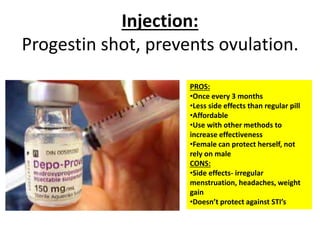
This document outlines various contraceptive methods for preventing pregnancy, including natural methods like abstinence and fertility awareness, barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms, hormonal methods like oral contraceptives and injections, and permanent sterilization procedures. Barrier methods use physical barriers to block sperm from reaching an egg, while chemical methods alter hormone levels to prevent ovulation. Each method is described along with its pros and cons in terms of effectiveness, side effects, costs, and protection against sexually transmitted infections.