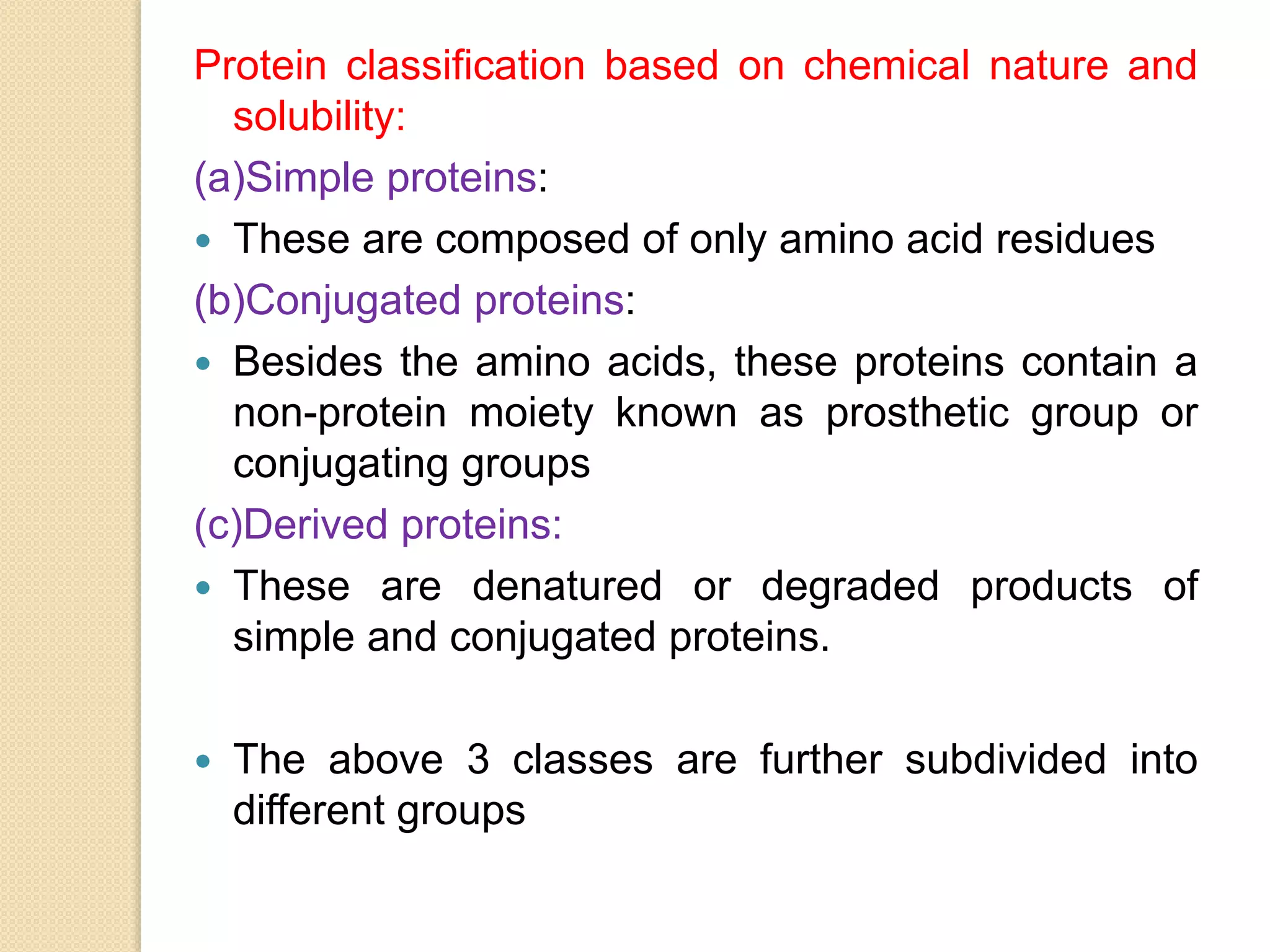
Proteins are polymers of amino acids and are the most abundant organic molecules in living systems. They perform a variety of essential functions including structural, enzymatic, hormonal, and more. There are 20 standard amino acids that are found in protein structures. Amino acids contain both amino and carboxyl groups and most exist in ionized form in biological systems. Proteins are classified based on their structure and function, with some serving static structural roles and others having dynamic roles like enzymes and hormones. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet.