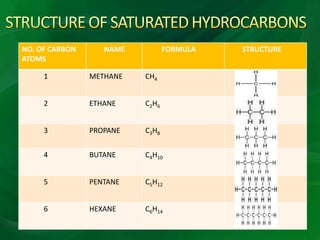
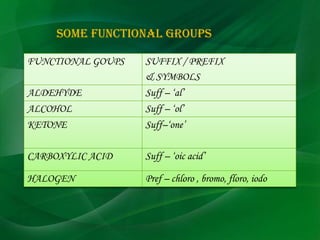
Carbon is a nonmetallic element that forms covalent bonds and exists in multiple allotropes depending on how its atoms are arranged. It can form linear, branched, or cyclic hydrocarbons ranging from methane with one carbon to complex molecules like cellulose. Key properties depend on factors like the number of carbon atoms, their arrangement into straight chains, branches, or rings, and whether bonds are single or double. Functional groups determine characteristic reactions by specific atoms within organic molecules.