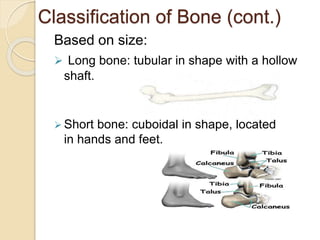
Bone provides the framework for the body, protects vital organs, and enables mechanical movement. There are two types of bones based on location - the axial skeleton which includes the skull, vertebrae, and ribs, and the appendicular skeleton which includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities. Bones can also be classified based on their shape as flat, tubular, irregular, or sesamoid bones. Microscopically, bone is made up of bone cells like osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes as well as a matrix containing collagen, minerals, and other components. Bones receive blood supply through nutrient arteries and are innervated by nerves accompanying the blood vessels.