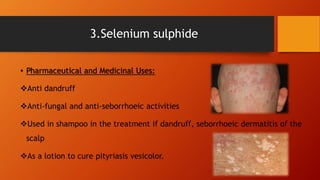
The document provides a comprehensive overview of sulphur and its compounds, including their physical and chemical properties, preparation methods, and medicinal uses. It specifically discusses sublimed sulphur, precipitated sulphur, and selenium sulphide, detailing their characteristics, tests for purity, and storage recommendations. Additionally, it highlights their applications in dermatological treatments and as antiseptics.