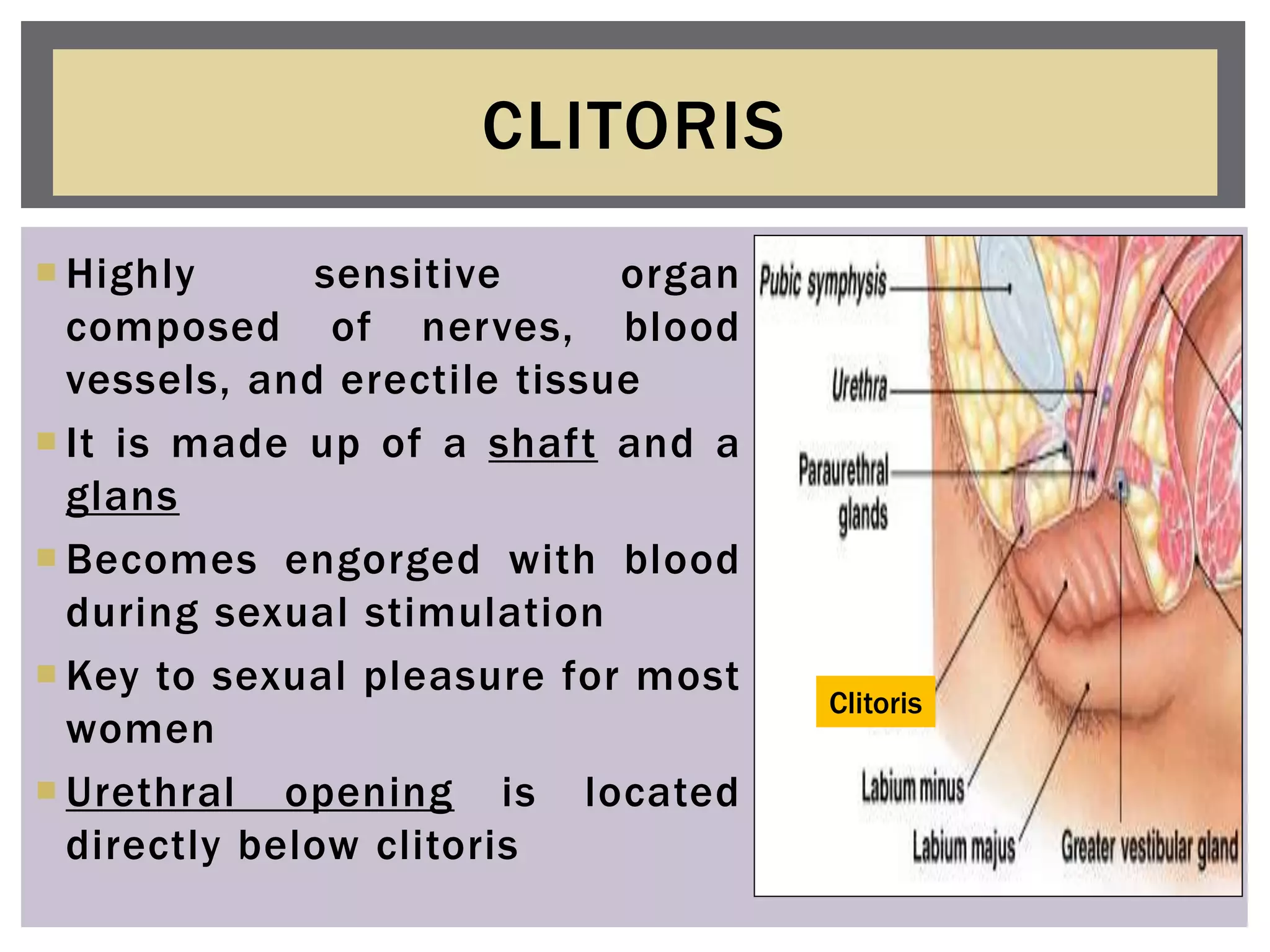
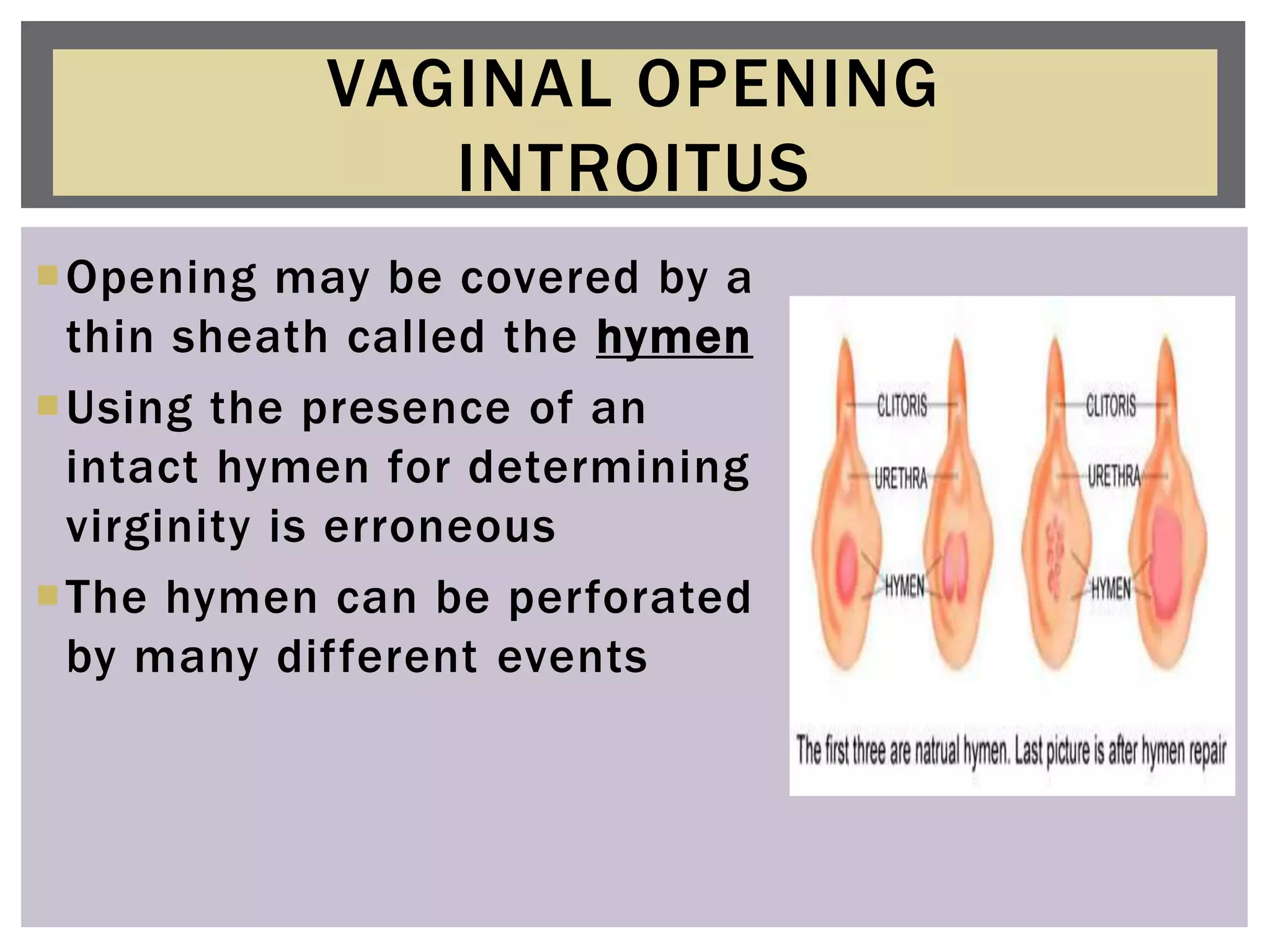
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the female reproductive system, detailing both internal and external structures and their functions in reproduction, sexual maturation, and childbirth. It describes key components such as the vulva, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, highlighting their roles in copulation, fertilization, and fetal development. Additionally, it mentions secondary characteristics such as menstruation and hormonal changes throughout a woman's life.