Botulinum toxin is produced by Clostridium botulinum bacteria. It works by blocking the release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions, preventing muscle contraction. There are several types of botulinum toxin, with type A (BTX-A) being the most widely used therapeutic agent. BTX-A is used to treat muscle spasticity and dystonia by temporarily weakening muscles via chemodenervation. Its applications in orthopedics include improving gait and limb function, preventing deformities, and reducing spasticity-related pain. Proper administration techniques like electrical stimulation are important for targeting specific muscles. Side effects are usually mild and local but precision is needed to avoid weakness
![VOL. 88-B, No. 8, AUGUST 2006 981
REVIEW ARTICLE
Botulinum toxin and its orthopaedic
applications
M. Ramachandran,
D. M. Eastwood
From The Royal
National
Orthopaedic
Hospital, Stanmore,
England
M. Ramachandran,
FRCS(Orth), Paediatric
Orthopaedic Fellow
D. M. Eastwood, MB, FRCS,
Consultant Orthopaedic
Surgeon
The Royal National
Orthopaedic Hospital, Brockley
Hill, Stanmore, Middlesex HA7
4LP, UK.
Correspondence should be sent
to Miss D. M. Eastwood; e-mail:
D.M.Eastwood@
btinternet.com
©2006 British Editorial Society
of Bone and Joint Surgery
doi:10.1302/0301-620X.88B8.
18041 $2.00
J Bone Joint Surg [Br]
2006;88-B:981-7.
Emile Pierre van Ermengem, Professor of Bac-
teriology at the University of Ghent, first dis-
covered the bacterium Clostridium botulinum
in the late 19th
century, naming it after the food
poisoning sustained after ingestion of blood
sausage described earlier that century by a Ger-
man physician, Justinus Kerner (the Latin for
sausage is botulus).1
Botulinum toxin (BTX)
was used successfully as a research tool in the
study of the physiology of the spinal cord in
the 1970s, and subsequently BTX-A injections
were first used therapeutically as a treatment
for strabismus in the early 1980s.2
The first
published report of the orthopaedic use of
BTX-A to treat spasticity in children with cere-
bral palsy was published in 1993.3
In this
review we describe the mechanism of action of
BTX, discuss the methods of administration
and consider some of the indications for its use
in both paediatric and adult orthopaedic prac-
tice.
Botulinum toxin and its mechanism of
action
Clostridium botulinum produces a complex
mixture of proteins containing botulinum
neurotoxin and several non-toxic proteins,
such as haemagglutinin.4
There are seven dif-
ferent serotypes of the neurotoxin, named A to
G. Although all inhibit release of acetylcholine
from nerve terminals, they vary greatly in their
intracellular protein targets, potency and dura-
tion of effect.5
BTX-A is the serotype which
has been studied most widely in terms of ther-
apeutic application. BTX-B and BTX-F have
also been used in clinical practice, but are less
potent than BTX-A and have a shorter dura-
tion of action.
The neurotoxin is synthesised as a relatively
inactive single-chain polypeptide with a molec-
ular mass of 150 kDa which is then cleaved
and hence activated, by proteases, into a 100
kDa heavy chain and a 50 kDa light chain, that
remain linked by a disulphide bond. These pro-
teases may either be endogenous which are
present in some clostridial strains, or exo-
genous such as trypsin which is used in the
commercial manufacture of neurotoxin. The
presence of high percentages of un-cleaved
neurotoxin in preparations of botulinum toxin
may be related to the formation of neutralising
antibodies.6
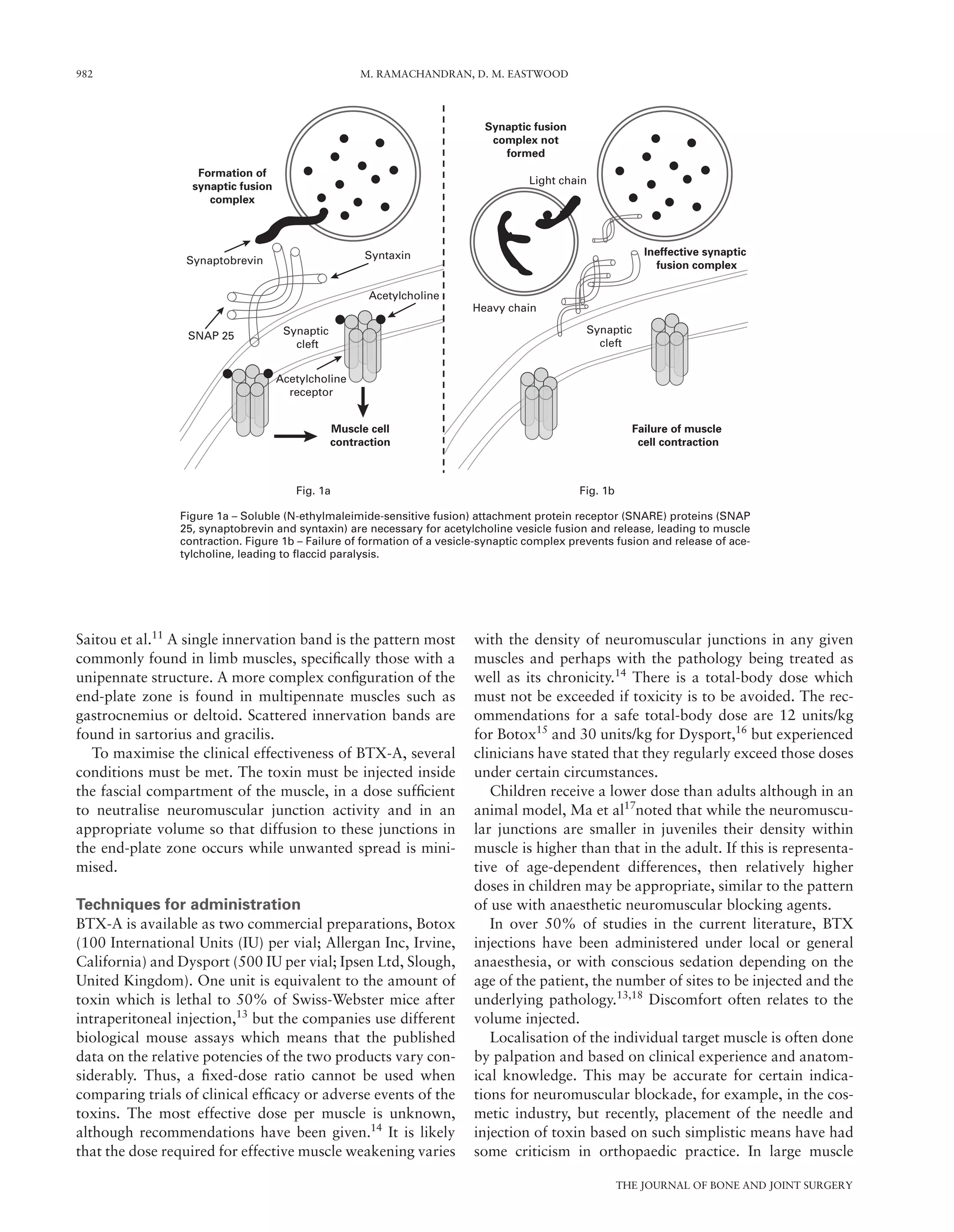
Botulinum neurotoxins bind via the heavy
chain to specific external high-affinity recep-
tors on the membranes of cholinergic neurones
which are internalised by endocytosis. Here,
the light chain binds with high specificity to
proteins which are involved with release of a
neurotransmitter into the synapse. The specific
protein complex involved, a soluble (N-ethyl-
maleimide-sensitive fusion (NSF)) attachment
protein receptor (SNARE) complex, mediates
the fusion of neurotransmitter-containing vesi-
cles with the synaptic membrane.7
The com-
plex consists of synaptobrevin which is
associated with synaptic vesicles, syntaxin and
synaptosome-associated protein of molecular
weight 25 kDa (SNAP-25). BTX-A destabilises
the SNARE complex by cleaving SNAP-25.
Other BTX serotypes cleave different proteins
within the complex (Fig. 1).7-9
By preventing release of acetylcholine at the
neuromuscular junction, BTX reduces mus-
cular activity in a dose-dependent manner.
Within four weeks, restoration of the turnover
of the SNARE protein complex allows exo-
cytosis of acetylcholine to resume. Nerve con-
duction is also re-established, initially by new
axonal sprouting and elongation of the end-
plate and, eventually, by retraction of the new
axonal sprouts.10
Clinically, this chemodener-
vation with muscle relaxation lasts for 12 to 16
weeks. A follow-up period of longitudinal
muscle growth and functional carry-over may
last for six months or more11
depending on the
pathology involved.
Coers12
showed that extrafusal muscle fibres
are innervated at the midpoint of the fibre and
thus neuromuscular junctions in any given
muscle lie within a defined end-plate zone, the
topography of which varies with the morphol-
ogy of the muscle itself. This was confirmed by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/botulinumtoxin-140313053331-phpapp02/75/Botulinum-toxin-1-2048.jpg)




![BOTULINUM TOXIN AND ITS ORTHOPAEDIC APPLICATIONS 987
VOL. 88-B, No. 8, AUGUST 2006
25. Childers MK. Targeting the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscles. Am J Phys
Med Rehabil 2004;83(suppl):38-44.
26. Crystal R, Malone AA, Eastwood DM. Motor points for neuromuscular blockade of
the adductor muscle group. Clin Orthop 2005;437:196-200.
27. Parratte B, Tatu L, Vuillier F, Diop M, Monnier G. Intramuscular distribution of
nerves in the human triceps surae muscle: anatomical bases for treatment of spastic
foot drop with botulinum toxin. Surg Radiol Anat 2002;24:91-6.
28. Shaari CM, George E, Wu BL, Biller HF, Sanders I. Quantifying the spread of bot-
ulinum toxin through muscle fascia. Laryngoscope 1991;101:960-4.
29. Shaari CM, Sanders I. Quantifying how location and dose of botulinum toxin injec-
tions affect muscle paralysis. Muscle Nerve 1991;16:964-9.
30. Preiss RA, Condie DN, Rowley DI, Graham HK. The effects of botulinum toxin
(BTX-A) on spasticity of the lower limb and on gait in cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg
[Br] 2003;85-B:943-8.
31. Herrmann J, Mall V, Bigalke H, et al. Secondary non-response due to develop-
ment of neutralising antibodies to botulinum toxin A during treatment of children with
cerebral palsy. Neuropediatrics 2000;31:333-4.
32. Cosgrove AP, Corry IS, Graham KH. Botulinum toxin in the management of the
lower limb in cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 1994;36:386-96.
33. Love SC, Valentine JP, Blair EM, et al. The effect of botulinum toxin A on the func-
tional ability of the child with spastic hemiplegia: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J
Neurol 2001;8(suppl 5):50-8.
34. Gough M, Fairhurst C, Shortland AP. Botulinum toxin and cerebral palsy: time for
reflection? Dev Med Child Neurol 2005;47:709-12.
35. Graham HK. Botulinum toxin type A management of spasticity in the context of ortho-
paedicsurgeryforchildrenwithspasticcerebralpalsy.EurJNeurol2001;8(suppl5):30-9.
36. Baker R, Jasinski M, Maciag-Tymecka I, et al. Botulinum toxin treatment of
spasticity in diplegic cerebral palsy: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
dose-ranging study. Dev Med Child Neurol 2002;44:666-75.
37. Koman LA, Mooney JF 3rd, Smith BP, Walker F, Leon JM. Botulinum toxin type
A neuromuscular blockade in the treatment of lower extremity spasticity in cerebral
palsy: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial: BOTOX Study Group.
J Pediatr Orthop 2000;20:108-15.
38. Sutherland DH, Kaufman KR, Wyatt MP, Chambers HG, Mubarak SJ. Double-
blind study of botulinum A toxin injections into the gastrocnemius muscle in patients
with cerebral palsy. Gait Posture 1999;10:1-9.
39. Ubhi T, Bhakta BB, Ives HL, Allgar V, Roussonis SH. Randomised double blind
placebo controlled trial of the effect of botulinum toxin on walking in cerebral palsy.
Arch Dis Child 2000;83:481-7.
40. Corry IS, Cosgrove AP, Duffy CM, et al. Botulinum toxin A compared with stretch-
ing casts in the treatment of spastic equinus: a randomized prospective trial. J Pediatr
Orthop 1998;18:304-11.
41. Corry IS, Cosgrove AP, Duffy CM, Taylor TC, Graham HK. Botulinum toxin A in
hamstring spasticity. Gait Posture 1999;10:206-10.
42. Westhoff B, Seller K, Wild A, Jaeger M, Krauspe R. Ultrasound-guided botuli-
num toxin injection technique for the iliopsoas muscle. Develop Med Child Neurol
2003;45:829-32.
43. Molenaers G, Desloovere K, De Cat J, et al. Single event multilevel botulinum
toxin type A treatment and surgery: similarities and differences. Eur J Neurol 2001;8
(suppl 5):88-97.
44. Boyd RN, Dobson F, Parrott J, et al. The effect of botulinum toxin type A and a vari-
able hip abduction orthosis on gross motor function: a randomized controlled trial. Eur
J Neurol 2001;8(suppl 5):109-19.
45. Pidcock FS, Fish DE, Johnson-Greene D, et al. Hip migration percentage in chil-
dren with cerebral palsy treated with botulinum toxin type A. Arch Phys Med Rehabil
2005;86:431-5.
46. Kay RM, Rethlefsen SA, Fern-Buneo A, Wren TA, Skaggs DL. Botulinum toxin
as an adjunct to serial casting treatment in children with cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint
Surg [Am] 2005;86-A:2377-84.
47. Corry IS, Cosgrove AP, Walsh EG, McClean D, Graham HK. Botulinum toxin A in
the hemiplegic upper limb: a double-blind trial. Dev Med Child Neurol 1997;39:185-93.
48. Fehlings D, Rang M, Glazier J, Steele C. An evaluation of botulinum-A toxin injec-
tions to improve upper extremity function in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
J Pediatr 2000;137:331-7.
49. Boyd RN, Morris ME, Graham HK. Management of upper limb dysfunction in chil-
dren with cerebral palsy: a systematic review. Eur J Neurol 2001;8(suppl 5):150-66.
50. Wasiak J, Hoare B, Wallen M. Botulinum toxin A as an adjunct to treatment in the
management of the upper limb in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Cochrane Data-
base Syst Rev 2004;4:CD003469.
51. Barwood S, Bailleiu C, Boyd RN, et al. Analgesic effects of botulinum toxin A: a
randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Dev Med Child Neurol 2000;42:116-21.
52. Hyman N, Barnes M, Bhakta B, et al. Botulinum toxin (Dysport) treatment of hip
adductor spasticity in multiple sclerosis: a prospective, randomised, double blind, pla-
cebo controlled, dose ranging study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2000;68:707-12.
53. Jost WH. Botulinum toxin in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 2006;253(suppl 1):16-20.
54. Miscio G, Del Conte C, Pianca D, et al. Botulinum toxin in post stroke patients:
stiffness modifications and clinical implications. J Neurol 2004;251:189-96.
55. Francisco GE, Boake C, Vaughn A. Botulinum toxin in upper limb spasticity after
acquired brain injury: a randomised trial comparing dilution techniques. Am J Phys
Med Rehabil 2002;81:355-63.
56. Woldag H, Hummelsheim H. Is the reduction of spasticity by botulinum toxin A
beneficial for the recovery of motor function of arm and hand in stroke patients? Eur
Neurol 2003;50:165-71.
57. Verplancke D, Snape S, Salisbury CF, Jones PW, Ward AB. A randomised con-
trolled trial of botulinum toxin on lower limb spasticity following acute acquired
severe brain injury. Clin Rehabil 2005;19:117-25.
58. Fock J, Galea MP, Stillman BC, Rawicki B, Clark M. Functional outcome follow-
ing botulinum toxin A injection to reduce spastic equinus in adults with traumatic
brain injury. Brain Inj 2004;18:57-63.
59. Van Rhijn J, Molenaers G, Ceulemans B. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment
of children and adolescents with an acquired brain injury. Brain Inj 2005;19:331-5.
60. Klaphajone J, Kitisomprayoonkul W, Sriplakit S. Botulinum toxin type A injec-
tions for treating neurogenic detrusor overactivity combined with low-compliance
bladder patients with spinal cord lesions. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2005;86:2114-18.
61. Schurch B, de Seze M, Denys P, et al. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effec-
tive treatment for neurogenic urinary incontinence: results of a single treatment ran-
domised, placebo controlled 6-month study. J Urol 2005;174:196-200.
62. Delgado MR, Wilson H, Johnston C, Richards S, Karol L. A preliminary report of
the use of botulinum toxin A in infants with club foot: four case studies. J Pediatr
Orthop 2000;20:533-8.
63. Mitchell PD, Tisdall M, Zadeh HG. Selective botulinum toxin injection in the treat-
ment of recurrent deformity following surgical correction of club foot: a preliminary
report of 3 children. Acta Orthop Scand 2004;75:630-3.
64. Alvarez CM, Tredwell SJ, Keenan SP, et al. Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot uti-
lizing botulinum A toxin: a new method and its short-term outcomes. J Pediatr Orthop
2005;25:229-35.
65. Cummings RJ, Shanks DE. Prospective, randomized, double-blind study of the use-
fulness of Botox as an adjunct to serial manipulation and casting for congenital club-
feet [abstract]. POSNA Annual Meeting, 2005.
66. Jacks LK, Michels DM, Smith BP, Koman LA, Shilt J. Clinical usefulness of bot-
ulinum toxin in the lower extremity. Foot Ankle Clin 2004;9:339-48.
67. Brunt D, Woo R, Kim HD, et al. Effect of botulinum toxin type A on gait of children
who are idiopathic toe-walkers. J Surg Orthop Adv 2004;13:149-55.
68. Cheng JC, Wong MW, Tang SP, et al. Clinical determinants of the outcome of man-
ual stretching in the treatment of congenital muscular torticollis in infants: a prospec-
tive study of eight hundred and twenty-one cases. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 2001;83-A:
679-87.
69. Joyce MB, de Chalain TM. Treatment of recalcitrant idiopathic muscular torticollis
in infants with botulinum toxin type A. J Craniofac Surg 2005;16:321-7.
70. Oleszek JL, Chang N, Apkon SD, Wilson PE. Botulinum toxin type A in the treat-
ment of children with congenital muscular torticollis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2005;
84:813-16.
71. Rollnik JD, Hierner R, Schubert M, et al. Botulinum toxin treatment of cocontrac-
tions after birth-related brachial plexus lesions. Neurology 2000;55:112-14.
72. Desiato MT, Risina B. The role of botulinum toxin in the neuro-rehabilitation of
young patients with brachial plexus birth palsy. Pediatr Rehabil 2001;4:29-36.
73. Price AE, Di Taranto P, Yaylali I, et al. The use of botulinum toxin type A as a sur-
gical adjunct in the management of the brachial plexus birth trauma [abstract].
POSNA Annual Meeting, 2005.
74. Morre HH, Keizer SB, van Os JJ. Treatment of chronic tennis elbow with botuli-
num toxin. Lancet 1997;349:1746.
75. Keizer SB, Rutten HP, Pilot P, et al. Botulinum toxin injection versus surgical treat-
ment for tennis elbow: a randomized pilot study. Clin Orthop 2002;401:125-31.
76. Hayton MJ, Santini AJ, Hughes PJ, et al. Botulinum toxin injection in the treat-
ment of tennis elbow: a double-blind, randomized, controlled, pilot study. J Bone
Joint Surg [Am] 2005;87-A:503-7.
77. Wong SM, Hui AC, Tong PY, et al. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with botulinum
toxin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 2005;143:
793-7.
78. Tuzuner S, Balci N, Ozkaynak S. Results of zone II flexor tendon repair in children
younger than age 6 years: botulinum toxin type A administration eased cooperation
during rehabilitation and improved outcome. J Pediatr Orthop 2004;24:629-33.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/botulinumtoxin-140313053331-phpapp02/75/Botulinum-toxin-7-2048.jpg)