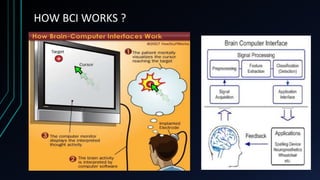
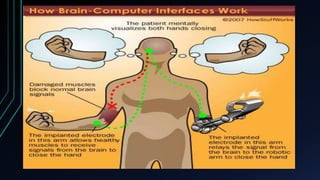
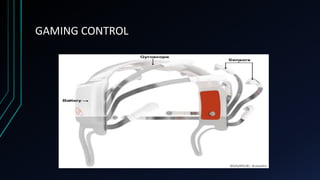
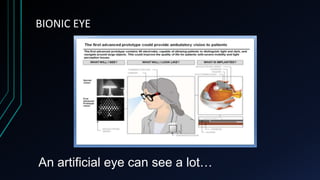
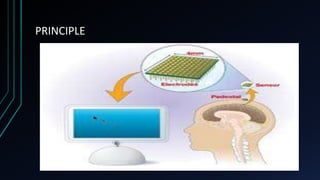
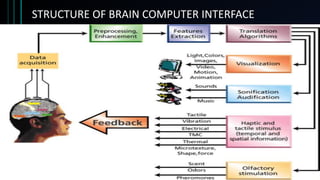
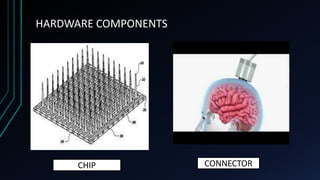
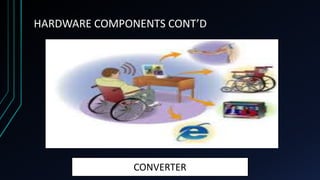
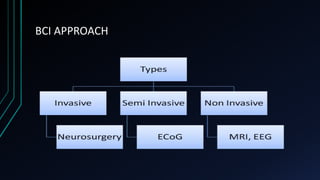
This document discusses brain-computer interfaces (BCI). A BCI allows direct communication between the brain and external devices, establishing a link for control. The structure of a BCI includes hardware components like a chip connector and converter to process brain signals, typically electroencephalography (EEG) readings. Experiments have successfully used BCIs on rats and monkeys to control devices via thought. Potential applications include assisting paralyzed patients, military/civilian research, gaming control, and a bionic eye. While BCIs offer advantages like direct brain communication and technological advancement, they also face challenges such as training requirements, costs, and potential security issues. Overall, BCIs represent an advancing paradigm that could enable new capabilities in machine control,



![EEG [Electro Encephalo Graph]
What is an EEG??](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/braincomputerinterfacing-140419121051-phpapp02/85/Brain-computer-interfacing-9-320.jpg)