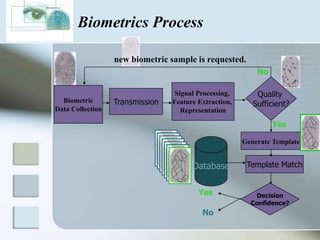
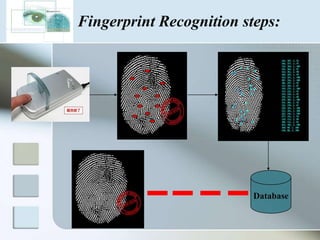
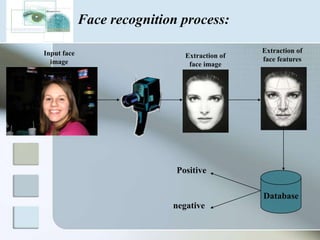
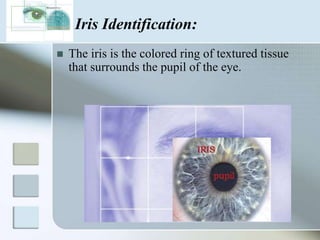
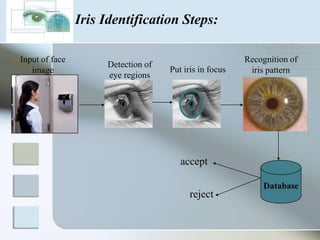
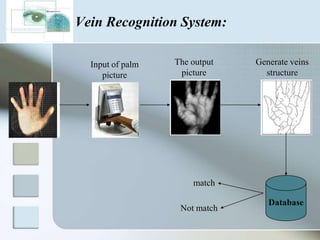
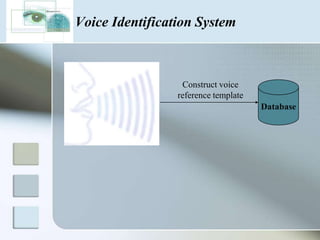
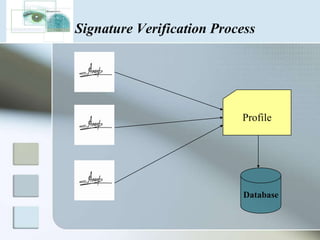
There are three main types of authentication: something you know, something you have, and something you are. Biometrics uses biological and behavioral characteristics to identify individuals, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, voice, gait, and signatures. Some common biometric technologies are fingerprint, face, iris, vein, voice, and signature recognition. Biometrics can be used for applications like access control, time/attendance tracking, airports, ATMs, and more. While biometrics provide security benefits, they also have disadvantages like cost, accuracy issues, and privacy concerns. The field continues to evolve as costs decrease and convenience increases.