Embed presentation
Downloaded 151 times

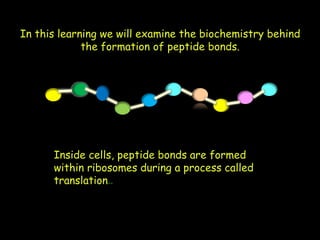
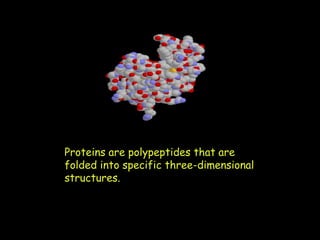

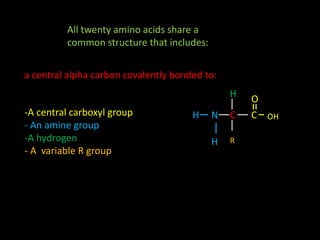
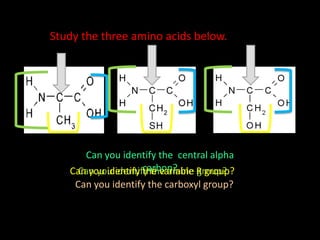

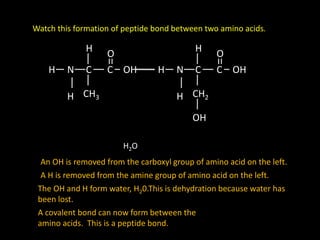

Peptide bonds form during translation within ribosomes and connect amino acids into polypeptide chains that fold into protein structures. A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed through a dehydration synthesis reaction between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amine group of the next. This reaction involves the loss of a water molecule as the carboxyl oxygen and amine hydrogen are removed to connect the amino acids. Peptide bonds make up the backbone of proteins by linking the 20 common amino acids together end to end.







