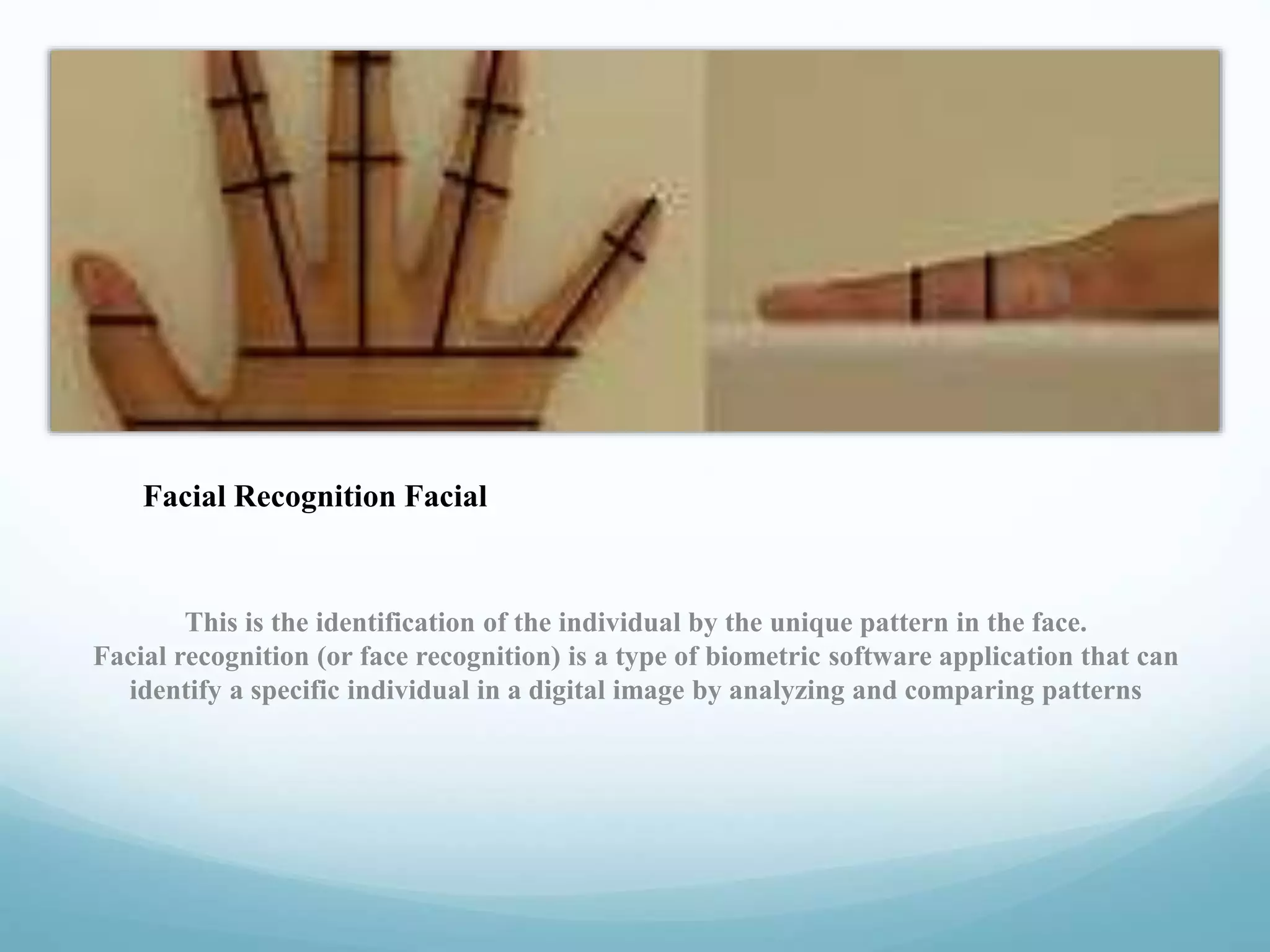
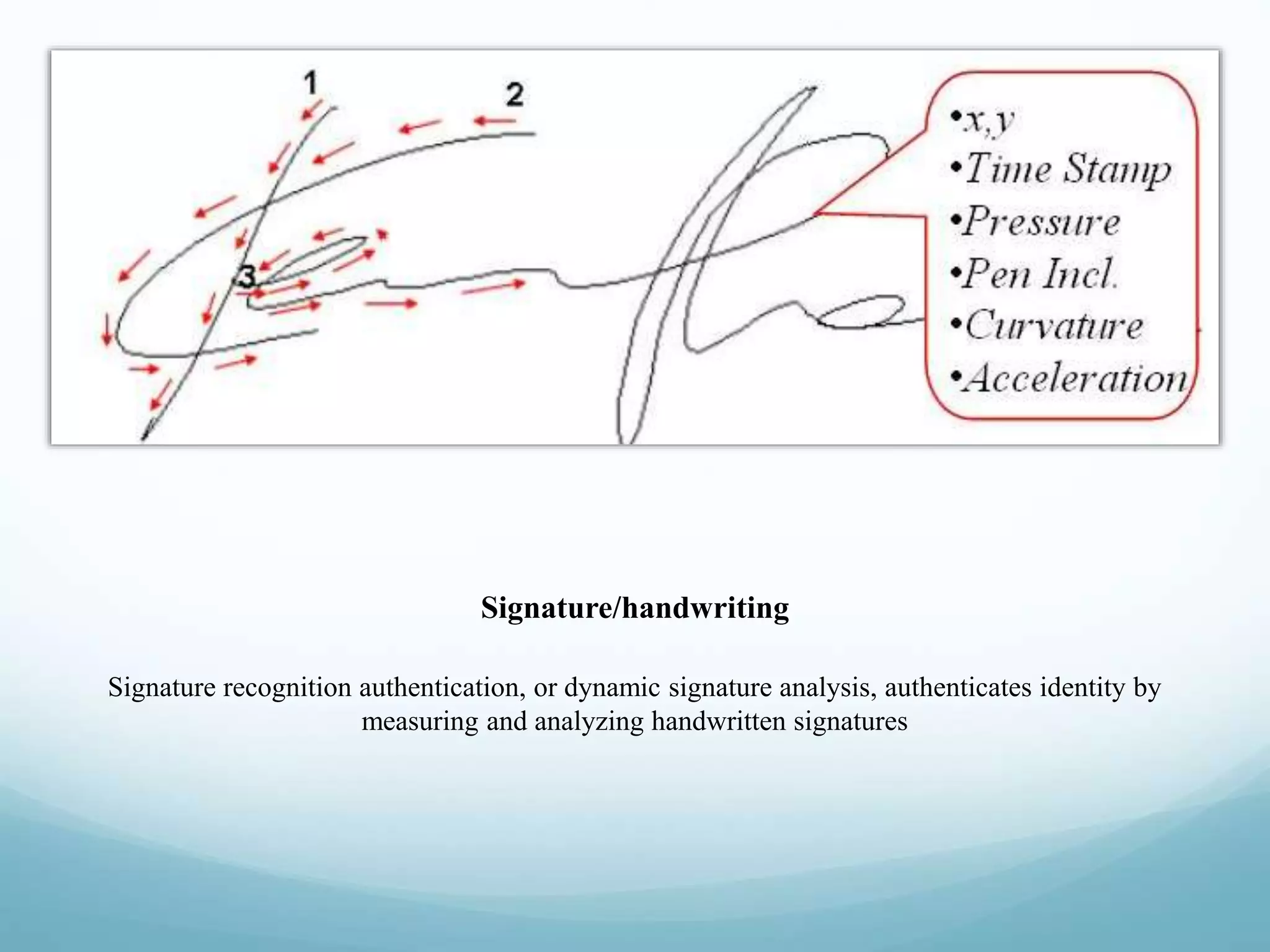
This document discusses emerging technologies related to computer inputs, outputs, and biometrics for user verification. It describes various input methods like keyboards, mice, and touch screens. It also covers output devices like screens, printers, and speakers. The document focuses on biometrics like fingerprint, facial, iris, retina, voice, signature/handwriting, and keystroke recognition. Biometrics provide automated user identification and verification by analyzing unique physiological or behavioral characteristics. Properly implemented biometrics can improve security, provide audit trails, and accurately verify identities.