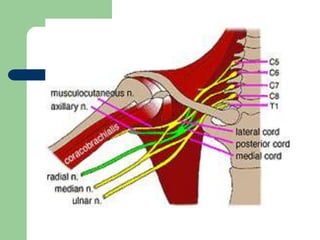
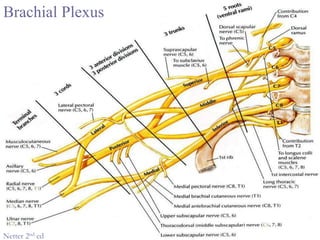
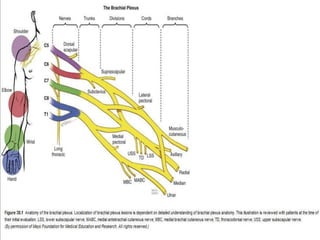
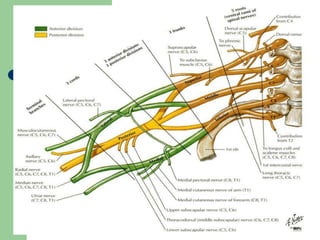
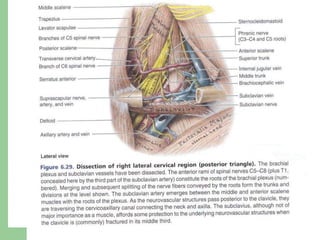
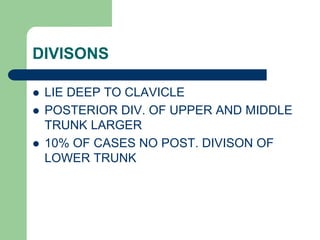
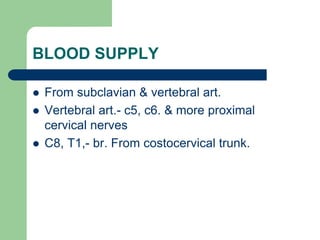
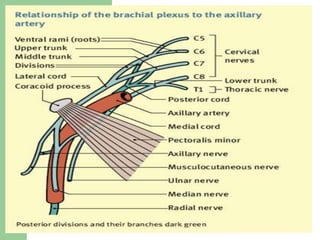
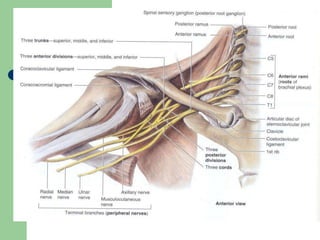
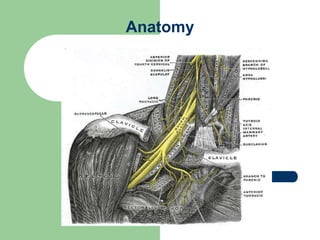
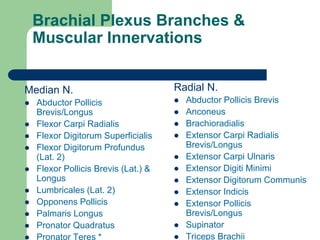
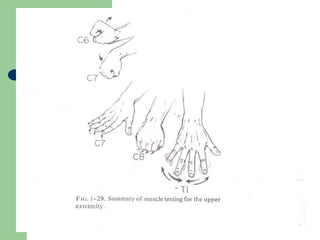
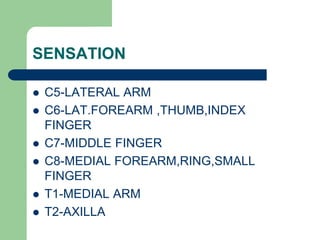
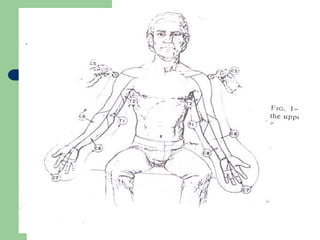
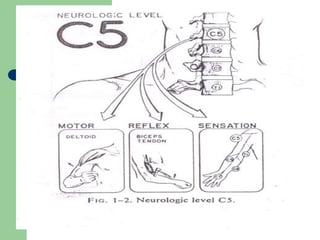
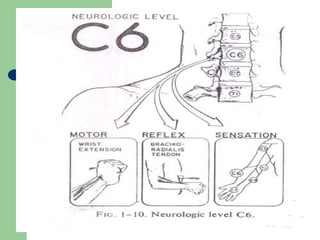
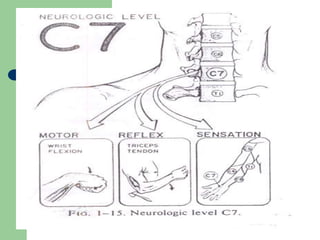
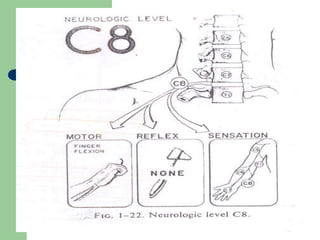
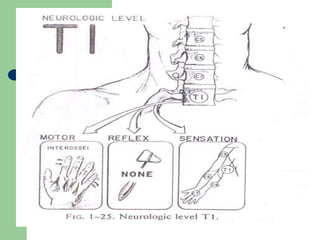
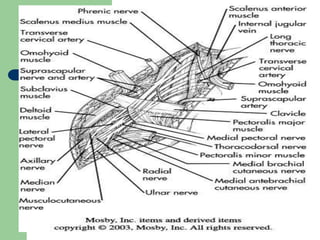
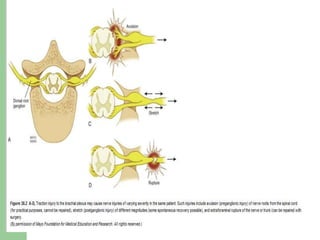
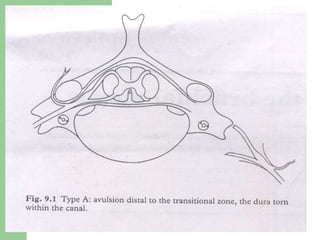
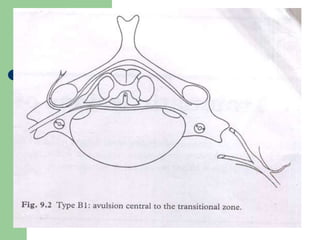
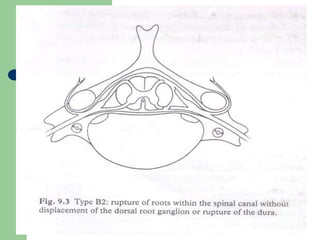
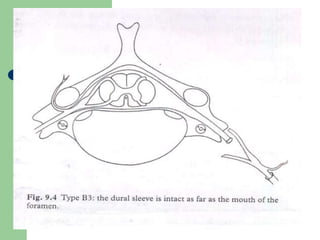
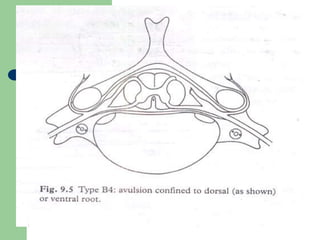
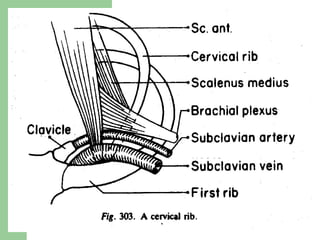
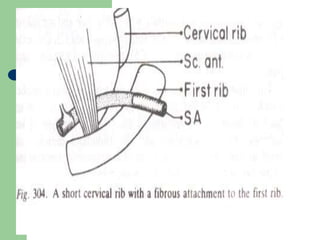
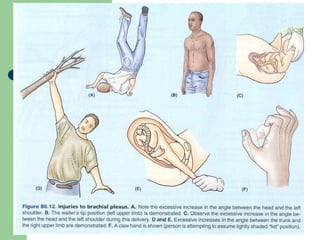
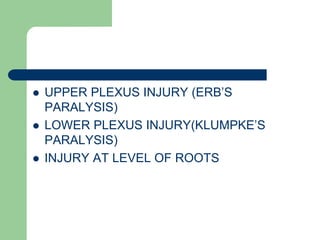
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that originates from the lower cervical and upper thoracic spinal nerve roots and provides motor and sensory innervation to the upper limb. It has five roots, three trunks, divisions, cords and branches. The roots emerge from the spinal nerves C5-T1. The cords are named lateral, posterior, and medial based on their relationship to the axillary artery. The plexus gives rise to many branches that innervate specific muscles and skin areas of the upper limb. Variations commonly occur in the formation of the lateral cord. Injuries can happen at the level of the roots, cords or branches and cause different functional deficits depending on the location and extent of injury