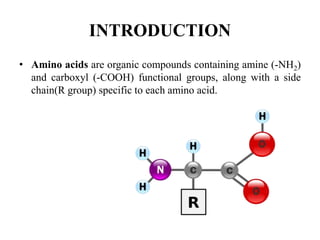
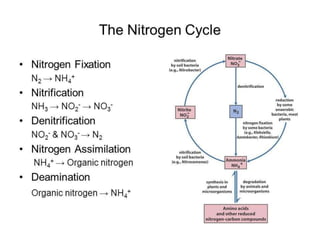
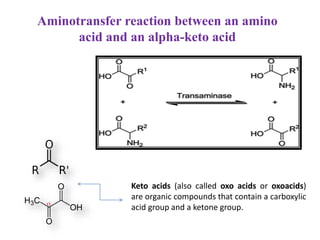
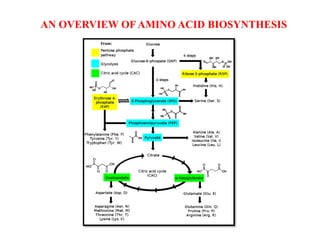
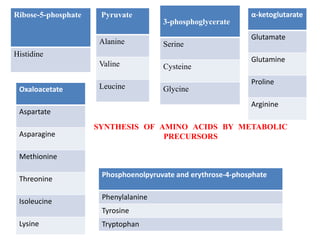
This document summarizes the synthesis of amino acids. It discusses three main steps: 1) the reduction of nitrogen to ammonia, 2) transamination reactions catalyzed by transaminases, and 3) the synthesis of amino acids from metabolic precursors like glycolysis intermediates. Amino acids are classified as nonpolar, polar, or sulfur-containing. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized de novo by humans and must be obtained through diet. Non-essential amino acids can be synthesized from other compounds. The document provides examples of transamination reactions and outlines biosynthesis pathways from common precursors like 3-phosphoglycerate and alpha-ketoglutarate.