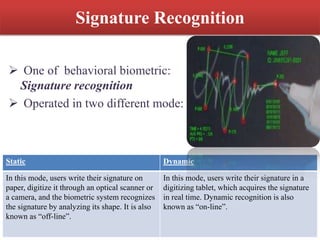
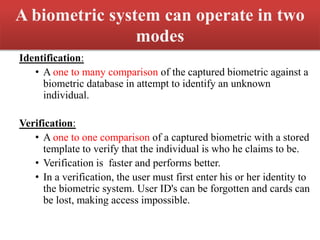
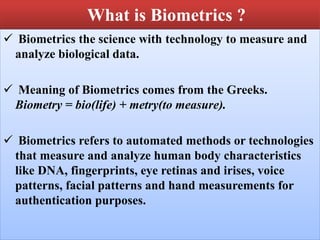
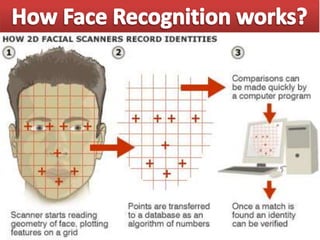
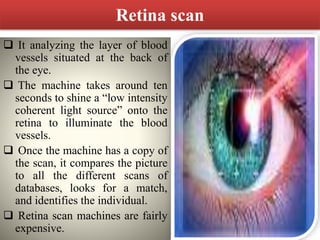
This document discusses biometric technology, which uses unique human characteristics like fingerprints, iris patterns, and voice to authenticate identity. It describes several types of biometric technologies including fingerprint recognition, iris scanning, retina scanning, facial recognition, voice recognition, and signature recognition. The document also covers how biometric systems work, advantages like increased security, and disadvantages like high costs and changing biometrics over time. It concludes that biometric technology provides a user-friendly way to interact with devices without needing passwords.




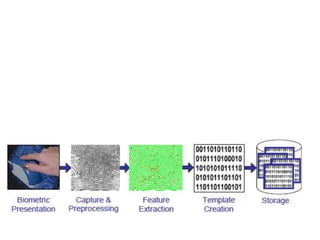
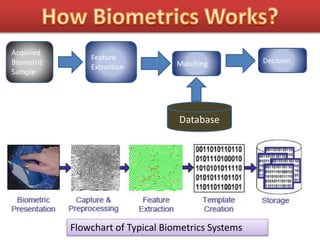





![Sensor
[Fingerprint
Sensor]
Pre-Processing
Matched
Profile
BIO-METRIC SYSTEM
Fingerprint
Extraction
Profile
Search
Stored
Profiles
Application
Activation
How Finger-Print Works?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sanjufinalppt-150824090338-lva1-app6891/85/Bio-Metric-Technology-17-320.jpg)