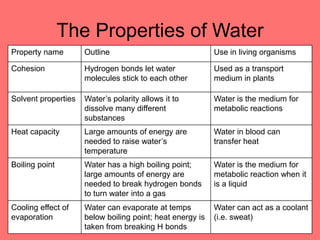
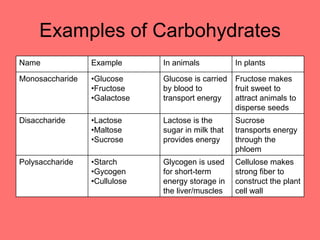
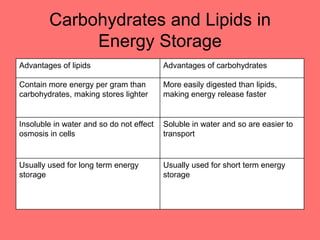
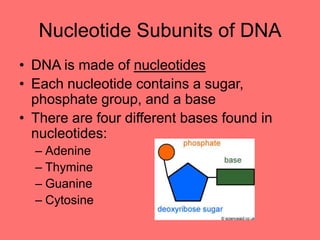
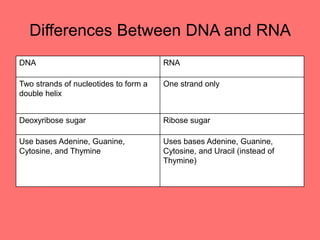
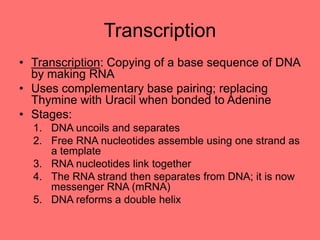
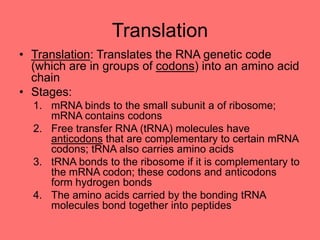
The document discusses the chemistry of life, focusing on the properties of water, essential elements, and the roles of organic compounds and macromolecules in living organisms. It details biochemical reactions such as condensation and hydrolysis, the structure and function of DNA and RNA, and the processes of transcription and translation. Additionally, it covers enzyme activity, cell respiration, and photosynthesis, highlighting factors that affect these biological processes.