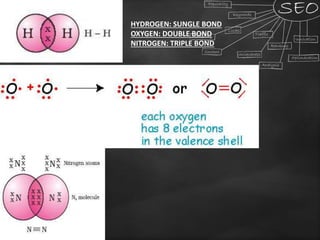
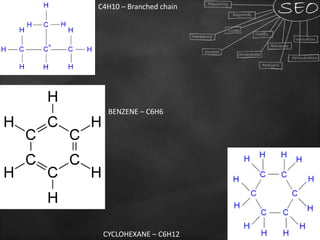
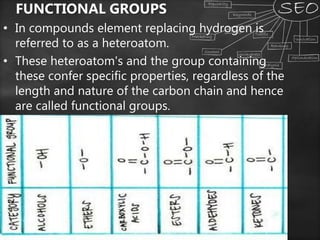
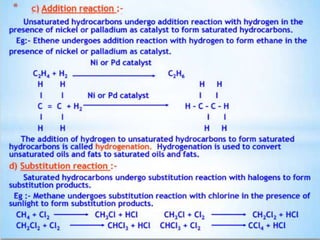
Carbon is a key element that forms the basis of many important compounds due to its ability to bond with other carbon atoms and elements. It exists in several allotropes with varying properties, including diamond and graphite. Carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds with other atoms, allowing it to create large, complex molecules through catenation. Saturated carbon compounds contain only single bonds, while unsaturated compounds contain double or triple bonds. Functional groups and structural isomers give compounds unique reactivity and properties. Important carbon compounds discussed include ethanol, ethanoic acid, soaps, and detergents.


![THE COVALENT BOND
• The relativity of an element is explained as their
tendency to attain a completely filled outer shell,
i.e., attain noble gas configuration.
• In the case of carbon, it has four electrons in its
outermost shell and needs to gain or lose four
electrons to attain noble gas configuration.
I] It could gain four electrons forming C4- anion.
Nut it would be difficult for the nucleus with 6
protons to hold on to 10 electrons.
II] it could lose four electrons forming C4+. But it
would require a large amount of energy to
remove four electrons leaving behind a carbon
cation with 6 protons holding just 2 electrons.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbon-170205084132/85/Carbon-and-Its-Compounds-3-320.jpg)