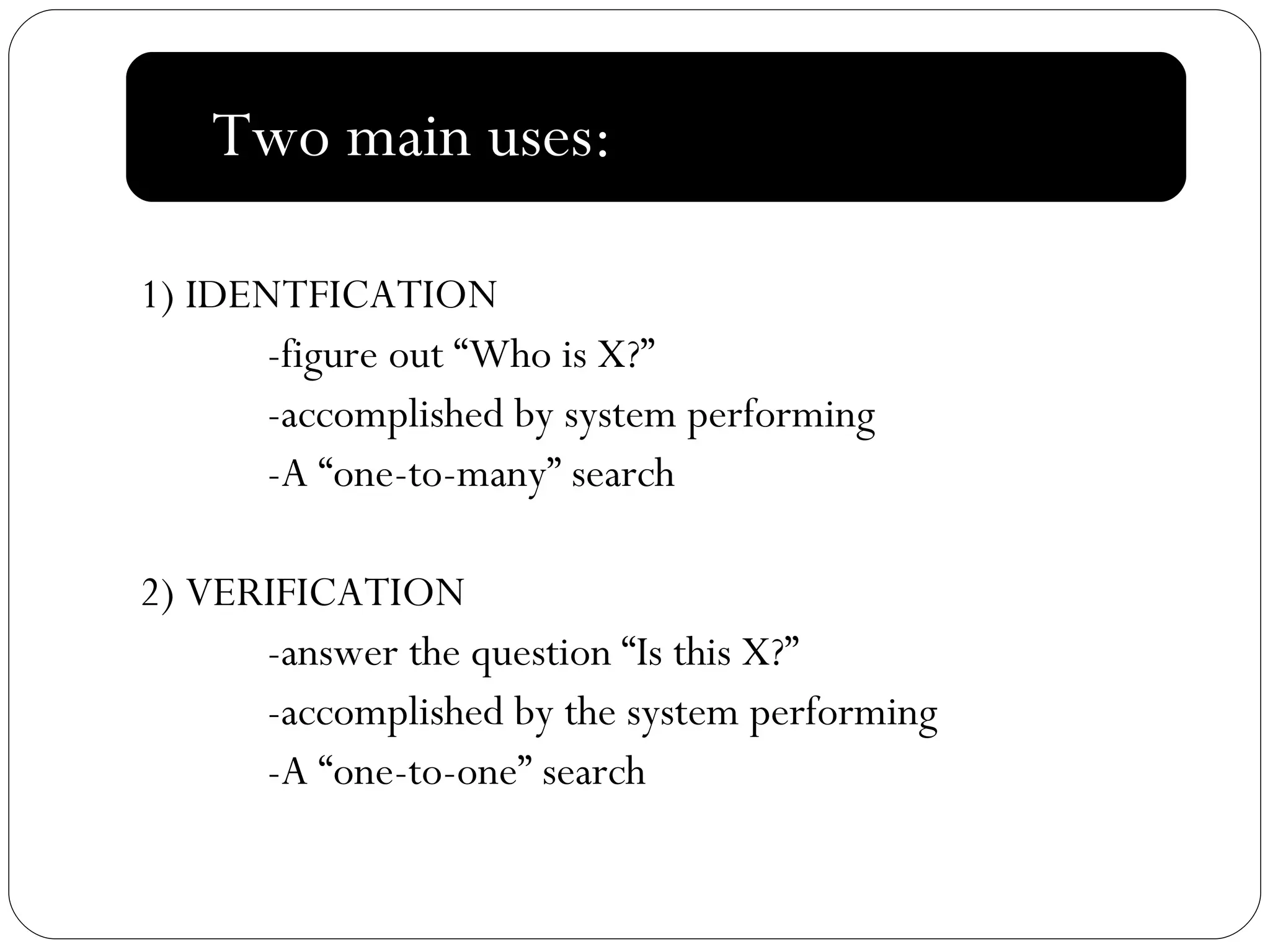
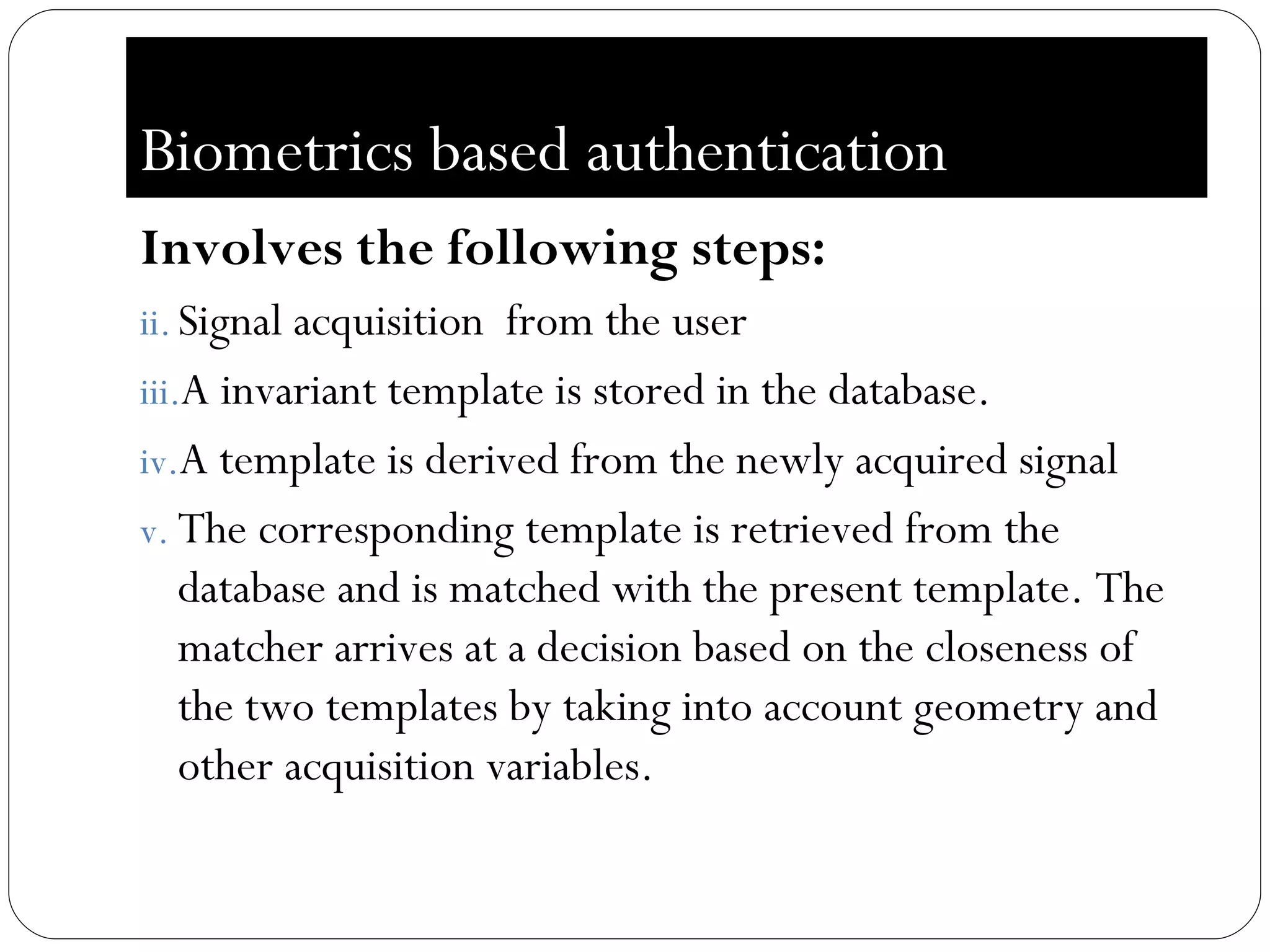
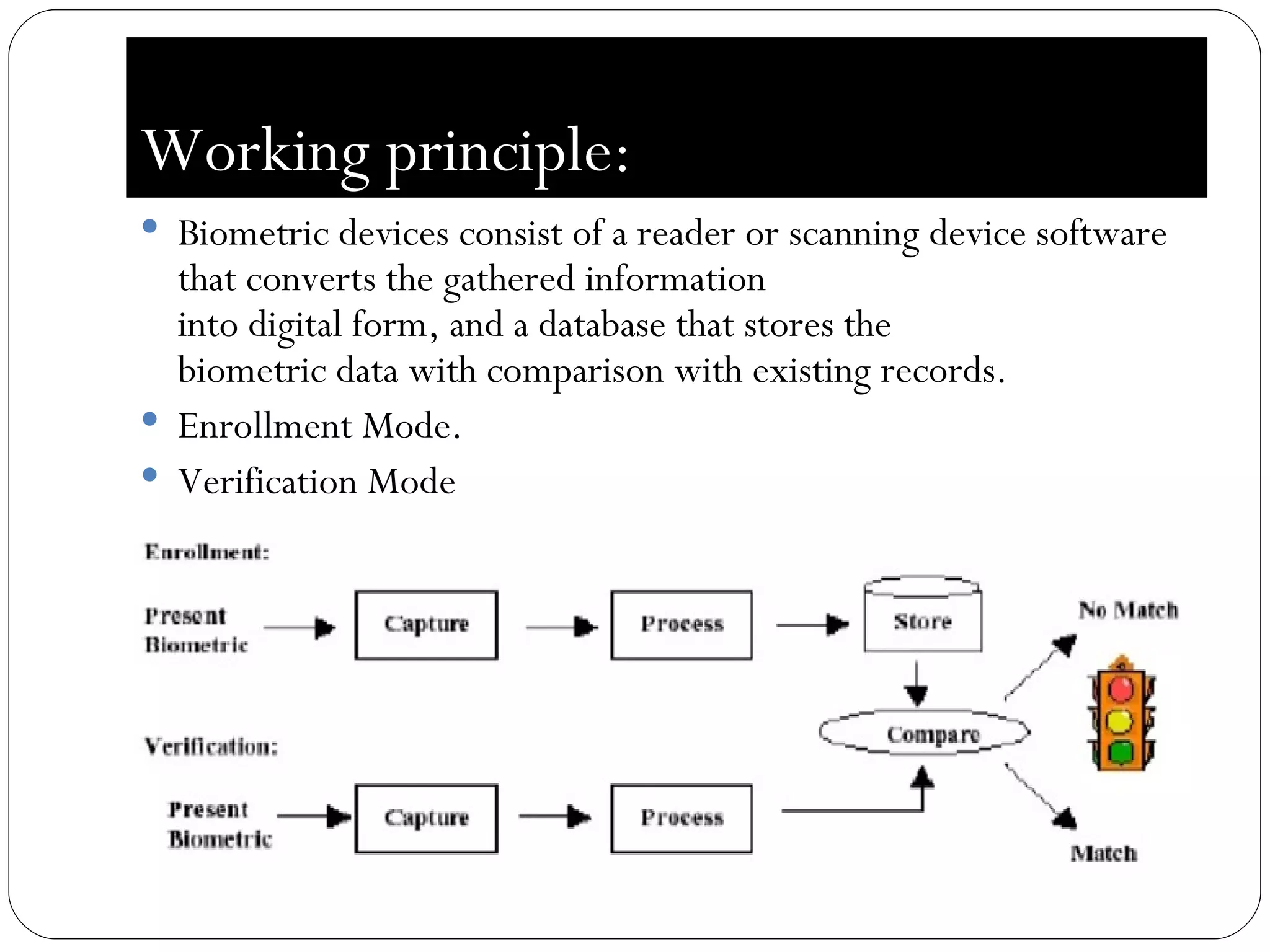
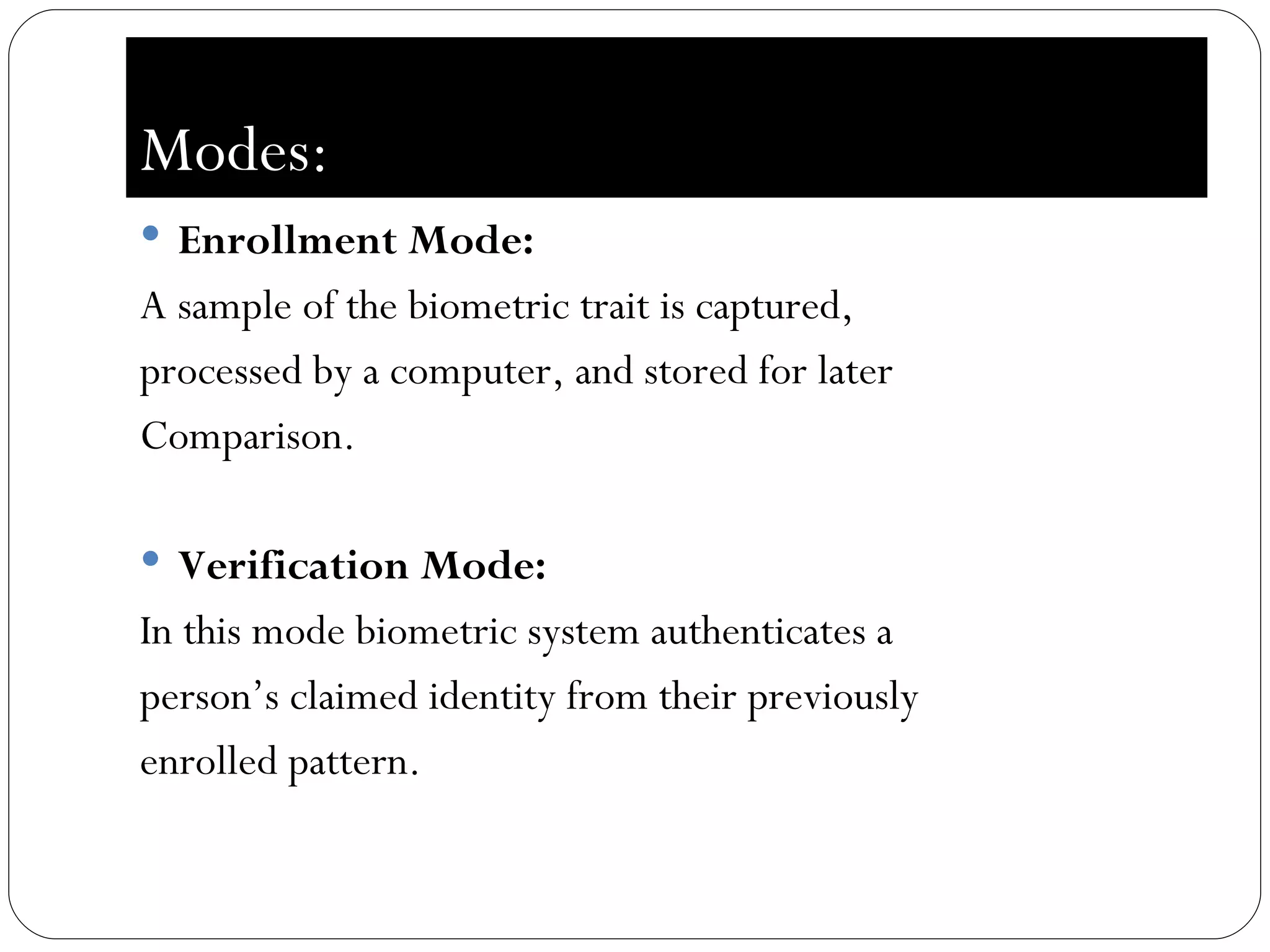
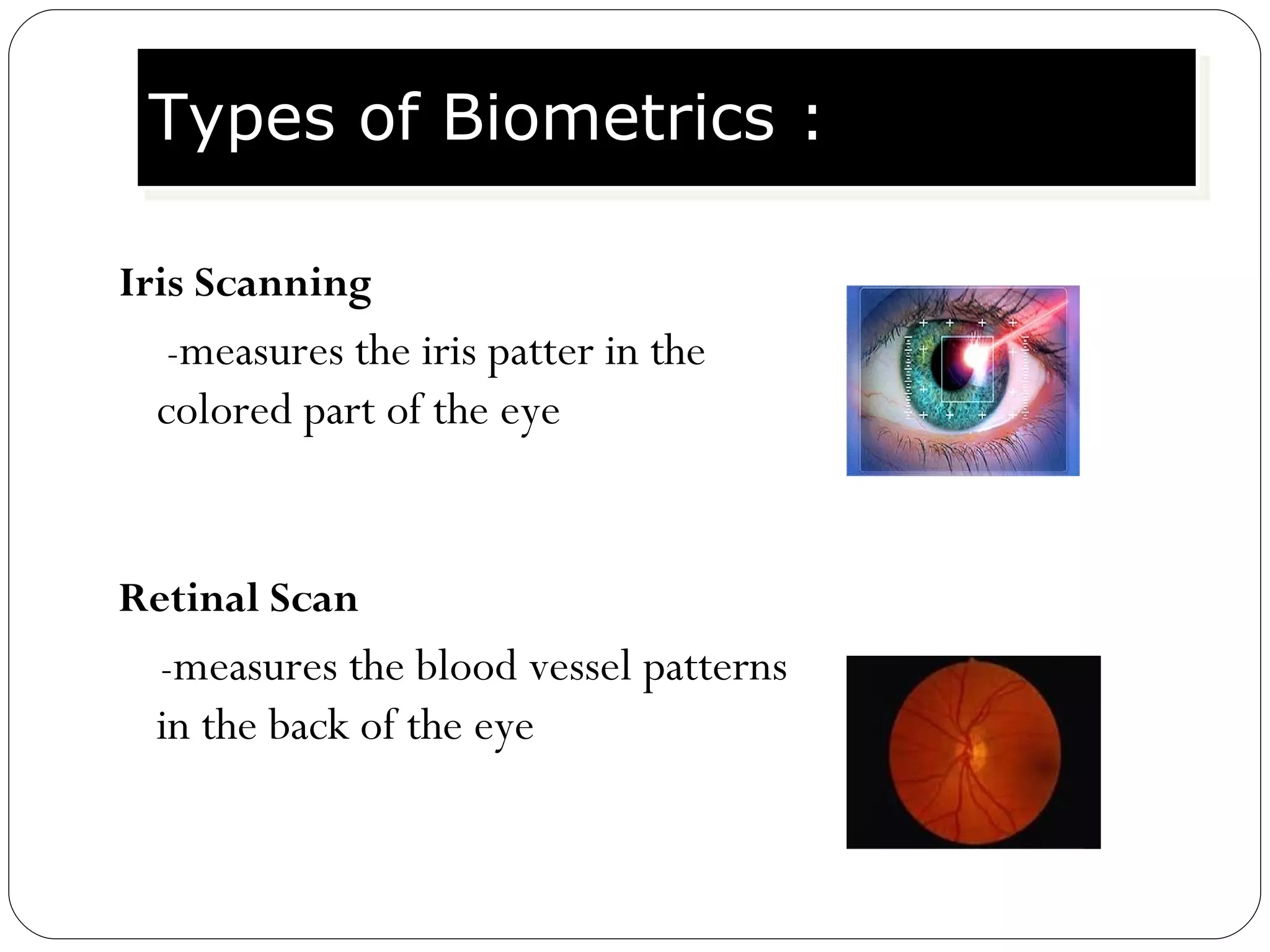
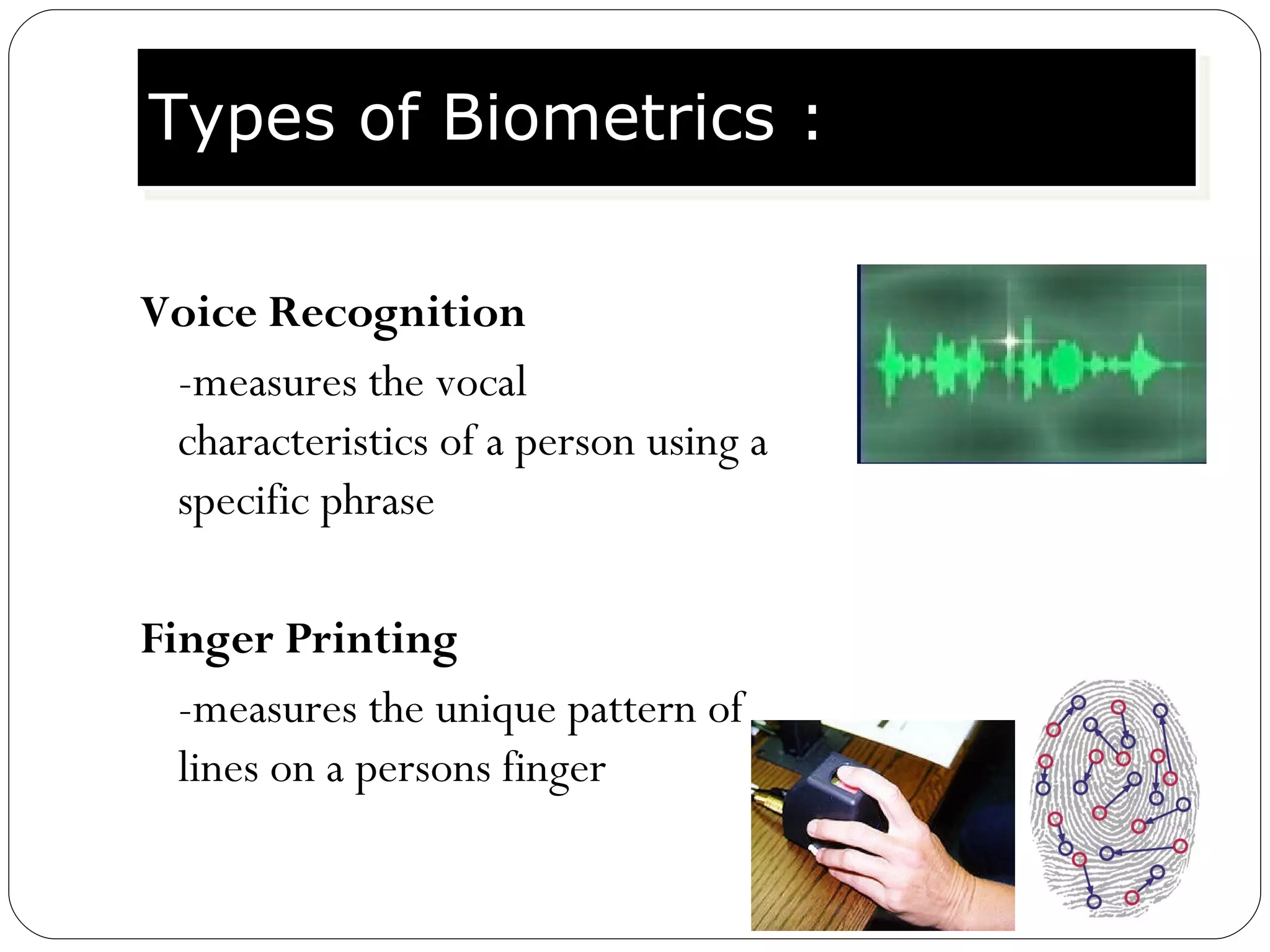
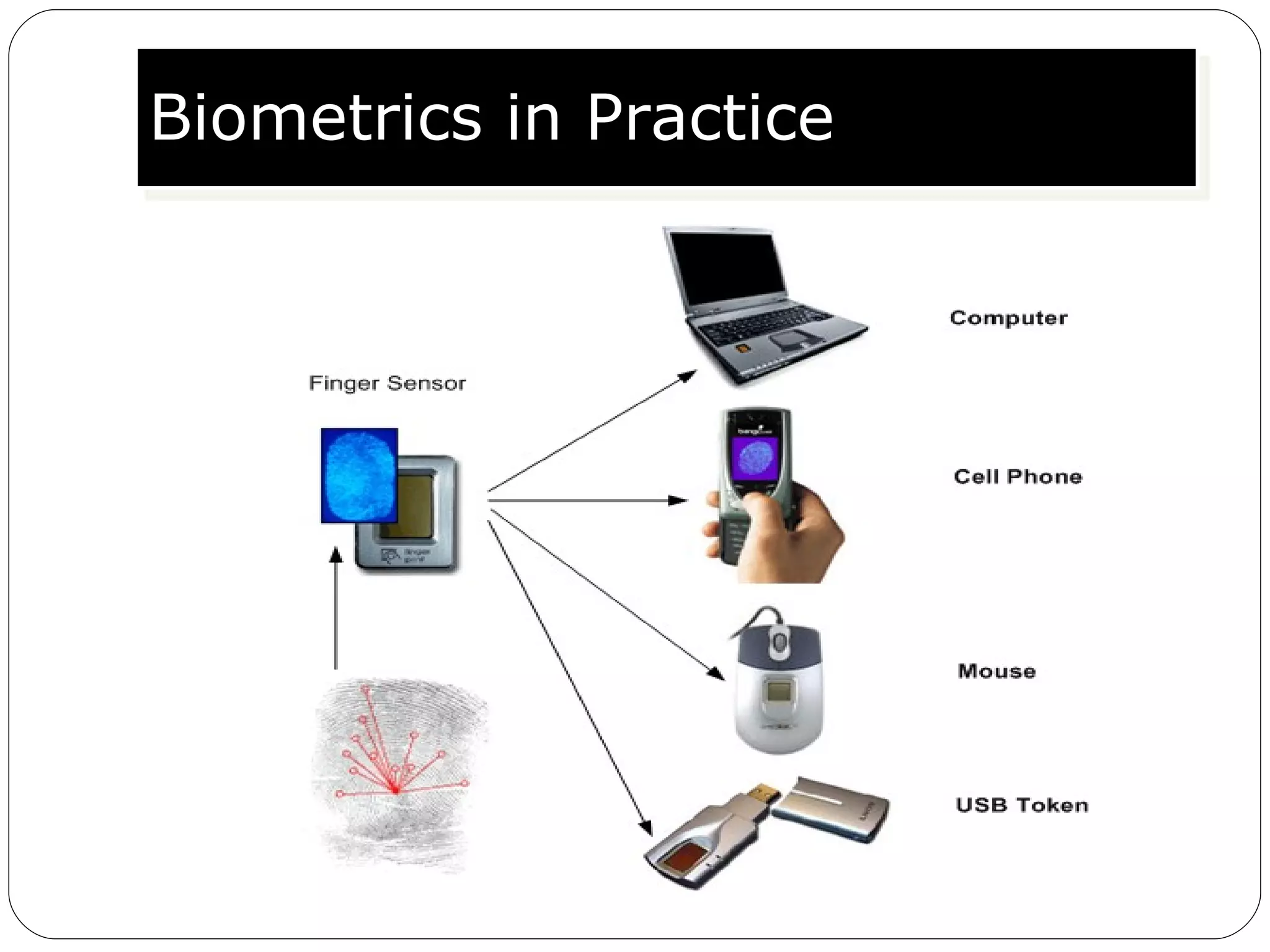
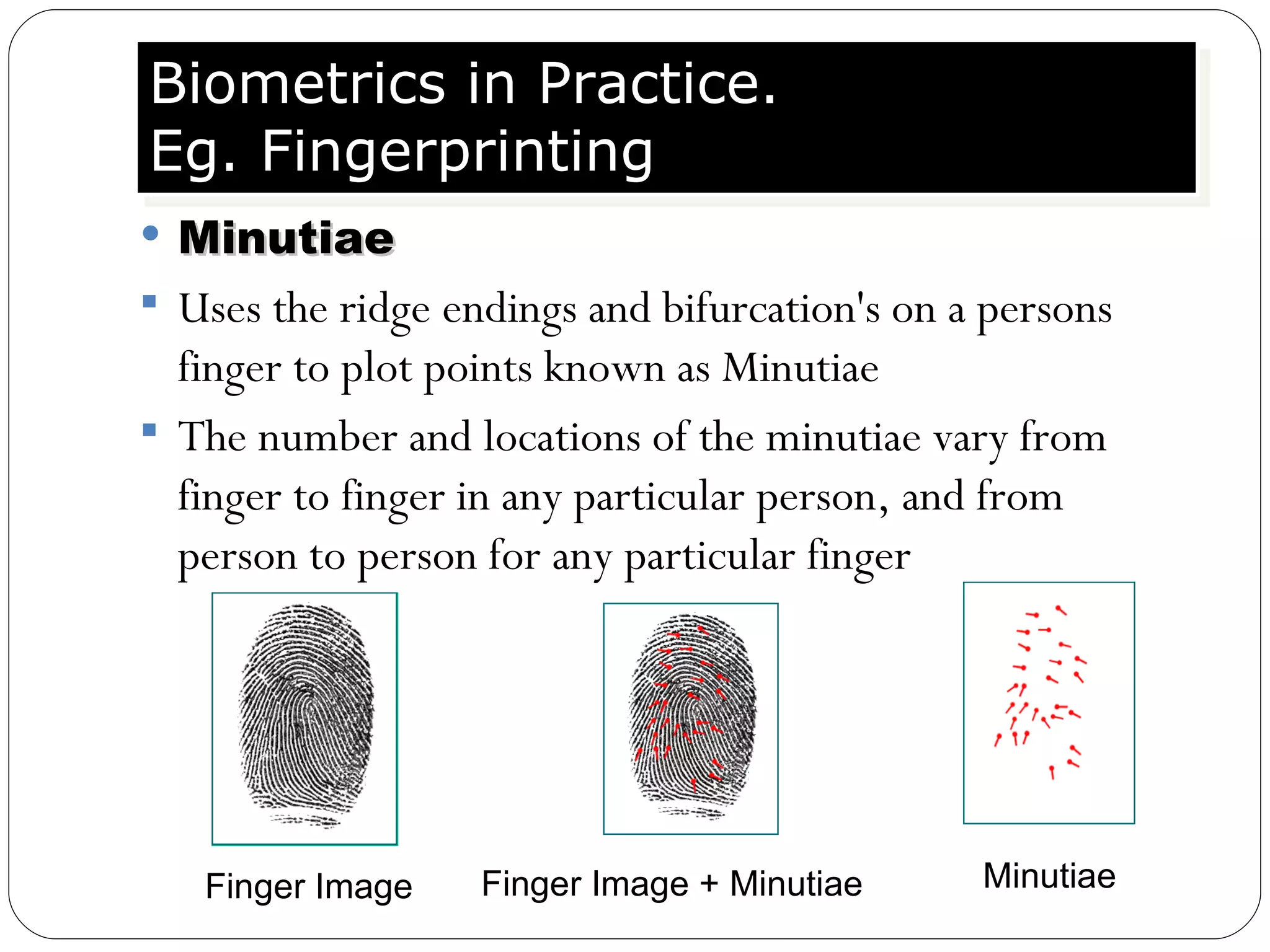
The document discusses biometrics, which uses measurable physiological or behavioral characteristics to identify or verify the identity of individuals. It defines biometrics and explains how they work by capturing a biometric trait, converting it to a digital template, and storing it in a database for future matching. Common biometric traits include fingerprints, iris scans, voice recognition, and facial recognition. While biometrics provide stronger authentication than passwords, they also pose privacy and performance issues if an individual's biometric template is compromised or their traits change over time.
![Too many Passwords to remember: A heavy web user have an average of 21 passwords. [81% users have common passwords and 31% write their passwords down or store them in a file.] Why Biometrics :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biometricsvinay-111226005652-phpapp01/75/Biometric-5-2048.jpg)