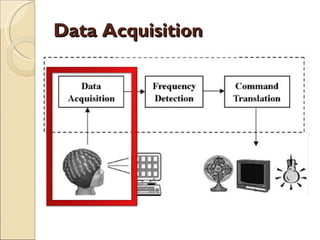
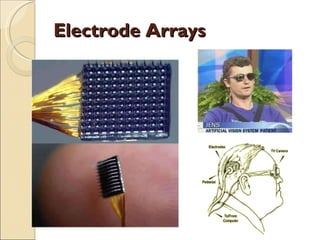
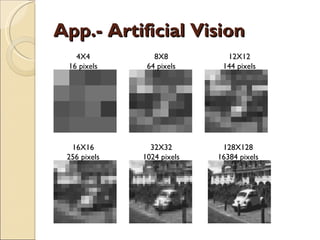
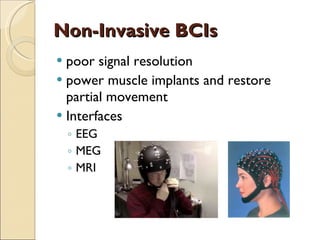
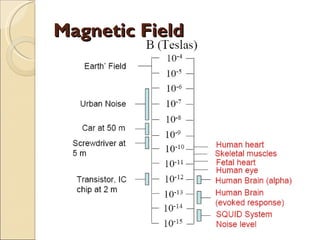
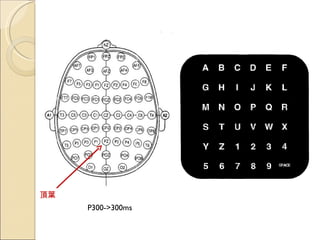
The document provides an overview of brain-computer interfaces (BCI), explaining their definition, working mechanisms, and various types including invasive, non-invasive, and partially-invasive BCIs. It covers brain wave control, data acquisition methods, and applications such as robotic control, alongside potential drawbacks and future developments in the field. Additionally, it highlights notable research examples and includes references for further reading.