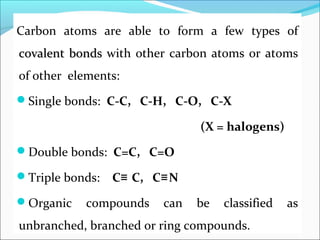
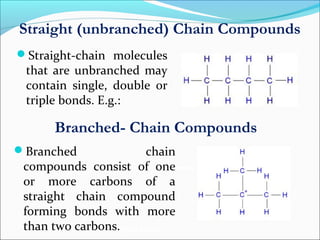
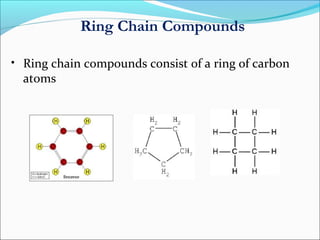
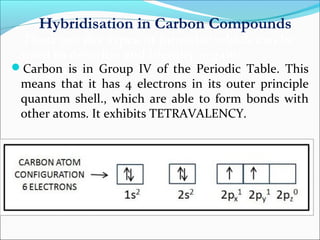
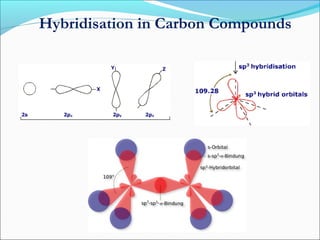
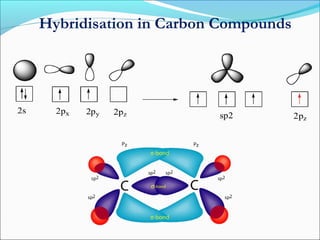
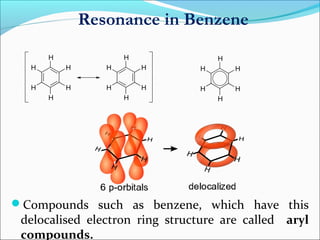
This document discusses carbon bonding and the formation of carbon compounds. It explains that carbon can form strong covalent bonds with other carbon atoms through a process called catenation, allowing it to form straight chains, branches, and rings. This bonding ability arises because carbon is tetravalent and can hybridize its orbitals, taking on different hybridization states like sp, sp2, and sp3. Some carbon compounds exhibit resonance, where electrons are delocalized over multiple carbon atoms. This results in more stable structures that are hybrids of different resonant forms. Overall, carbon's unique bonding properties allow it to form a diverse array of stable organic compounds.