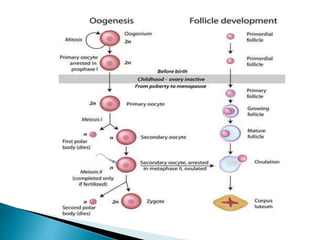
The document summarizes the process of oogenesis in females. It begins with primordial germ cells differentiating into oogonia in the ovaries during early fetal development. These oogonia undergo mitosis and some undergo meiosis I to form primary oocytes, though meiosis stops at prophase I. From birth until puberty, the number of primary oocytes decreases from hundreds of thousands to around 40,000. After puberty, hormones stimulate a few primordial follicles to grow into primary and secondary follicles each month, with one becoming dominant and ovulating after completing meiosis I and II.