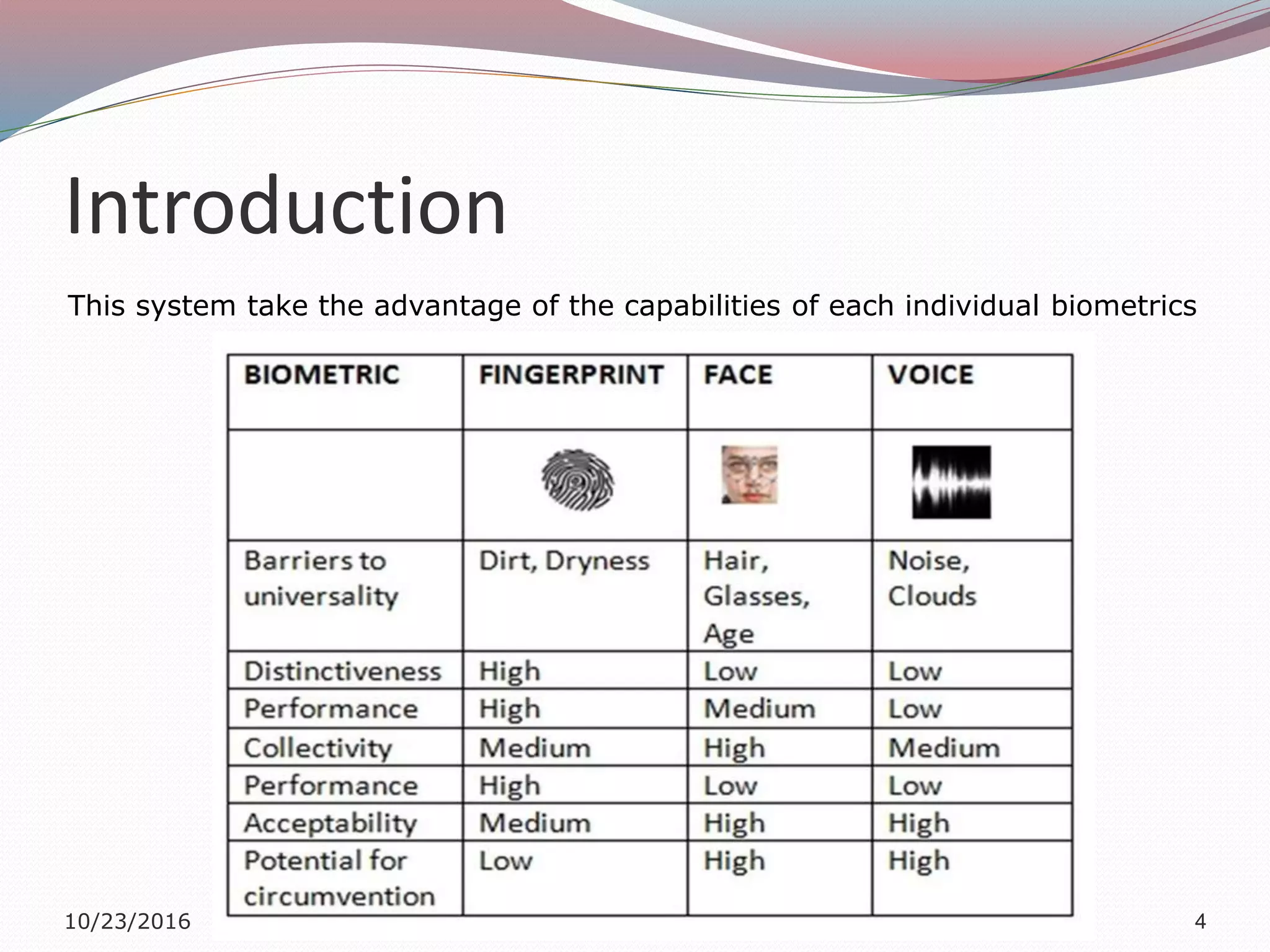
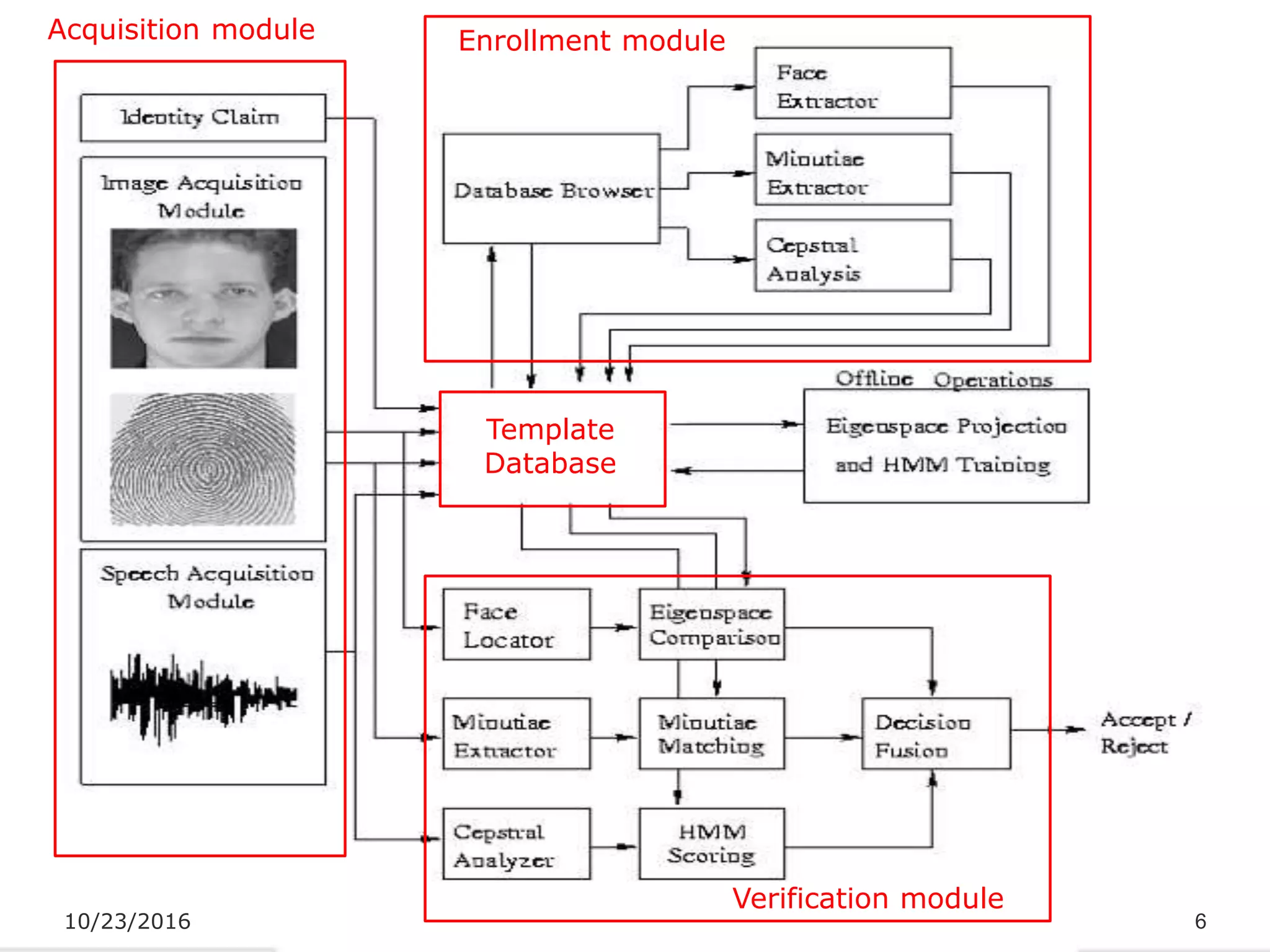
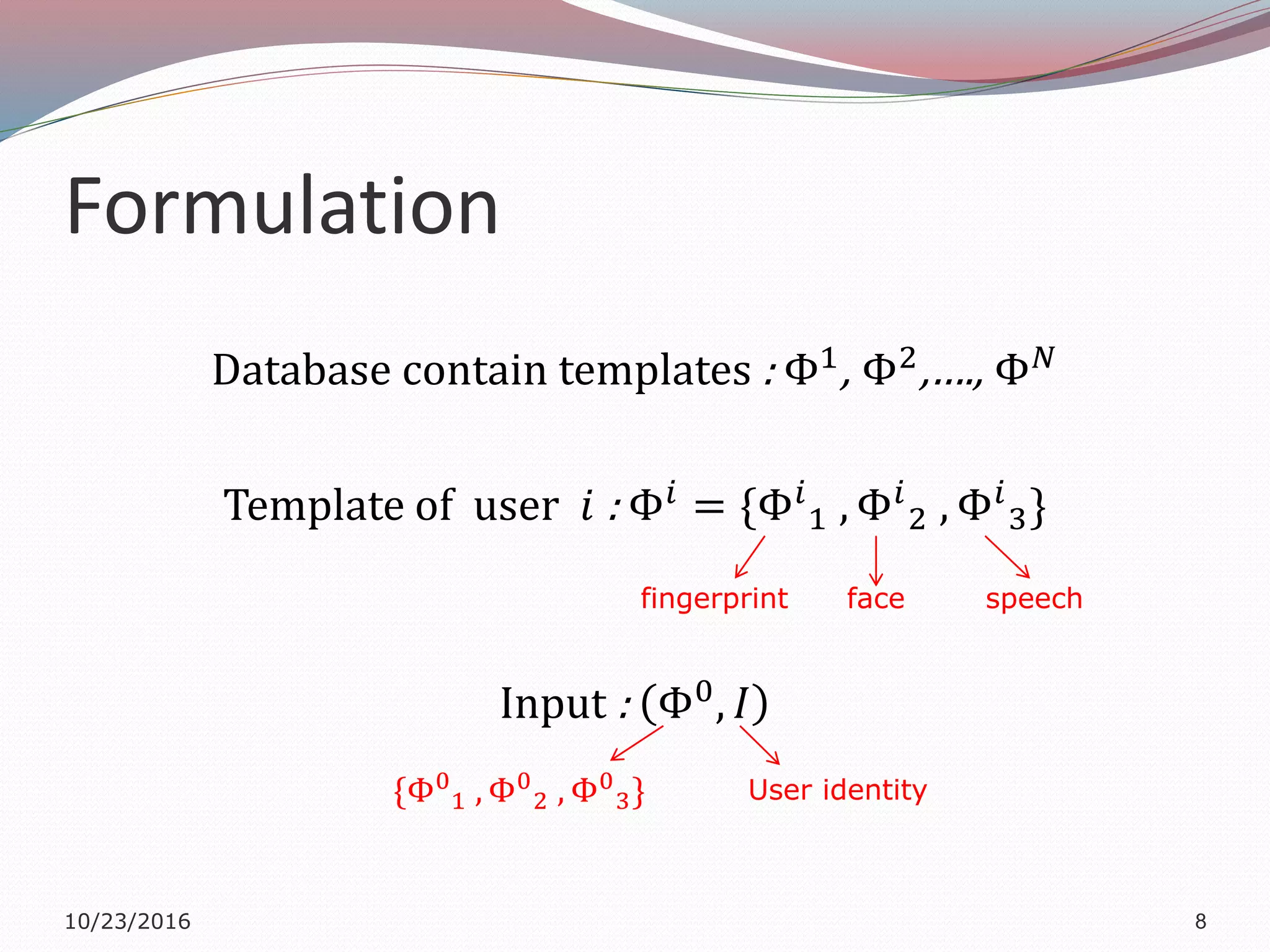
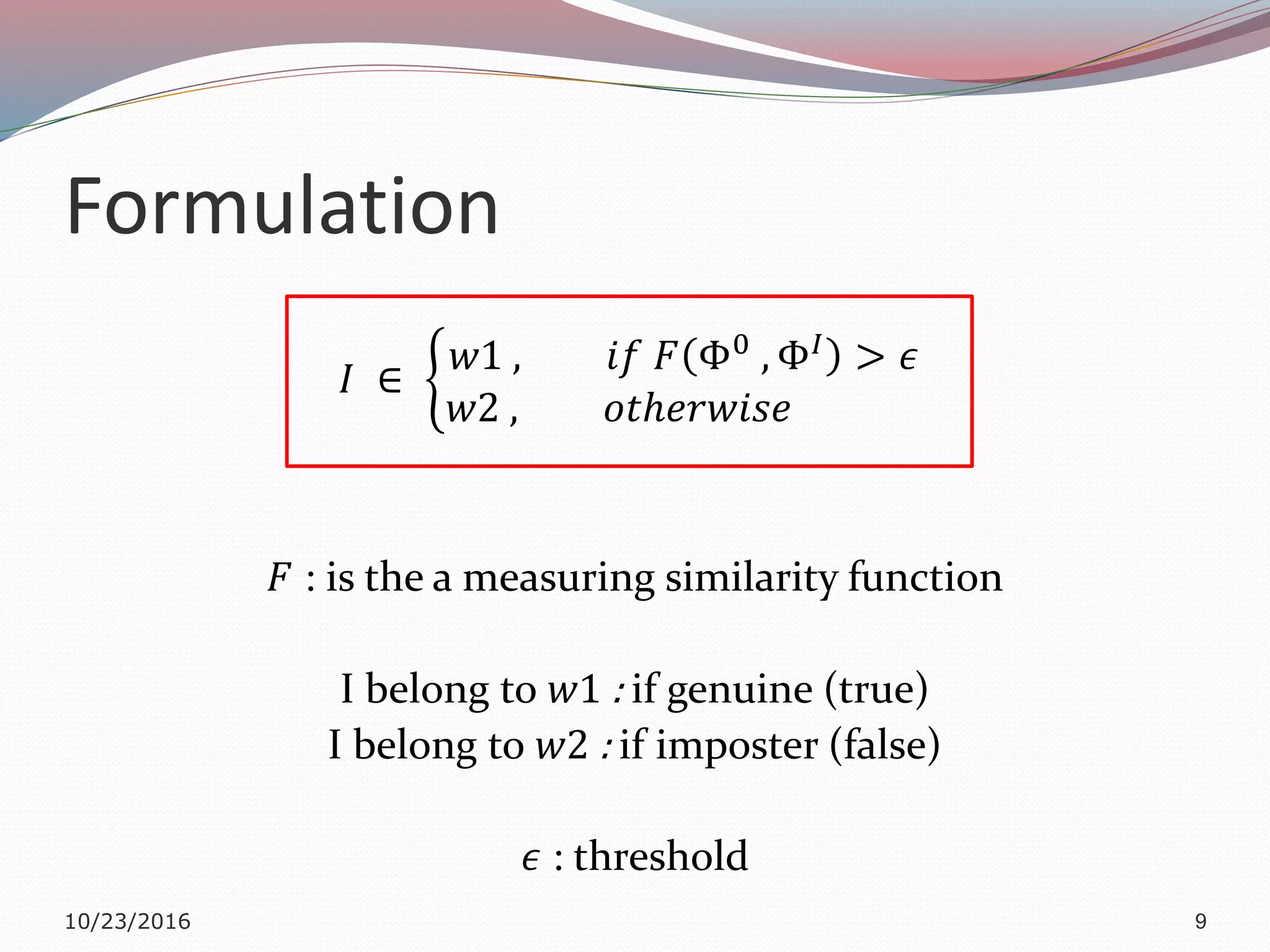
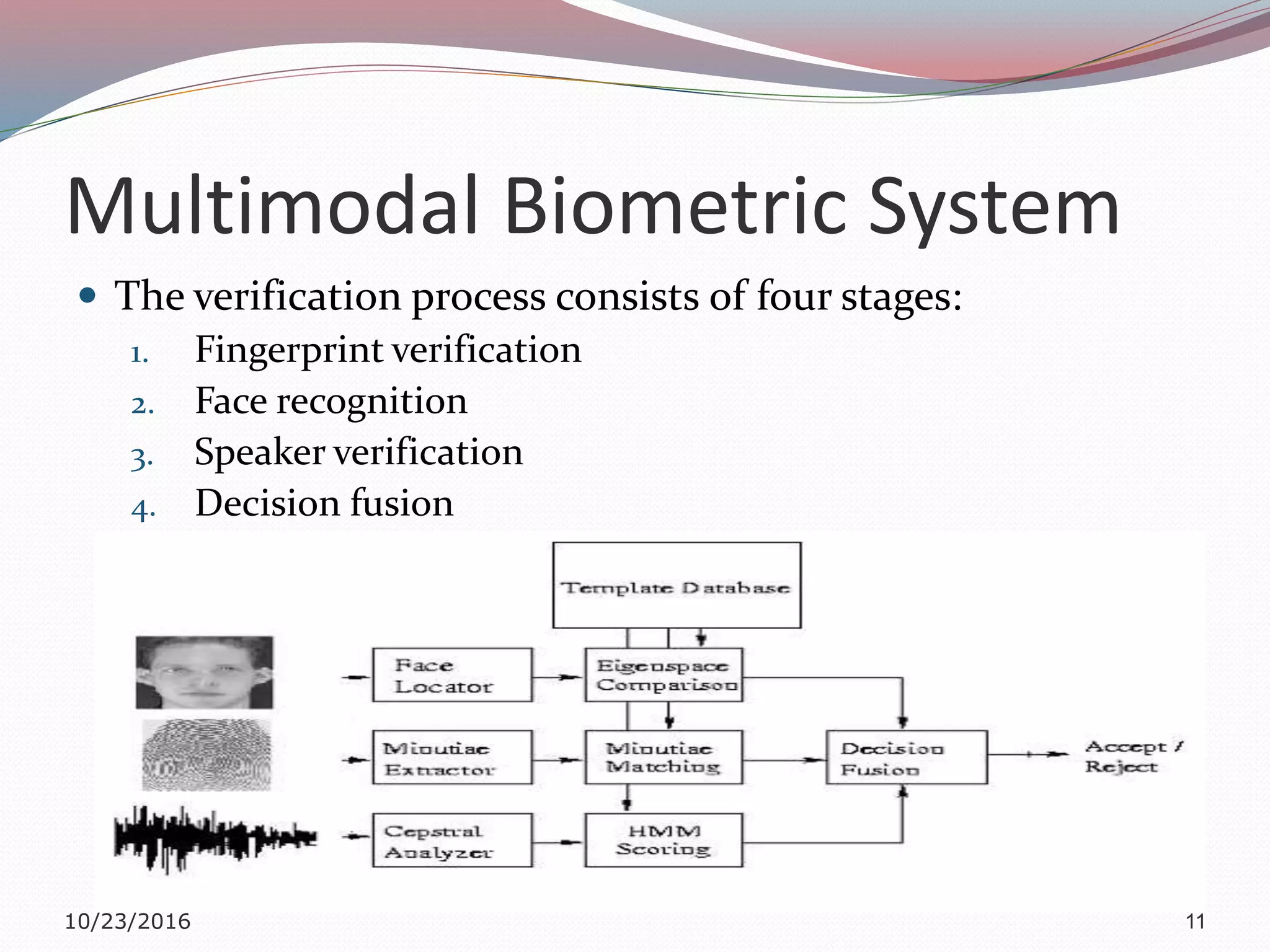
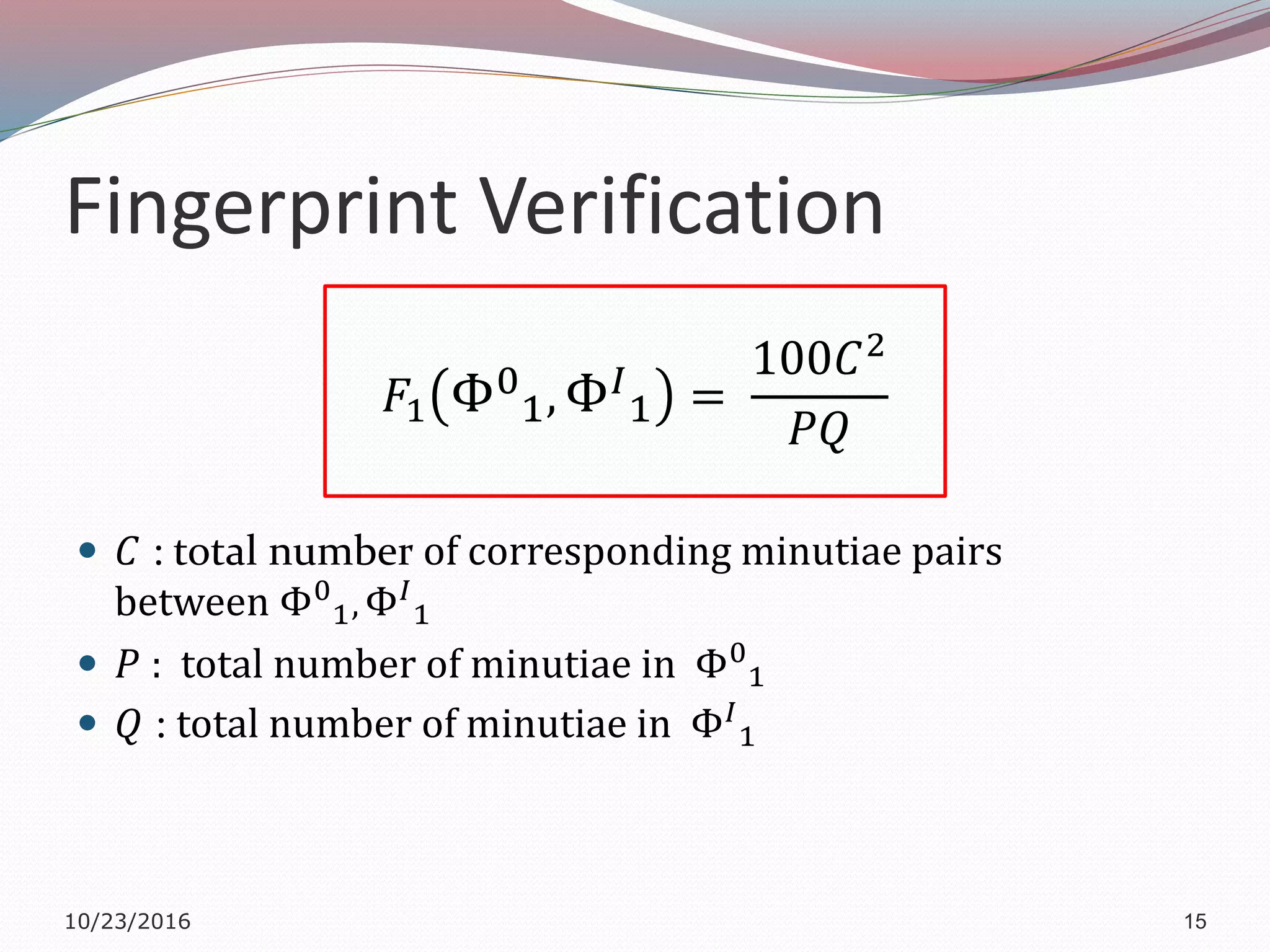
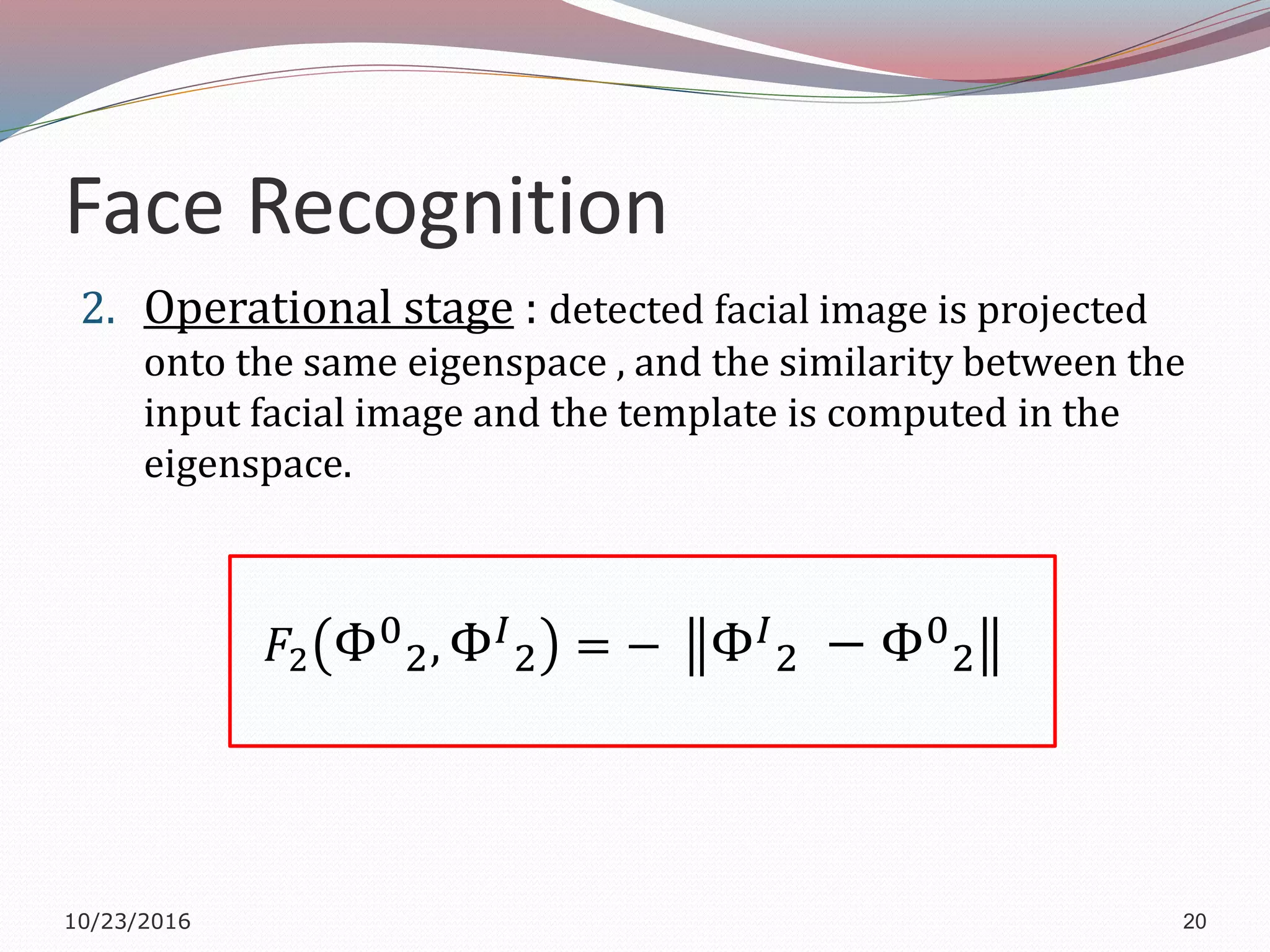
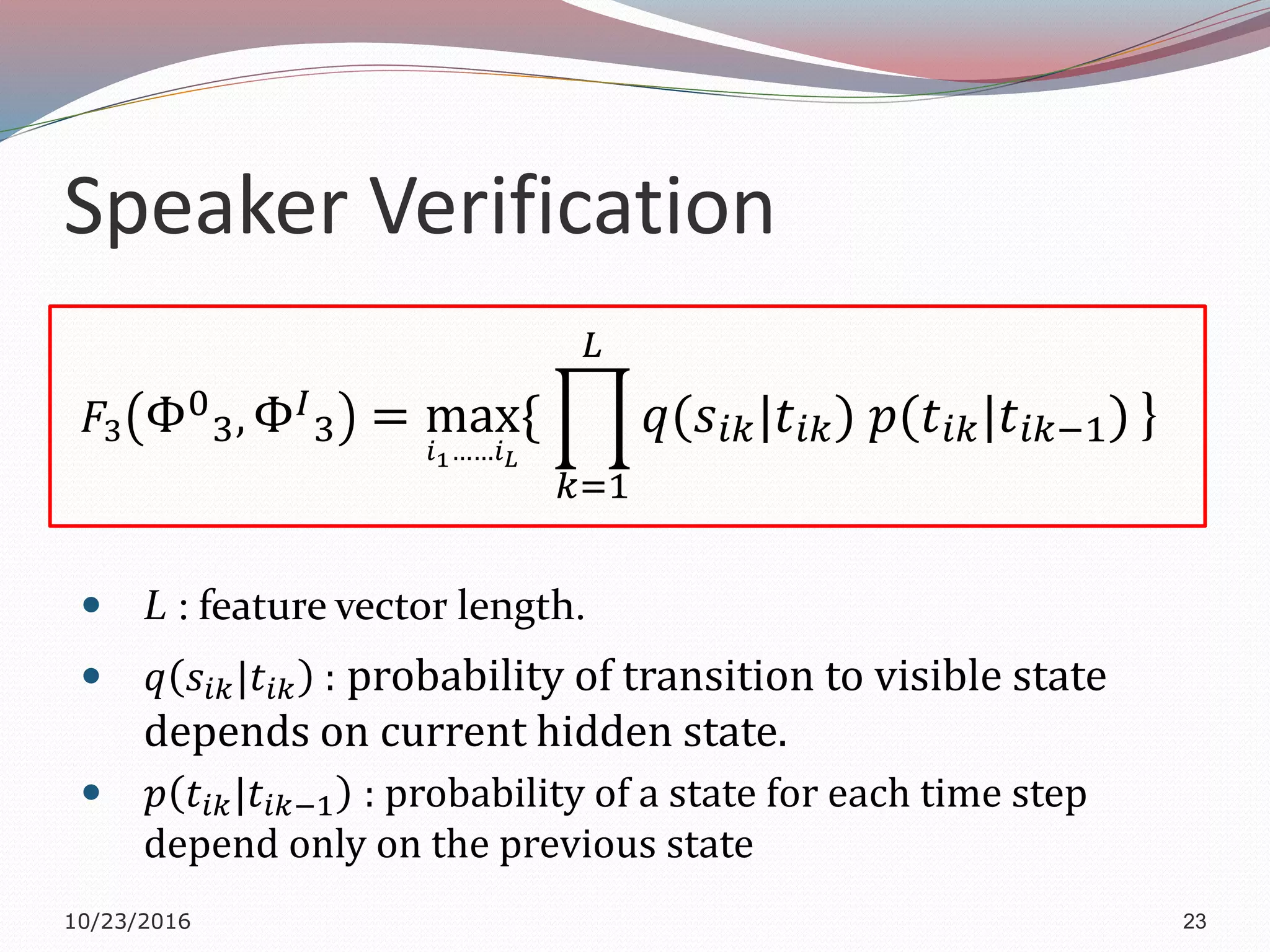
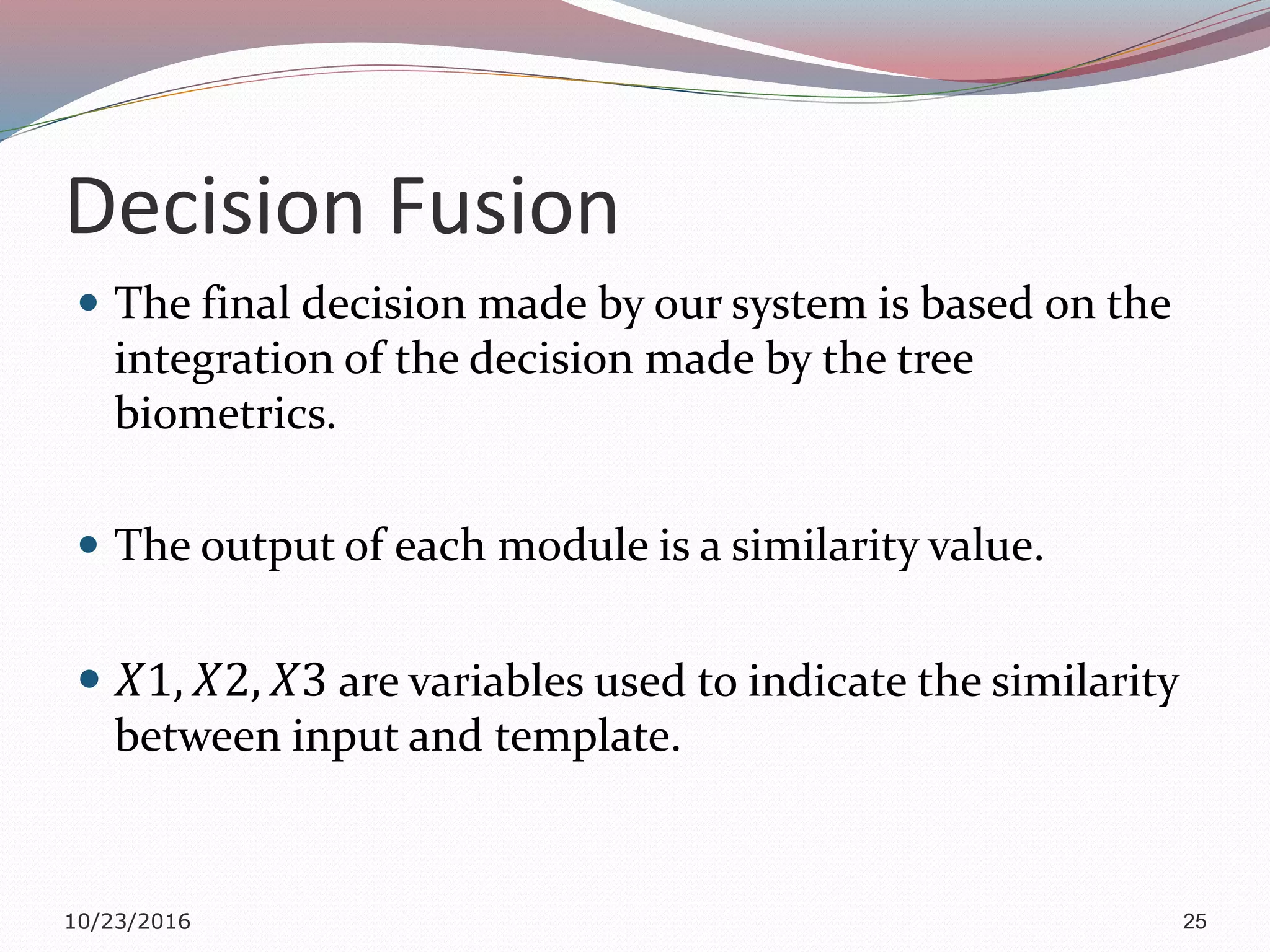
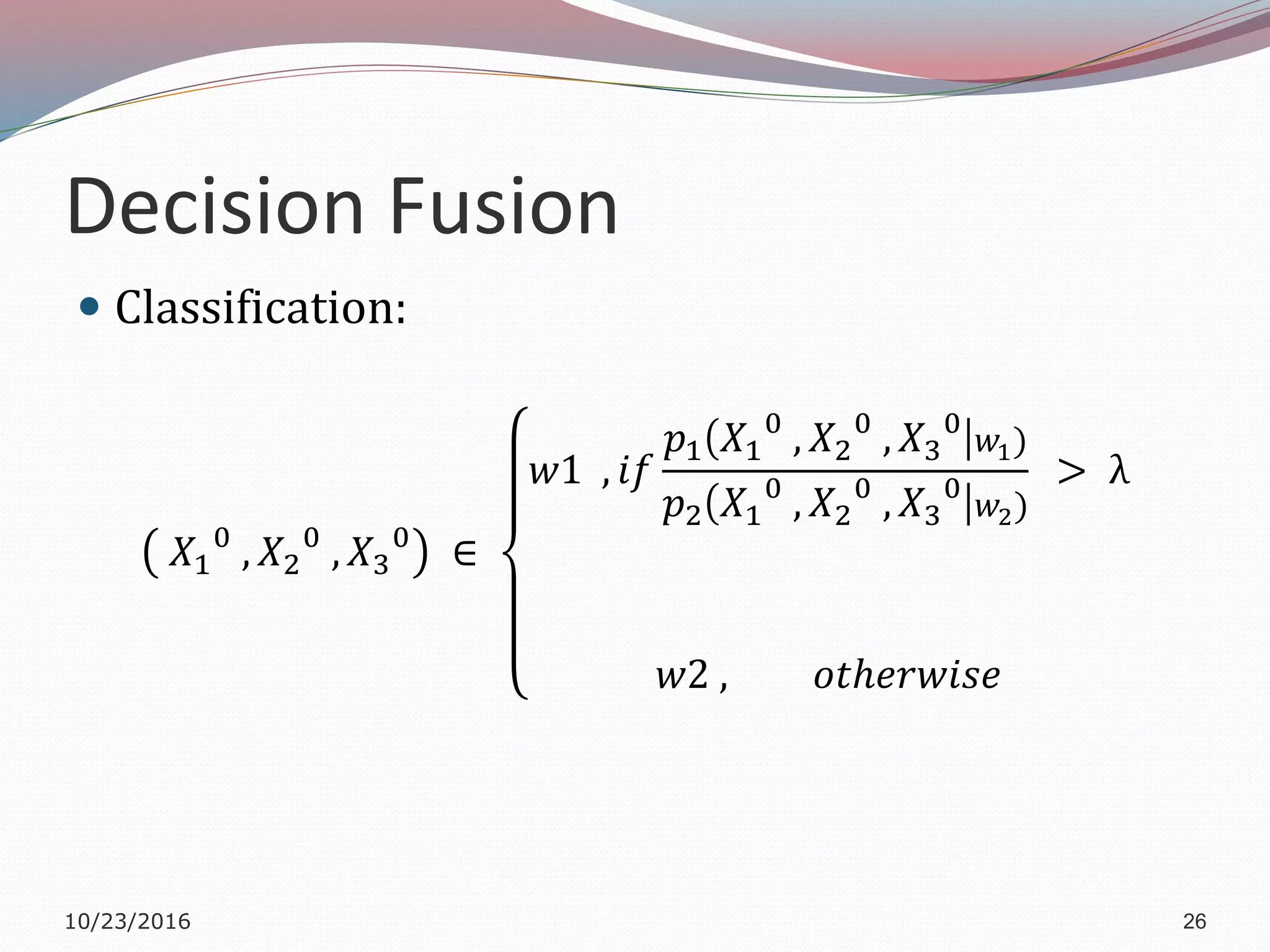
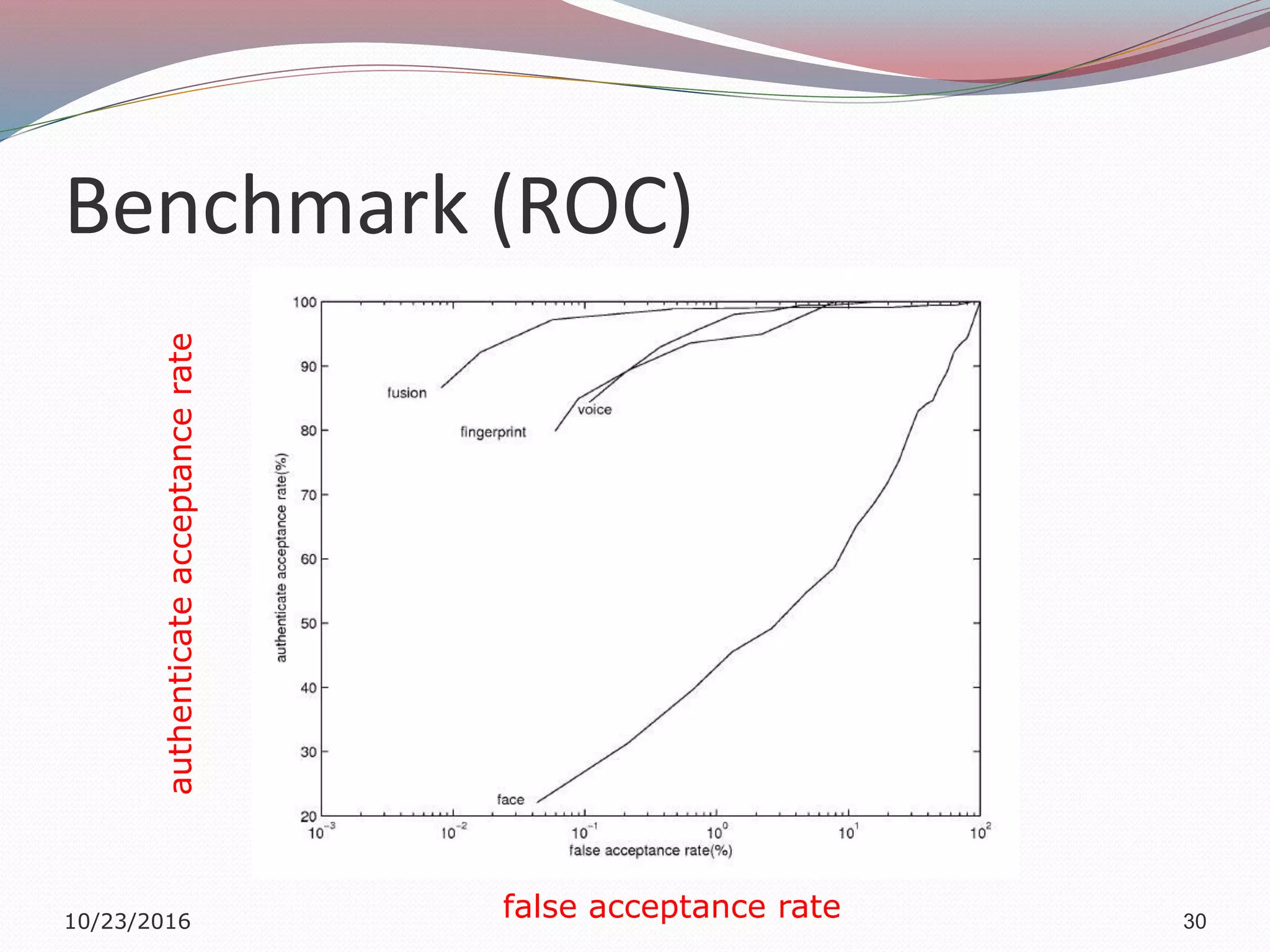
The document discusses a multimodal biometric system that integrates fingerprint verification, face recognition, and speaker verification to improve performance in user identification. It outlines the components and processes of the system, including data acquisition, template matching, and decision fusion. The findings suggest that this integration enhances verification accuracy compared to individual biometric methods.