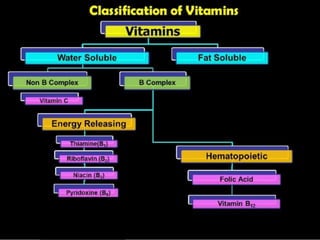
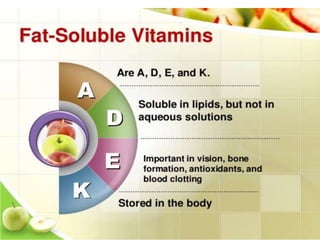
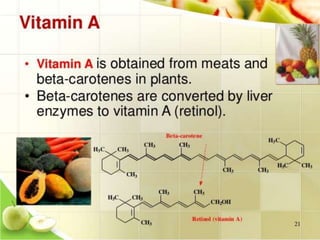
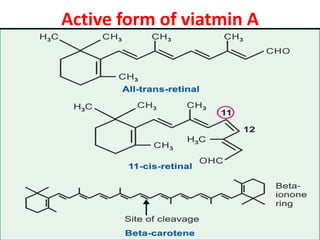
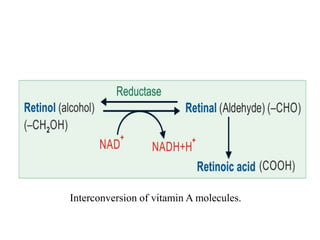
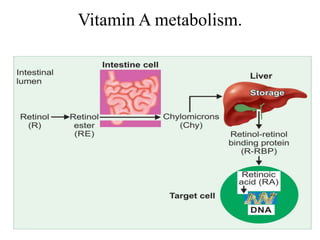
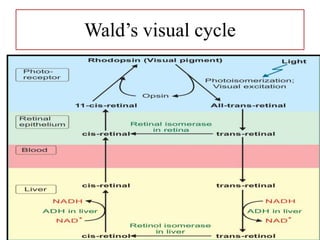
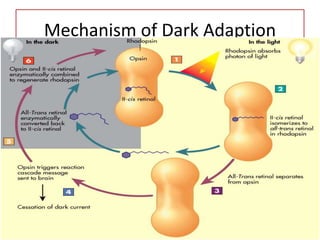
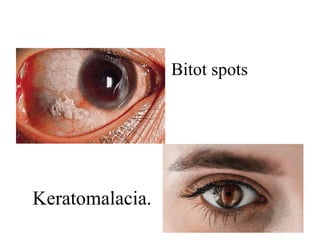
This document discusses vitamin A, including its recommended daily allowances, dietary sources, active forms, role in vision and the visual cycle, and deficiency manifestations. The RDA of vitamin A is 400-600 μg/day for children, 750-1000 μg/day for men, and 750 μg/day for women and 1000 μg/day during pregnancy. Animal sources like milk, liver, and fish liver oils as well as carotenoid-containing vegetables like carrots are good sources. Deficiency can cause night blindness, Bitot's spots, dry eyes, corneal softening and blindness as well as skin and immune system issues.