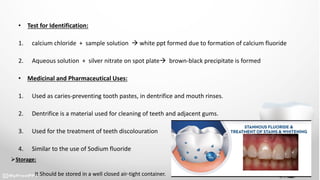
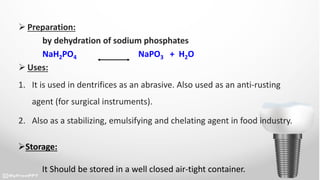
This document discusses various dental products used to treat dental issues and promote oral hygiene. It describes sodium fluoride, stannous fluoride, dicalcium phosphate, calcium carbonate, sodium metaphosphate, zinc chloride, and strontium chloride. Sodium fluoride and stannous fluoride help prevent dental caries by depositing on tooth surfaces and inhibiting acid production. Dicalcium phosphate, calcium carbonate, and sodium metaphosphate act as cleaning and polishing agents in toothpastes. Zinc chloride and strontium chloride are used as desensitizing agents to reduce tooth sensitivity. All products should be stored in airtight containers.