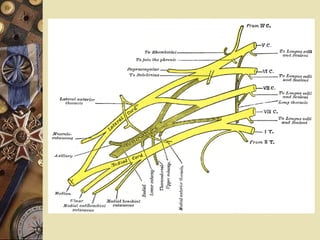
The document discusses the brachial plexus, which is formed by the anterior rami of cervical and upper thoracic spinal nerves. It describes the roots, trunks, divisions, cords and branches of the brachial plexus. Common brachial plexus injuries are also summarized, including their causes, types, investigations, treatments, and specific injuries like Erb's palsy and Klumpke's paralysis.