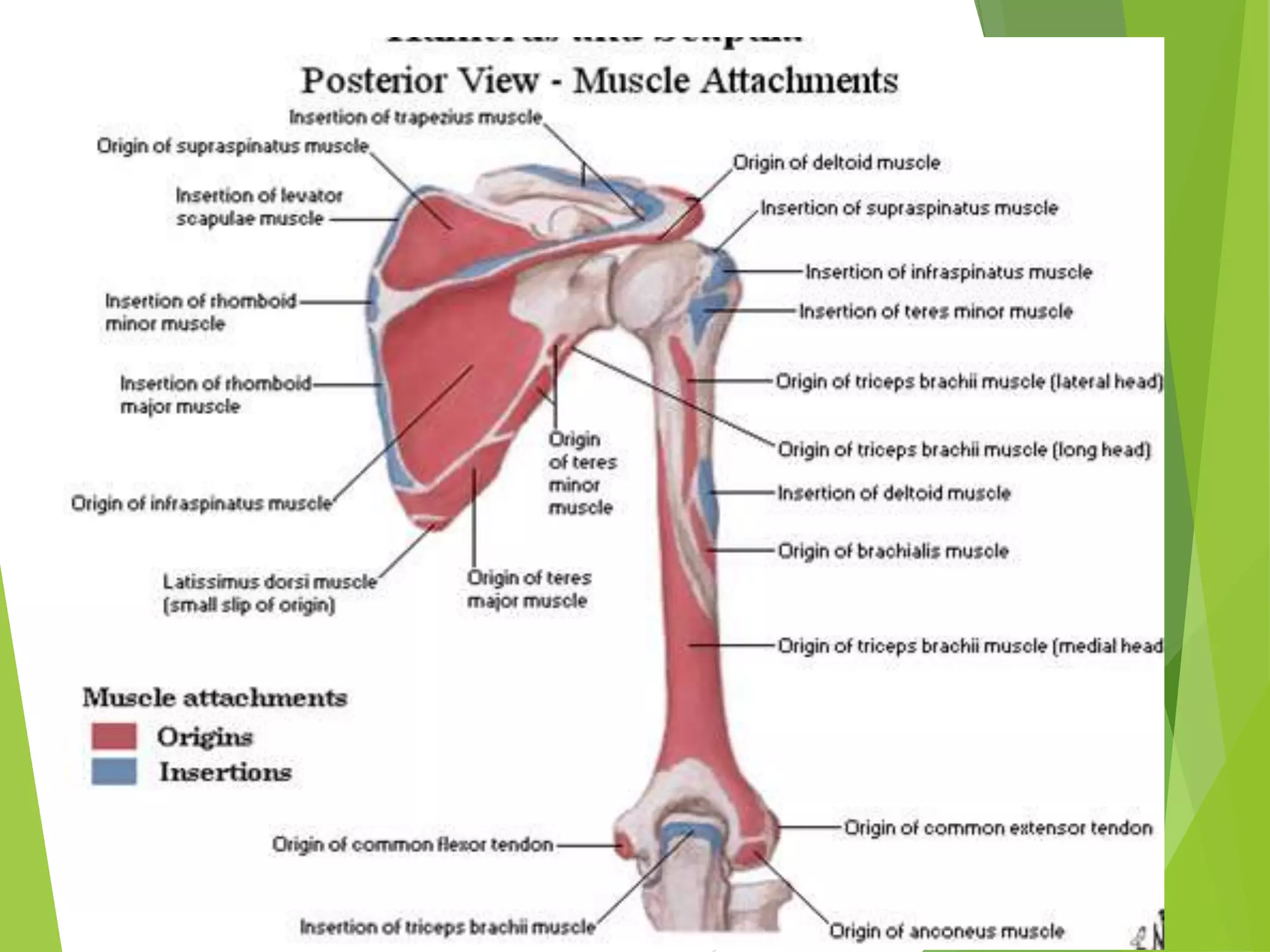
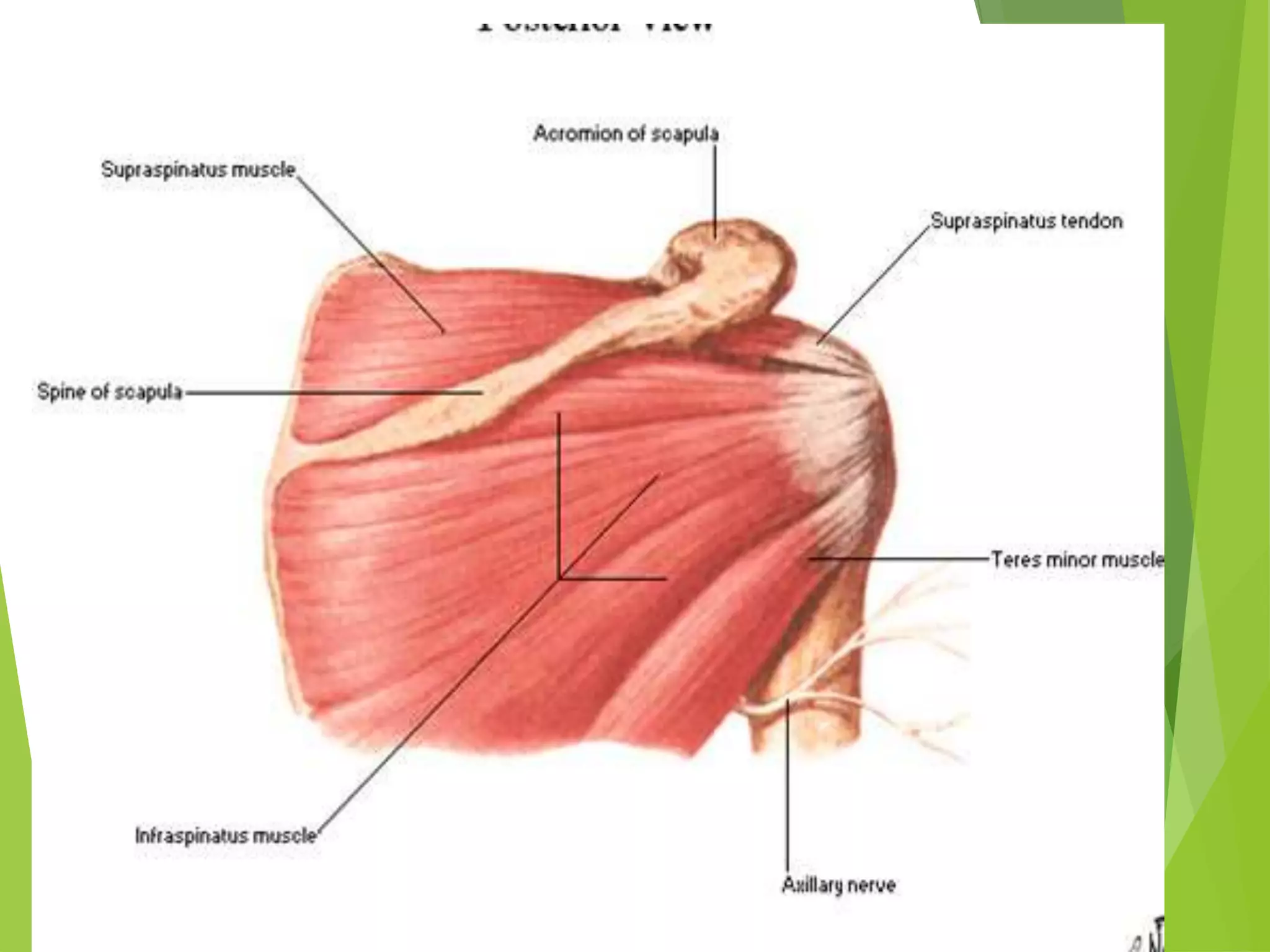
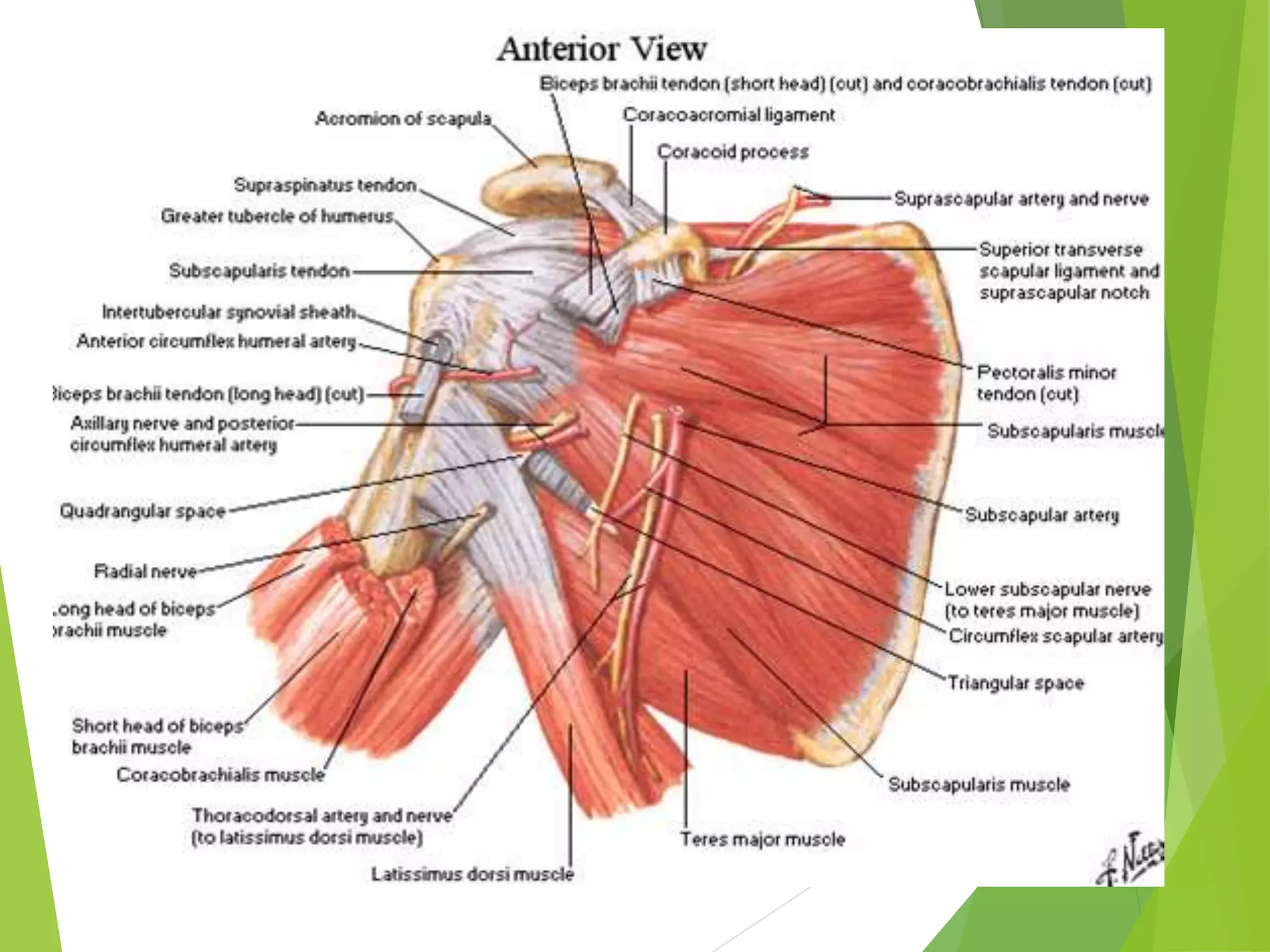
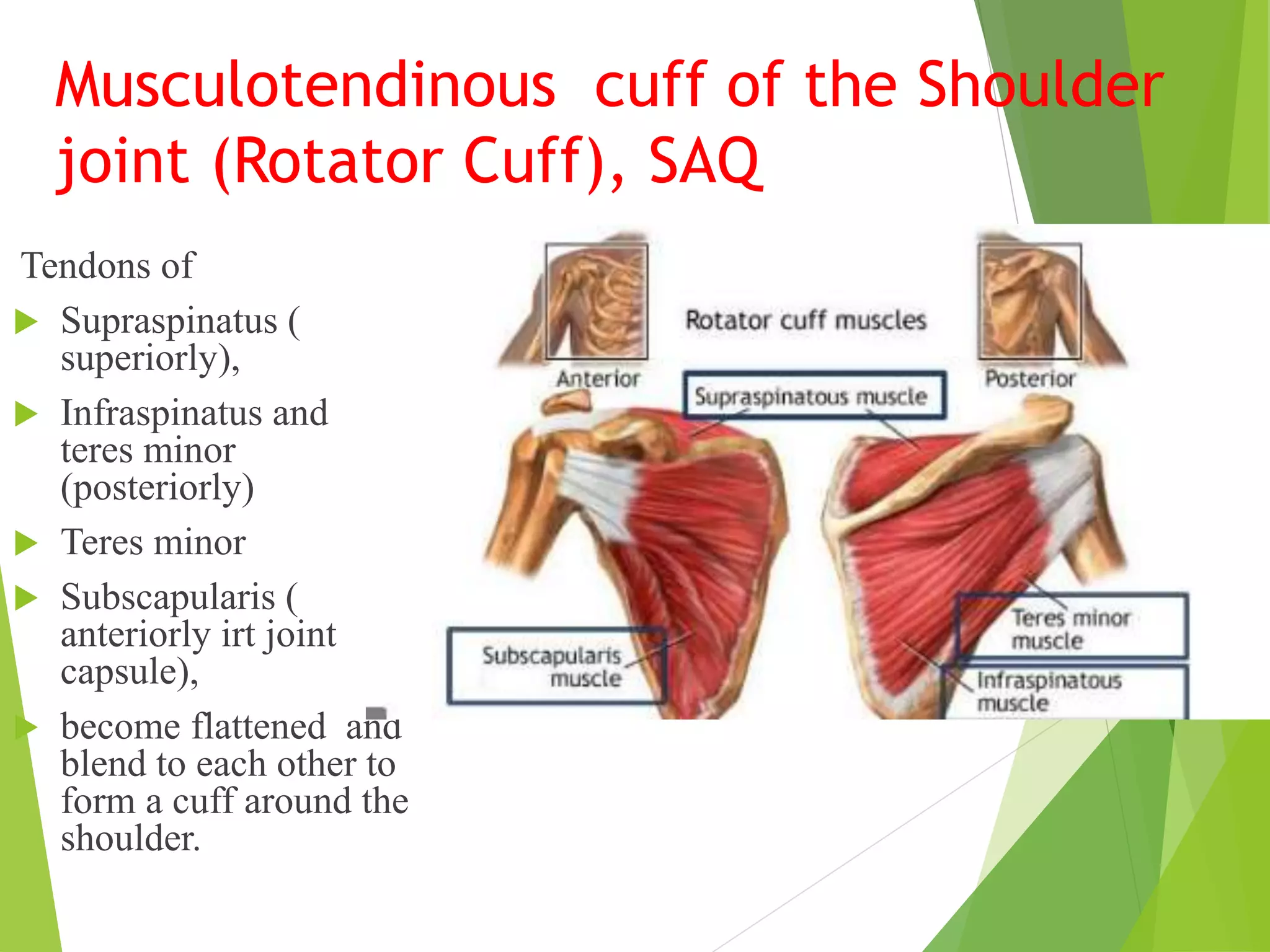
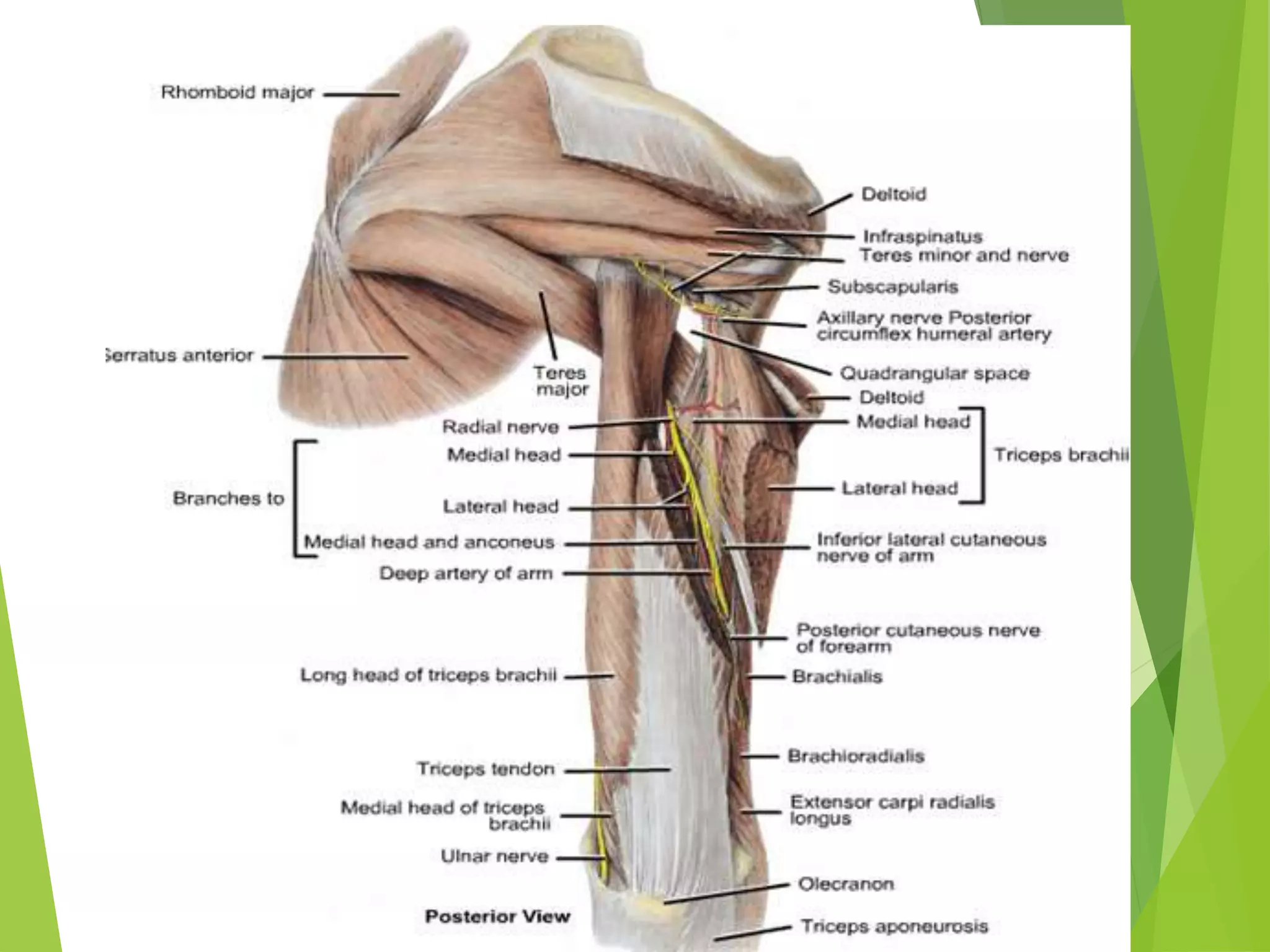
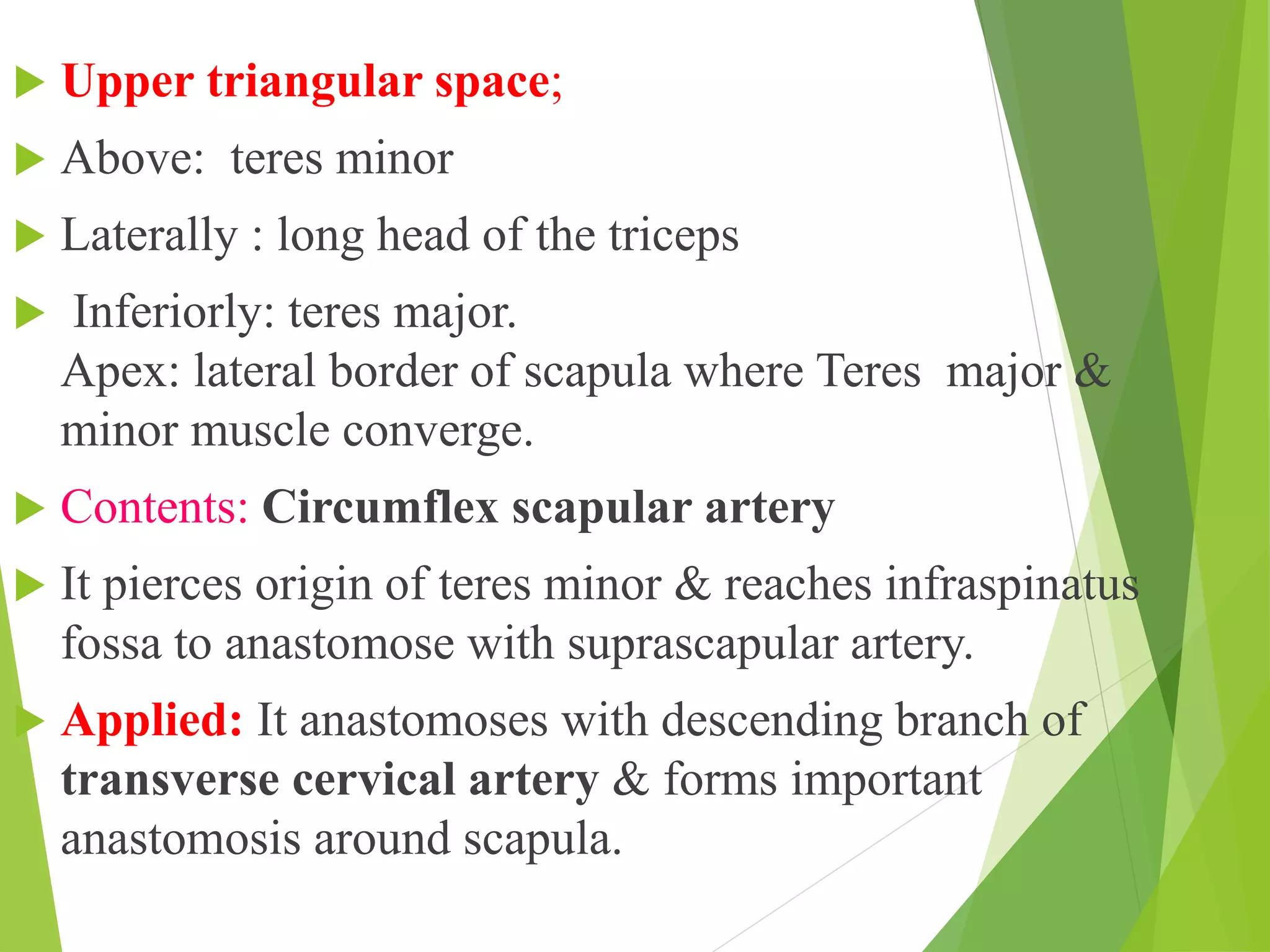
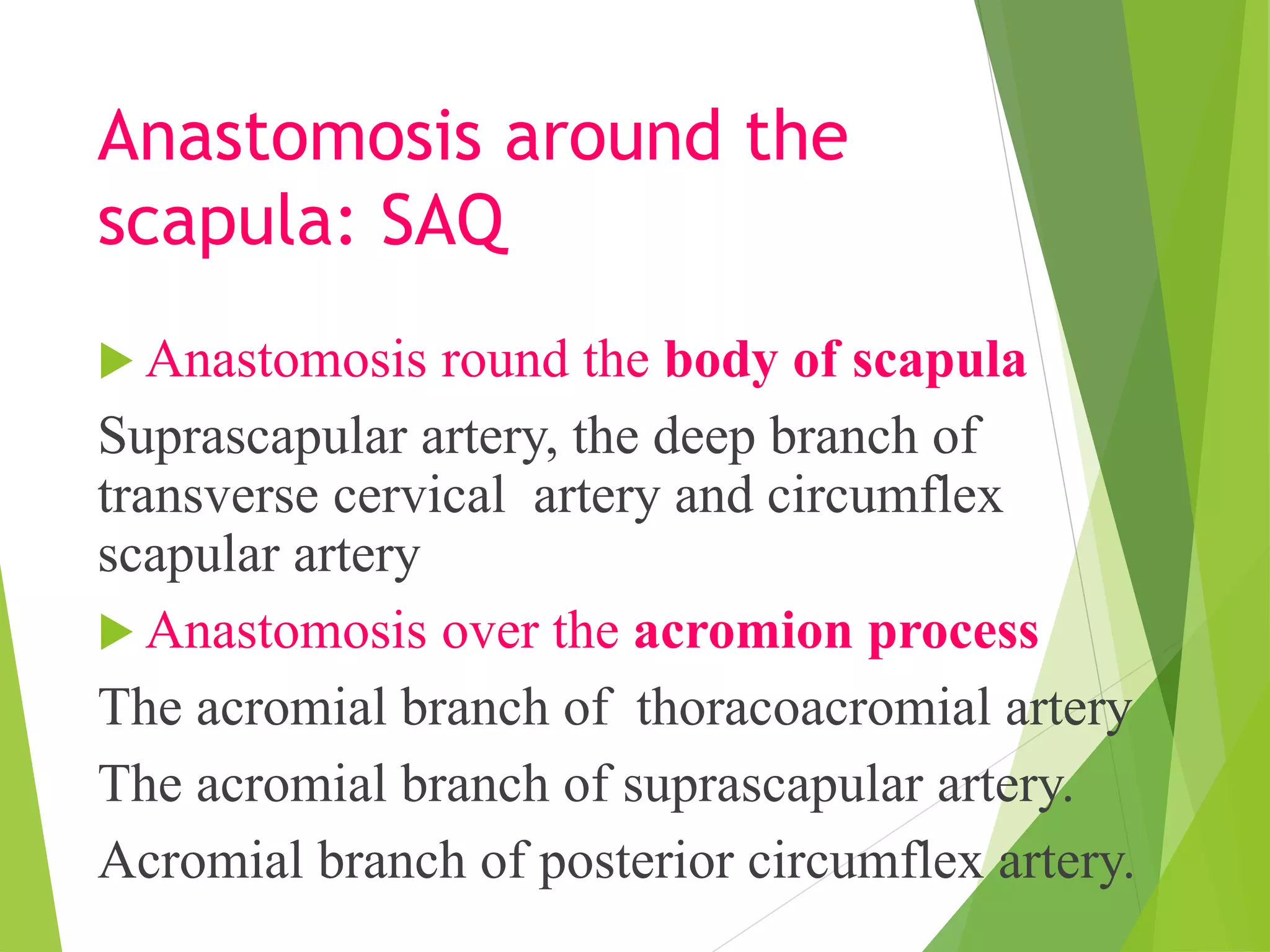
This document describes the muscles of the scapular region including the deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis, and teres major. It discusses the origin, insertion, nerve supply and action of each muscle. It also describes the rotator cuff muscles that form a musculotendinous cuff around the shoulder joint, providing stability. The document outlines the quadrangular space and upper and lower triangular spaces in the scapular region and their clinical relevance. It concludes with a discussion of important anastomoses of arteries around the scapula.