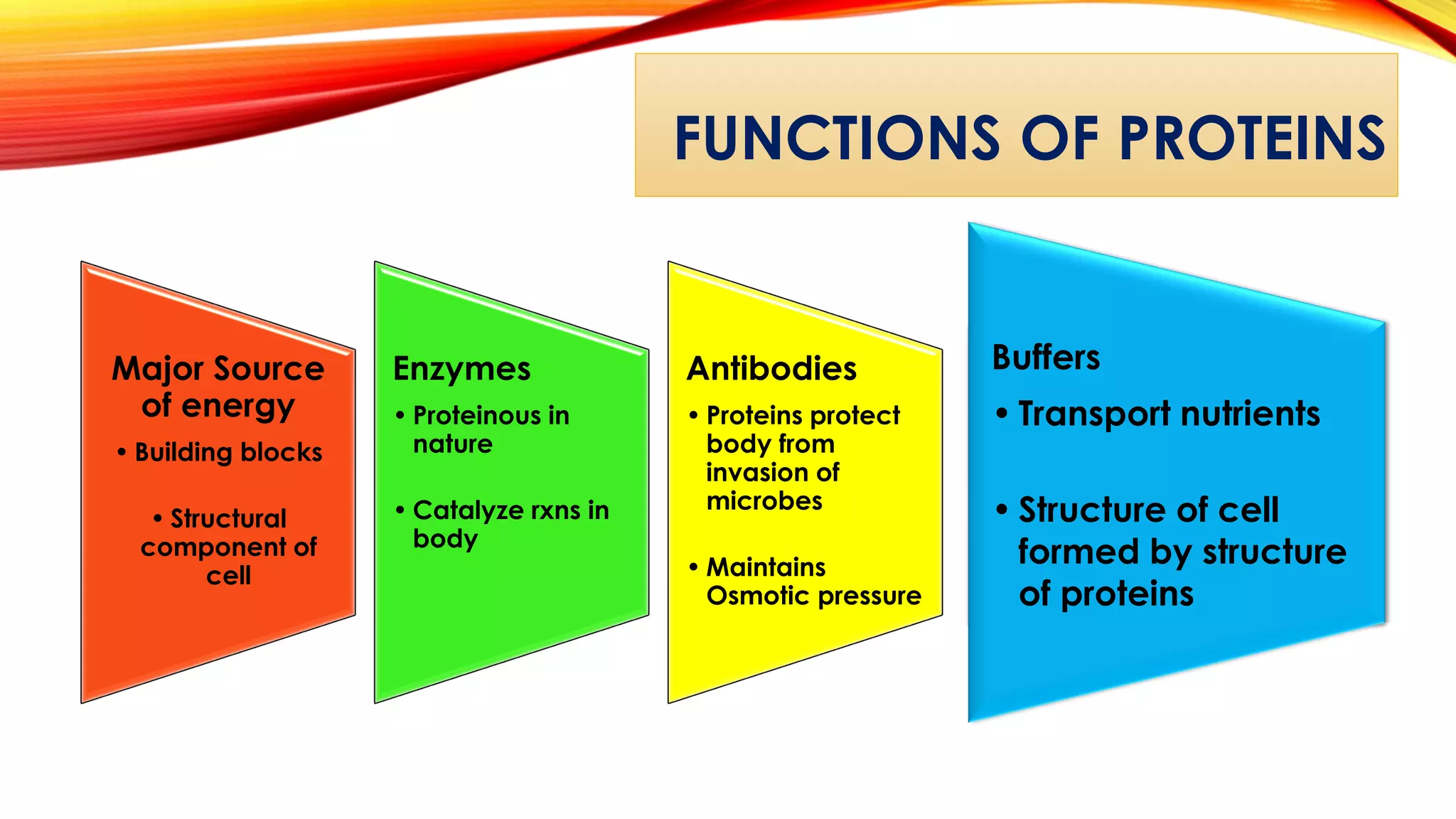
Proteins are macromolecules composed of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. They have primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels of structure which determine their function. Examples of different types of proteins include fibrous, globular, defense, contractile, and respiratory proteins. Insulin has an A chain and B chain linked together and derived from proinsulin. Myoglobin contains iron and captures oxygen in muscles. Hemoglobin transports oxygen in blood and is composed of four polypeptide subunits. Proteins serve important roles like structure, enzymes, antibodies, transport, and as a nutrient source. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and have both polar and nonpolar varieties with different structures and functions